English for computing
ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ АГЕНТСТВО ПО ОБРАЗОВАНИЮ
ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ ВЫСШЕГО ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ
«ТЮМЕНСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ НЕФТЕГАЗОВЫЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ»
Т.А. Забкова
English for computing
Часть 1
Учебное пособие

Тюмень 2006
Забкова Т.А. English for computing.: В 2 ч. Ч.1 /Т.А. Забкова: Учебное пособие. – Тюмень, 2006. – 154 с.
Предлагаемое пособие включает в себя комплекс заданий и упражнений, позволяющие выработать разнообразные навыки и умения: быстрое чтение информационных блоков, извлечение необходимой информации, овладение элементами монологической и диалогической речи по технической тематике. Тексты подобраны с учетом лексического минимума, необходимого для совершенствования навыков поискового чтения с полным пониманием текста.
Данное учебное пособие по дисциплине «Иностранный язык» (английский язык) предназначено для студентов I курса по специальности - 220301 Автоматизация технологических процессов и производств (нефтегазодобыча) очной формы обучения. Может быть использовано на аудиторных и внеаудиторных занятиях.
Целью данного пособия является научить студентов использовать полученную техническую информацию в устном и письменном виде.
Пособие состоит из 10 разделов, объединенных единой структурой, в каждом из которых рассматривается определенная техническая проблема.
Рецензенты: Л.М. Бискер, кандидат политологических наук, доцент кафедры гуманитарных и социально-экономических дисциплин ЯНГИ (филиал) Тюменского государственного нефтегазового университета; Э.Ю. Иванова, кандидат филологических наук, старший преподаватель кафедры гуманитарных дисциплин филиала Тюменского государственного университета в г. Новый Уренгой
© Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования «Тюменский государственный нефтегазовый университет», 2006
Contents
INTRODUCTION……………………………………………………………………………..4
UNIT 1. COMPUTER SCIENCE ……………………………………………………………..5
UNIT 2. COMPUTERS AND SOCIETY …………………………………………………...15
UNIT 3. THE HISTORY OF COMPUTING………………………………………………...26
UNIT 4. TYPES OF COMPUTERS………………………………………………………….38
UNIT 5. COMPUTER ESSENTIALS……………………………………………………..…50
UNIT 6. PROCESSING HARDWARE………………………………………………………67
UNIT 7. STORAGE SYSTEM…………………………………………………………….....80
UNIT 8. INPUT HARDWARE…………………………………………………………...….97
UNIT 9. OUTPUT HARDWARE……………………………………………………….….110
UNIT 10. TYPES OF SOFTWARE……………………………………………………..….125
PAIR WORK…………………………………………………………………………...…...139
GLOSSARY…………………………………………………………………………………141
LITERATURE………………………………………………………………………………153
Введение
Геополитическая и экономическая ситуация в мире сложилась таким образом, что английский язык является ведущим средством международного общения, особенно в сфере информационных технологий. Подавляющее большинство русских терминов в данной области являются англоязычными заимствованиями. Многие языки программирования составлены на основе английского языка. Английский язык является обязательным для работы в Интернет, несмотря на стремительное развитие сайтов и поисковых систем на других языках. Таким образом, спецификой курса обучения иностранному языку студентов данных специальностей является не только достижение оптимального уровня иноязычной коммуникативной компетенции и межкультурной коммуникации, но и развитие навыков грамотного использования специальных терминов на государственном языке РФ, являющихся англоязычными заимствованиями.
Данное учебное пособие рассчитано на 120-140 часов аудиторных занятий. Пособие ставит своей задачей закрепить и систематизировать навыки иноязычного общения, полученных в средней школе, расширить лексический запас общенаучного характера, и подготовить к переводу, реферированию, аннотированию текстов по специальности и подготовке соответствующих устных публичных выступлений.
Основной структурной единицей учебного пособия является Unit, объединенный единой тематикой и структурой. Каждый из 10 разделов состоит из 5 подразделов: “Language Material”, “Reading Practice”, “Listening Practice”, “Oral Practice”, “Writing Practice”. Языковой материал включает упражнения на развитие произносительных навыков, словаря-минимума, рассмотрение синонимов, антонимов, многозначности и словообразования. В разделе “Reading Practice” представлено несколько разноуровневых аутентичных текстов и упражнений к ним, первый текст рассматривается как основной. Тематика текстов: определение области информатики, связь компьютеров и общества, история развития компьютеров, архитектура компьютеров, устройства обработки и сохранения данных, типы программного обеспечения. Текстовый материал учебного пособия, подобранный из оригинальных английских и американских источников с учетом их информативности и соответствия научно-техническим достижениям, изложен по принципу возрастания трудности, постепенного усложнения языка и тематики и имеет профессиональную направленность. Учебное пособие направлено на развитие четырех видов чтения - изучающего, ознакомительного, поискового и просмотрового, выбор которых определяется задачей, поставленной при работе с оригинальной литературой. Текстовые упражнения обеспечивают внедрение в содержание оригинального текста, “высвечивание” его языковых особенностей, извлечение информации из составных частей текста и возможные способы интерпретации содержательной стороны всего текста. Лексические упражнения имеют целью расширить границы языкового запаса обучающихся, показать синонимические ресурсы языка, антонимические параллели, полисемантические связи в структуре слов, полифункциональность языковых единиц, контекстуальное значение слов, интернациональный характер лексики английского языка.
Раздел “Listening Practice” включает в себя рассказы, диалоги для прослушивания, а также задания к ним, здесь автор предусматривает постепенное усложнение языкового материала текстов для аудирования. Раздел “Oral Practice” объединяет проблемные ситуации, по которым необходимо высказать свою точку зрения. В каждом уроке-теме имеются задания, требующие от студентов участия в обсуждении определенной темы. В конце учебного пособия представлен Глоссарий специальных терминов и аббревиатур по предложенной тематике.
UNIT 1
COMPUTER SCIENCE
Unit 1 presents introductory information about computers in a comprehensive, straightforward manner and is an attempt to provide information about basic computing concepts. You will also learn some of the basic issues, definitions, and concepts related to computers and their use.
Test Concepts
Computers are everywhere – in our homes, our schools, our shops, offices and hospitals. We use them every day, but what do we know about them? Most machines are designed to do one job. Computers are different: they are general purpose machines. By changing the program instructions, computers can be used to process information in different ways.
Language Material
1. Translate into Russian words-internationals.
to specify, to specialize, specialist, specific, productivity, optimal, problem, logic, logical, operation, program, virus, expert, instruction, differentiation, artificial, defend, method, computer, mathematics, designer, device, manager, calculator, function, algebra, algebraic.
2. Learn by heart the following vocabulary:
|
addition
artificial
computer science
comparing
device
differentiation
division
integrating
matching
multiplication
productivity
selecting
|
сложение
разумный, искусственный
информатика
сравнение
устройство
дифференциация
деление
интеграция, объединение в одно целое -
подборка пары
умножение
производительность
отбор, выбор, подбор, селекция
|
labour sorting
subtraction
to concern
to divide
to improve
to intend
to shorten as far as
as well as
thus
in order to
|
труд
сортировка
вычитание
рассматривать
делить, подразделять
улучшать
намереваться
сокращать до;
насколько
также как
таким образом
чтобы
|
3. Find in the right column the Russian equivalents to English words and expressions:
|
1. modern technologies
2. to work out programs
3. programming language
4. computer-aided-manufacturing
5. new ways
6. to defend from viruses
7. hardware
8. to offer solutions
9. to deal (with)
10. to solve problems
11. computer-aided-design
12. software
13. to meet up-to-date demands
|
a. программное обеспечение
b. отвечать современным требованиям
c. аппаратная часть
d. иметь дело (с кем-л., чем-л.)
e. автоматизированное проектирование
f. защищать от вирусов
g. предлагать решения
h. разрабатывать программы
i. автоматизированное производство
j. решать проблемы
k. язык программирования
1. современные технологии
m. новые способы, пути
|
4. Find noun in each line.
|
1.
|
a) labour
|
b) solve
|
c) concern
|
d) artificial
|
|
2.
|
a) applied
|
b) solution
|
c) shorten
|
d) divide
|
|
3.
|
a) improve
|
b) perform
|
c) multiplication
|
d) such
|
|
4.
|
a) logical
|
b) designing
|
c) defend
|
d) virus
|
|
5.
|
a) division
|
b) solve
|
c) work out
|
d) know
|
5. Find in each line word that is given at the beginning.
|
science
|
а) занятие
|
b) исследование
|
с) производительность
|
d) наука
|
|
applied
|
а) накапливать
|
b) прикладной
|
с) совместный
|
d) ловкий
|
|
field
|
а) производство
|
b) устройство
|
с) сфера, область
|
d) труд
|
|
knowledge
|
а) труд
|
b) исследование
|
с) сложение
|
d) знание
|
|
to improve
|
а) применять
|
b) намереваться
|
с) улучшать
|
d) решать
|
|
productivity
|
а) продукт
|
b) процесс
|
с) производительность
|
d) товар
|
|
labour
|
а) труд
|
b) развитие
|
с) закон
|
d) забота
|
|
to divide
|
а) выполнять
|
b) подразделять
|
с) рассматривать
|
d) проявлять
|
6. A great many words in English have more than one meaning. Note different meanings for words “science” and “combination”.
|
science
|
наука
|
New developments in science and technology are enriched all our lives. Economics is an inexact science.
|
|
|
естественные науки
|
Philosophers did not use a distinction between arts and science.
|
|
|
умение, опыт
|
They offered me the job because I had o lot of science.
|
|
|
знание
|
Science can penetrate many of nature’s mysteries.
|
|
|
|
|
|
combination
|
соединение, комбинация
|
His treatment was a combination of surgery, radiation and drugs. She brings to the job a rare combination of youth and experience. The room was decorated in a combination of greens and blues. This combination of qualities is generally supposed to be extremely rare.
|
|
|
союз, объединение
|
A combination of internal and external factors caused the company to close down.
|
7. English has a lot of different words with similar but slightly differing meanings. Look at these words that are synonyms.
goal – aim, object, intention, ambition, destination.
house – building, residence, apartment.
to perform – to do, to act, to achieve, to execute, to accomplish, to fulfill, to complete.
to shorten – to curtail, to reduce, to cut, to retrench.
to concern – to apply to, to consider.
8. Consider antonyms, the words that mean the opposite of the word in bold type.
quick – slow, languid, creeping, crawling, tardy, sluggish, lazy, snail-like.
different – similar, like, alike, correspondent, harmonious, homogeneous, common, same.
important – slight, trivial, light, petty, unimportant, subordinate, nonessential, inconsiderable, shallow, weak, worthless, powerless, insignificant.
to defend – to desert, to abandon, to leave, to forsake, to quit, to resign, to relinquish, to renounce, to vacate, to give up.
9. Consider the grammar:
to defend from – защищать(ся), оборонять(ся) ч.-л. от к.-л.
Thus in order to elaborate up-to-date and inexpensive programs as well as to defend them from viruses, it is important to know some programming languages.
to suffer from – страдать от ч.-л./ к.-л.
The number of people suffering from heart disease has increased.
to protect smb/sth from – защищать к.-л./ч.-л. от ч.-л.
Sun oil can protect skin from the sun.
10. Find in each line the word - synonym to the first word.
|
science
|
a) sorting
|
b) product
|
c) artificial
|
d) knowledge
|
|
device
|
a) productivity
|
b) artifice
|
c) division
|
d) novice
|
|
to perform
|
a) to solve
|
b) to support
|
c) to accomplish
|
d) to offer
|
|
to divide
|
a) to separate
|
b) to defend
|
c) to deal
|
d) to elaborate
|
|
to work out
|
a) to use
|
b) to elaborate
|
c) to store
|
d) to speed
|
|
goal
|
a) labour
|
b) software
|
c) solution
|
d) aim
|
|
to intend
|
a) to shorten
|
b) to purpose
|
c) to concern
|
d) to improve
|
11. Find in each line the word - antonym to the first word.
|
different
|
a) complex
|
b) similar
|
c) distinct
|
d) diverse
|
|
to divide
|
a) to unite
|
b) to part
|
c) to share
|
d) to execute
|
|
complex
|
a) sluggish
|
b) definite
|
c) simple
|
d) equal
|
|
quick
|
a) unfair
|
b) instantly
|
c) thus
|
d) slow
|
|
to elaborate
|
a) to deform
|
b) to plain
|
c) to join
|
d) to diminish
|
12. Try and complete the following crossword "Computer science".
1. The study or knowledge which can be made into system and which depends on seeing, understanding and testing facts.
2. A high-level language which is used by students who require a simple language to begin programming.
3. The rate at which a worker, a company or a country produces goods, and the amount produced compared with how much time, working money is needed to produce them.
4. Knowledge or skill which comes from practice rather than books.
5. The study or science of different numbers and calculations; one of the main subjects taught at schools and colleges.
6. The result of education.
7. An electronic device used to process information.
8. An useful thing or idea which produced by scientists for the first time.
13. Word Bingo.
Look at the list of the words given below. Write down any five words. The teacher is going to read the definitions of all the words in random order. If you hear the definition of one of the words you have chosen, cross it out. The first student to cross out all the words he or she has chosen calls out “Bingo” and reads the words to prove his/her claim.
Words: science, mathematics, computer, knowledge, solution, labour, designer, goal, main, help, problem, addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, using, operation.
Word-building
Model 1
Основа глагола + er/or существительное со значением лица, производящего действие или орудие действия
|
to produce - производить
to design - конструировать, проектировать
to manage - руководить, заведовать
to manufacture - производить, обрабатывать
|
producer - производитель
designer - проектировщик, конструктор
manager - руководитель
manufacturer - производитель
|
Model 2
Основа глагола или существительного + ist существительное со значением лица, производящего действие
|
science - наука
final - финал
theory - теория
art - искусство
|
scientist - ученый
finalist - финалист
theorist - теоретик
artist - искусствовед
|
14. Make new words using the models 1-2.
|
to generate
biology
to distribute
instrumental
|
to work
to type
to operate
fatal
|
to invent
to tour
to hunt
to machine
|
to supply
to terror
to incubate
plural
|
15. Make your own examples with the models 1-2.
Reading Practice
16. Read the text. Try to understand it and be ready to answer the questions.
TEXT 1A
COMPUTER SCIENCE
Computers today are far more than the number crunchers. Today, computers are used to store and manage information in the form of words, numbers, sounds, and pictures.
With the invention of the computer, a few people began to see the potential for faster management of this information flow. Even though computers were at first used mainly for mathematical calculation, it wasn’t long before businesses began to understand how their ability to speed the handling of information could be used as a competitive advantage over other companies that had not yet computerized. Soon businesses were racing to convert information into forms that could be managed by computers.
Computer science is the study of computers and how they can be used. Specialists in computer science say that this field of knowledge is very interesting because it deals with computer-aided-design (CAD) and computer-aided-manufacturing (CAM).
Computers are intended to improve the productivity of labour of scientists, designers, engineers, managers, and other specialists, because computers offer quick and optimal solutions. One of the main goals of using CAD/CAM is to shorten the time between designing and manufacturing.
Today, much of the world’s information has been computerized and the race has changed to finding new ways to use it. The world's businesses, libraries, governments, and educational institutions now need people who are willing to learn new ways to process information. The end of the twentieth century will mark a new beginning both for computer professionals and for computer users. It will be the period in which we all come to terms with the computer. Computers came in our life and to our houses and now we can solve our everyday problems with their help. We now realize that although computers will affect everyone’s life, we won't have to change the way we do things because computer professionals are finding ways to adapt the computer to our needs, instead of the other way around. In fact, as computers take on additional roles in our lives, we may not even realize that we are using a computer. Soon computers, in one form or another, will have a role to play as we use automobiles or public transportation to get to work, as we buy products and services, as we teach, as we learn, as we are entertained, and as we carry out our jobs at every level in every occupation.
Computer can perform many functions: they can do mathematical, and logical operations, mathematical operations including arithmetic and algebraic operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, raising to a power, differentiating and integrating. Logical operations include comparing, selecting, sorting and matching.
Computers can be divided into simple and complex devices. Simple computers such as calculators can perform addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. As far as complex computers are concerned they can do different logical operations and some of them even have artificial intelligence.
Thus in order to elaborate up-to-date and inexpensive programs as well as to defend them from viruses, it is important to know some programming languages. There are low-level programming languages such as a machine language and an assembly language and high-level programming languages, for instance, FORTRAN, PASCAL, ADA, C, BASIC, etc.
17. Choose the correct answer.
1. What do specialists in computer science deal with?
a. description how computers were first developed, how they evolved, and how they influence our lives today;
b. computer-aided-design (CAD) and computer-aided-manufacturing (CAM);
с. presentation introductory information about computers.
2. What are the computers used for?
a. for improving of the productivity of labour of scientists, designers, managers and other specialists by offering quick and optimal solutions to them;
b. for calculations;
с. for creating and manipulating text and pictures.
3. What operations can simple devices perform?
a. make decisions based on accumulated evidence;
b. to display and manage graphics, fonts, and other page design features like lines and boxes, a close representation;
с. addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
4. What operations do complex computers perform?
a. different logical operations;
b. automate tasks that previously are being carried out by specially trained employees;
с. output information in such forms as payroll checks.
5. What are CAD/CAM systems intended to do?
a. to elaborate new program languages;
b. to perform different calculations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division;
c. to shorten the time between designing and manufacturing.
6. What high-level programming languages do you know?
a. assembly languages;
b. FORTRAN, COBOL, BASIC, ADA;
с. machine languages.
18. Choose the phrases on the right which complete the sentences on the left.
|
1. Experts in computer science deal with ...
|
a) manufacturing cars;
b) computer-aided-design;
c) increasing the productivity of cars.
|
|
2. One of the aims of using computers is ...
|
a) to work out up-to-date demands;
b) to shorten the time between designing and manufacturing;
c) to construct hardware’s.
|
|
3. Simple devices can ...
4. Complex computers can ...
|
a) do logical operations;
b) perform such operations as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division;
c) output information in such forms as payroll checks;
d) make decisions based on accumulated evidence.
|
|
5. High-level programming languages are ...
|
a) BASIC, FORTRAN, ADA;
b) assembly languages;
c) machine languages.
|
Writing Practice
19. Translate into English in writing:
В последнее время очень популярна стала информатика, так как невозможно представить нашу повседневную жизнь без компьютера. Компьютеры направлены на увеличение производительности труда ученых, проектировщиков, управляющих, бухгалтеров и т.п. Компьютеры, отвечающие современным требованиям, принимают быстрые и оптимальные решения наших проблем. Информатика - это комплексная научно-техническая дисциплина, занимающаяся изучением структуры и общих свойств информации, информационных процессов, разработкой на этой основе информационной техники и технологий, а также решением научных, инженерных проблем создания, внедрения и эффективного использования компьютерной техники и технологий во всех сферах общественной практики. Специалисты в области компьютерных исследований занимаются автоматизированным производством и проектированием, одной из задач является сокращение времени между проектированием и производством.
20. Give the main idea of extract “Computer science” in 20 sentences.
21. Read the article below and decide which of the expressions in the box best describe computers.
|
a miraculous device
|
communication
|
calculator
|
|
sophisticated
|
complex
|
typewriter
|
TEXT 1B
WHAT CAN COMPUTERS DO?
to encounter - встречаться, сталкиваться
to spring to life - появляться
miraculous - чудный
appropriate - соответствующий, подходящий
gadget – приспособление, устройство, техническая новинка, полезная мелочь
ignition – воспламенение, зажигание, прокаливание
Computers and microchips have become part of our everyday lives: we visit shops and offices which have been designed with the help of computers, we read magazines which have been produced on computer, and we pay bills prepared by computers. Just picking up a telephone and dialing a number involves the use of a sophisticated computer system, as does making a flight reservation or bank transaction.
We encounter daily many computers that spring to life the instant they’re switched on (e.g. calculators, the car’s electronic ignition, the timer in the microwave, or the programmer inside the TV set), all of which use chip technology.
What makes computer such a miraculous device? Each time you turn it on, it is a tabula rasa that, with appropriate hardware and software, is capable of doing anything you ask. It is a calculating machine that speeds up financial calculations. It is an electronic filing cabinet which manages large collections of data such as customers’ lists, accounts, or inventories. It is a magical typewriter that allows you to type and print any kind of document – letters, memos or legal documents. It is a personal communicator that enables you to interact with other computers and with people around the world. If you like gadgets and electronic entertainment, you can even use your PC to relax with computer games.
22. Read the translation of the third paragraph given below. Compare it with the original and say if everything is right.
Что делает компьютер таким чудесным устройством? Общеизвестно, что каждый раз как вы включаете компьютер с соответствующим оборудованием и мягким обеспечением, вы можете выполнить все, что ни попросите. Это калькулятор, который ускоряет финансовые расчеты. Это кабинет, заполненный электроникой, которая управляет большим количеством данных, таких как списки покупателей, счета или изобретения. Это магическая печатная машинка, которая позволяет вам напечатать любой документ - письма, заметки или юридические документы.
23. Find the answers to these questions in the text.
1. Name some types of devices that use “computers on a chip”.
2. What uses of handheld computers are mentioned in the text?
3. What are the benefits of using computers with the following items?
a) Security systems
b) Cars
c) Phones
4. What smart devices are mentioned in the text?
5. What are smart cards used for?
6. What are the advantages of multimedia?
7. What can medical expert systems do?
8. How can computers help the disabled?
9. What types of computing systems are made available to people in remote locations using electronic classrooms or boardrooms?
10. What aspects of computing can people power determine?
TEXT 1C
COMPUTERS MAKE THE WORLD SMALLER AND SMARTER
The ability of tiny computing devices to control complex operations has transformed the way many tasks are performed, ranging from scientific research to producing consumer products. Tiny “computers on a chip” are used in medical equipment, home appliances, cars and toys. Workers use handheld computing devices to collect data at a customer site, to generate forms, to control inventory, and to serve as desktop organisers.
Not only computing equipment getting smaller, it is getting more sophisticated. Computers are part of many machines and devices that once required continual human supervision and control. Today, computers in security systems result in safer environments, computers in cars improve energy efficiency, and computers in phones provide features such as call forwarding, call monitoring, and call answering.
These smart machines are designed to take over some of the basic tasks previously performed by people; by so doing, they make life a little easier and a little more pleasant. Smart cards store vital information such as health records, drivers’ licenses, bank balances, and so on. Smart phones, cars, and appliances with built in computers can be programmed to better meet individual needs. A smart house has a built-in monitoring system that can turn lights on and off, open and close windows, operate the oven, and more.
With small computing devices available for performing smart tasks like cooking dinner, programming the VCR, and controlling the flow of information in an organization, people are able to spend more time doing what they often do best - being creative. Computers can help people work more creatively.
Multimedia systems are known for their educational and entertainment value, which we call “edutainment”. Multimedia combines text with sound, video, animation, and graphics, which greatly enhances the interaction between user and machine and can make information more interesting and appealing to people. Expert systems software enables computers to “think” like experts. Medical diagnosis expert systems, for example, can help doctors pinpoint a patient's illness, suggest further tests, and prescribe appropriate drugs.
Connectivity enables computers and software that might otherwise be incompatible to communicate and to share resources. Now that computers are proliferating in many areas and networks are available for people to access data and communicate with others, so personal computers are becoming interpersonal PCs. They have the potential to significantly improve the way we relate to each other. Many people today telecommute - that is, use their computers to stay in touch with the office while they are working at home. With the proper tools, hospital staff can get a diagnosis from a medical expert hundreds or thousands of miles away. Similarly, the disabled can communicate more effectively with others using computers.
Distance learning and videoconferencing are concepts made possible with the use of an electronic classroom or boardroom accessible to people in remote locations. Vast databases of information are currently available to users of the Internet, all of whom can send mail messages to each other. The information superhighway is designed to significantly expand this interactive connectivity so that people all over the world will have free access to all these resources.
People power is critical to ensuring that hardware, software, and connectivity are effectively integrated in a socially responsible as way. People - computer users and computer professionals - are the ones who will decide which hardware, software, and networks endure and how great an impact they will have on our lives. Ultimately people power so must be exercised to ensure that computers are used not only efficiently but in a socially responsible way.
24. Reread the text to find the answers to these questions:
a) Match the terms in Table A with the statements in Table B.
|
Table A
|
|
Table B
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Edutainment
2. Multimedia
3. Expert system
4. Telecommute
5. Information superhighway
|
|
- Software that enables computers to “think” like experts
- Use computers to stay in touch with the office while working at home
- Internet system designed to provide free, interactive access to vast resources for people all over the world
- Multimedia materials with a combination of educational and entertainment content
- A combination of text with sound, video, animation, and graphics
|
b) Mark the following statements as True or False:
- Desktop organisers are programs that require desktop computers.
- Computers are sometimes used to monitor systems that previously needed human supervision.
- Networking is a way of allowing otherwise incompatible systems to communicate and share resources.
- The use of computers prevents people from being creative.
- Computer users do not have much influence over the way that computing develops.
Oral Practice
25. Put the sentences in the right order.
1. make, or, reservation, transaction, a flight, computers, bank.
2. calculations, speed up, computers, financial.
3. on, produced, read, been, which, magazines, have, we, computer.
4. to interact, computer, people, enables, other, you, around, with, and, computers, with, the, world.
5. pay, bills, by, prepared, we, computers.
6. designed, been, we, shops, visit, and, computers, of, offices, which, have, with, the, help.
7. the, with, type, computer, of, the, you, can, and, help, any, of, print, document, kind.
8. PC, you, games, can, to, use, computer, your, relax, with.
26. Give definitions to the following words and expressions:
science, knowledge, computer-aided-design, computer-aided-manufacturing.
27. Questions for group discussion:
1. Why is the computer science so important in our life nowadays?
2. What problems can computer science solve?
3. What operations can computer perform?
4. Today, the number of jobs that are related to the use of computers or the maintenance of computers is growing steadily. Describe four different computer-related jobs and the skills these jobs require.
Listening Practice
28. Listen to the text and make a list of at least seven tasks done by robots and androids.
29. Refer to the text to find the terms for these definitions.
- a science field that tries to improve computers and robots with features associated with human intelligence;
- programs used by computers;
- stage of mass production in which parts of a product move along for progressive assembly;
- small devices used for doing various tasks;
- robots that look like human beings.
UNIT 2
COMPUTERS AND SOCIETY
Unit 2 focuses your attention on the way computers are used throughout society and how they are affecting our lives. It points out how computers are being utilized in almost every aspect of our lives. In this chapter, you will learn about the following topics:
- the computer and its users;
- computers in the workplace.
Terms Concepts
Today, computers and electronic technologies have been incorporated into almost every aspect of society. Computers now play a role in how we learn, how we spend and take care of our money, and how we are entertained.
Some people are concerned about computer-related health issues such as the effect of radiation from the cathode-ray tube (CRT) technology used in many computer displays and the physical effects of the day-to-day use of computers.
Language Material
1. Consult a dictionary and practise the pronunciation of the following words:
procedure, direct, disease, instantaneously, to forecast, finance, financial, evidence, data, diagnose, technology, knowledgeable, score board, credential, to enhance, to convey.
2. Learn by heart the following vocabulary:
|
ability
account
capability
capacity
credentials
database
inventory
procedure
simulation
society
stock
variety
|
способность, умение
счет, отчет, причина, основание
способность
емкость, способность, мощность
аттестаты, сертификаты
база данных
оборудование
операция, процедура
моделирование, имитация
общество
запас, акция
разнообразие
|
to acquire
to carry out
to confront
to convey
to eliminate
to enhance
to install
to involve
to provide
to require
to store
to update
|
приобретать, получать
выполнять, осуществлять
противостоять, стоять лицом к лицу
перевозить, передавать
устранять, исключать, уничтожать
усиливать, увеличивать, повышать
устанавливать
включать, вовлекать, содержать
обеспечивать, принимать меры
требовать, нуждаться
хранить, запасать,
улучшать, усовершенствовать
|
3. Read the words, translate them in writing and learn by heart:
|
access
advertisement
customer
|
currency
development
destination
|
to arrive
to create
to use
|
available
entire
huge
|
4. Match the English word combinations in the left-hand column with the Russian equivalents in the right-hand column:
|
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
|
dimension
manufacturing stage
patient appointment
remote location
simulation
treatment procedure
to convey
to detect
to enhance
to involve
to keep track
to update
|
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
k.
l.
m.
|
стадия производства
отдаленное местоположение
моделирование, имитация
процесс лечения
перевозить, сообщать, выражать
открывать, обнаруживать
вовлекать, включать в себя
следить, быть в курсе
измерение, величина
совершенствовать, обновлять, увеличивать
прием пациентов
повышать, увеличивать
|
5. Note additional meanings for word “way”.
|
the way
|
путь, дорога
|
There is a way between the two cities.
|
|
|
сторона, направление
|
Look both ways before crossing the road.
|
|
|
расстояние
|
You came all this way to see us?
|
|
|
поведение, характер
|
It was not his way to admit that made a mistake.
|
|
|
метод, средство, способ
|
Personal computers have given teachers new ways to individualize instruction.
|
|
|
образ жизни
|
The computer has changed the way we work, the way we learn, the way we communicate, the way of our living.
|
|
|
область, сфера
|
He is in computing way.
|
|
|
обычай, привычка
|
It is not in his way to communicate.
|
|
|
состояние
|
The computer is in a bad way.
|
6. Consider the grammar:
to rely on/upon – полагаться, доверять, быть уверенным в ч-л, к-л.
You may rely on modern computer technologies, they are high reliable.
Around the world, investment brokers, financial advisors, and the stock exchanges themselves rely on huge databases of information about world financial markets.
to depend on – зависеть от ч.-л.
- “What time will you arrive?”
- “I don’t know. It depends on the traffic.”
to congratulate on – поздравлять к.-л. с ч.-л.
I congratulated her on her success in the exam.
to insist on – настаивать на ч.л.
I wanted to go alone but they insisted on coming with me.
to spend on – тратить на ч.-л.
How much money do you spend on food each week?
to act on / upon sth. – влиять, действовать на ч.-л.
Why didn’t you act on her suggestion?
7. Learn the synonyms:
to arrive – to come, to reach, to attain, to land, to visit, to appear.
entertainment – amusement, enjoyment, fun, pleasure, recreation, banquet, merrymaking.
to maintain – to support, to hold, to uphold, to defend, to content, to carry, to keep, to confirm.
prediction – prognostication, announcement, foretelling, preannouncement, soothsaying, fortune-telling, prognosis, forecast.
transaction – doing, proceeding, business, act, matter, action, event, deal, sale, selling, buying, purchase, purchasing, performance, execution.
to store – to keep, to save, to hold, to maintain, to support.
8. Notice the antonyms:
ability – incompetence, ignorance, weakness, dullness, stupidity, inability, limitation.
advantage – disadvantage, loss, drawback, hindrance, handicap, obstruction, barrier, restriction.
to create – to destroy, to demolish, to wreck, to frustrate, to blast, to blight, to ruin, to fail.
to develop – to curtail, to shorten, to conceal, to hide, to narrow, to lessen, to compress.
to send – to give, to get, to receive, to hold, to keep, to retain, to secure, to maintain, to hide.
9. Which of the listed below terms have Russian equivalents?
analysis, to analyze, broker, capability, company, credit, graphics, technology, technophobia.
10. Find in each line word that is given at the beginning:
|
to acquire
|
a) сканировать
|
b) следить
|
c) выражать
|
d) приобретать, достигать
|
|
to enhance
|
a) перевозить
|
b) вовлекать
|
c) проверять
|
d) расширять, увеличивать
|
|
to mean
|
a) превращать
|
b) причинять
|
c) означать
|
d) моделировать
|
|
to provide
|
a) создавать
|
b) обновлять
|
c) делать
|
d) запасать, обеспечивать
|
|
to require
|
a) описать
|
b) достигать
|
c) требовать
|
d) вовлекать
|
|
message
|
a) сообщение
|
b) мера
|
c) мерить
|
d) имитация
|
11. Give definitions to the following using the vocabulary:
education, medicine, feedback, advertisement, library, manufacturing.
12. Find in each line the word – synonym to the first word.
|
capability
|
a) energy
|
b) honesty
|
c) opportunity
|
d) assembly
|
|
variety
|
a) monotony
|
b) difference
|
c) sameness
|
d) participle
|
|
to manage
|
a) to govern
|
b) to mismanage
|
c) to bungle
|
d) to misdirect
|
|
to transmit
|
a) to invent
|
b) to supply
|
c) to transfer
|
d) to appear
|
13. Find in each line the word – antonym to the first word.
|
to change
|
a) to barter
|
b) to exchange
|
c) to alter
|
d) to remain
|
|
to combine
|
a) to deny
|
b) to blush
|
c) to separate
|
d) to praise
|
|
extensively
|
a) frosty
|
b) intensively
|
c) hardly
|
d) recently
|
|
rapidly
|
a) quickly
|
b) slowly
|
c) speedily
|
d) expressly
|
|
significant
|
a) prominent
|
b) meaningful
|
c) unimportant
|
d) grave
|
14. Read and translate the following expressions.
|
computer tomography (CAT)
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
computerized learning program
large amounts of data
cash and checks
|
to maintain information
tissue chemistry
teaching credential
electric appliance
financial advisor
|
banking transaction
to detect problem
health care system
product delivery
at high speed
|
15. Try and complete the following crossword.
1. An electronic device used to process information.
2. A form of amusement and enjoyment; way of spending free time.
3. The arrangement of the parts in any man-made product, such as a machine or work of art, as this influences the product’s practical usefulness, artistic quality.
4. The science of treating and understanding illness.
5. The activity of buying and selling goods and services.
6. A process of promoting, selling and distributing of product or service.
7. The process by which a person’s mind and character are developed through teaching, or through formal instruction at a school or at college.
8. A room or building containing the books that can be looked at or borrowed by members of the public or by members of the group or organization that owns the collection.
9. To make or produce by machinery, etc.
16. Word Bingo.
Look at the list of the words given below. Write down any five words. The teacher is going to read the definitions of all the words in random order. If you hear the definition of one of the words you have chosen, cross it out. The first student to cross out all the words he or she has chosen calls out “Bingo” and reads the words to prove his/her claim.
Words: banking, body, business, computer, communication, device, education, e-mail, entertainment, evidence, image, fax machine, feedback, finance, library, medicine, message, phone, science, society, system, text, transaction.
Word-building
Model 4
Основа глагола + tion/sion/ion существительное
|
to include - включать
to continue - продолжать
to produce - производить
to consider - рассматривать
|
inclusion - включение
continuation - продолжение
production - производство
consideration - рассмотрение
|
Model 5
Основа глагола + ment существительное
|
to assess - оценивать
to move - двигать
to establish - устанавливать
to replace - заменять
|
assessment - оценка
movement - движение
establishment - создание, установление
replacement - замена
|
Model 6
Прилагательное глагол
|
clean - чистый
dirty - грязный
empty - пустой
free - свободный
|
to clean - чистить
to dirty - грязнить
to empty - опустошать
to free - освобождать
|
17. Make new words using the models 4-6.
|
to animate
to advertise
to examine
light
to engage
to oppose
to invest
|
to communicate
to astonish
to inform
close
to environ
to predict
to judge
|
to construct
to argue
to instruct
dolly
to entertain
to prepare
to manage
|
to create
to develop
to institute
faint
to fulfill
to reproduce
to settle
|
to destine
to depart
to locate
hollow
to govern
to represent
to pay
|
to decide
to enforce
to limit
invalid
to improve
to simulate
to treat
|
18. Read the text and define the parts of speech of the words in a bold type. Name their meaning. Translate the text.
to consume - потреблять
dispenser – распределитель, раздаточное устройство
stopover – остановка в пути
Computers can help students to perform mathematical operations and solve difficult questions. They can be used to access the Internet, teach courses such as computer-aided design, language learning, programming, mathematics, etc.
PCs are also used for administrative purposes: for example, schools use databases and word processors to keep records of students, teachers and materials.
Race organizers and journalists rely on computers to provide them with the current positions of riders and teams in both the particular stages of the race and in the overall competition.
Workstations in the race buses provide the timing system and give up-to-the-minute timing information to TV stations. In the press room several PCs give real-time information on the state of race. Computer databases are also used in the drug-detecting tests for competitors.
Computers store information about the amount of money held by each client and enable staff to access large databases and carry out financial transactions at high speed. They also control the automatic cash dispensers which, by the use of a personal coded card, dispense money to clients.
Airline pilots use computers to help them control the plane. For example, monitors display data about fuel consumption and weather conditions.
In airport control towers, computers are used to manage radar systems and regulate air traffic.
On the ground, airlines are connected to travel agencies by computer. Travel agents use computers to find out about the availability of flights, prices, times, stopovers, and many other details.
Reading Practice
19. Write a list of as many uses of the compute, or computer applications, as you can think of.
20. Now read the text below and underline any applications that are not in your list.
TEXT 2A
COMPUTERS IN OUR LIVES
We use computers and computerized devices every day. Today’s “personal” computers fit nicely on our desktops. Today, computers can be carried in a briefcase or even in a pocket and new, easier-to-use computer programs make them easier to use. In a few short years, the computer has changed the way we work, the way we learn, and the way we communicate.
The computer becomes more involved in our daily lives, and for many it has meant a change in how we do our jobs. As we carry out our daily tasks, we now confront computers everywhere - in our banking transactions, to detect problems with our automobiles, to program our VCRs (video cassette recorders) and our microwave ovens, even to check the prices of our groceries at the supermarket.
Education
In education, personal computers have given teachers new ways to individualize instruction. New types of computerized learning programs can combine text, graphics, and even on-screen digitized video to give students more realistic, motivational lessons. Today, schools and universities provide a variety of courses about using computers. Many high schools and colleges are now requiring all students to take at least one course on using computers and some states now require all teachers to be knowledgeable about computers and computer programs before they can acquire teaching credentials.
Medicine
Computers are now so widely used in medicine. They are changing the structure of our society's health care system. They are used extensively for basic tasks such as keeping track of patient appointments, but they are now also widely used for both diagnosis and treatment procedures. Laboratory tests on blood and tissue chemistry have become dependent on computer analysis. In addition, such computer-based technologies as computer tomography (CAT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide direct evidence of disease. Computers are being used in this way to enhance the physician's capability to see what is going on inside the human body.
Science
Because science is involved in the analysis of large amounts of data, scientists were among the first computer users. Computers are used to construct simulations of real objects and environments in order to analyze and make predictions. They are used for analysis of many different types of statistical data. And now, new graphics capabilities are providing scientists, with the ability to create computer-enhanced analyses of many different types of images including the analysis of images that are transmitted from spacecraft visiting other planets.
Communication
In the last few decades, computer-based technologies led to a redesign of our telephone systems, and new technologies have created new ways to convey information. FAX machines and computers that can communicate with FAX machines now quickly send copies of documents across the country or across the world. Computers are now used to prepare memos, letters, and business information. Electronic mail (e-mail) systems provide individual computer users with an “address” to which computer messages can be sent. Once sent by the computer, the e-mail message will arrive almost instantaneously at its destination, where it will be stored until the addressee uses a computer to access it.
Business
Almost every business, whether large or small, has “computerized”. And every aspect of business - from sales to product delivery - now involves the use of a computer. In marketing, the computer is used to maintain information about customers and accounts. In manufacturing, the computer is used to keep track of raw materials, production, and inventory. And most large businesses now have a special department to manage the computers and the flow of computerized business information.
Banking and Finance
The computerized system is rapidly eliminating the need for cash and checks in our society. Computers now give banks a way to electronically transfer funds from one account to another without the need for paperwork. The customers can use credit and debit cards at remote locations. Computers are also used extensively in the world of stocks and investments. Around the world, investment brokers, financial advisors, and the stock exchanges themselves rely on huge databases of information about world financial markets. This computerized financial network has created a global market for currencies and financial instruments.
Entertainment and Recreation
Computers can be found throughout the entertainment industry. Computers are used to create the special effects used in television advertisements, the colourful displays on the score boards at sports arenas, and the cards that are displayed on the screen. Computer games are becoming more and more lifelike as the computer’s capability to portray graphics is constantly improved. In the motion picture industry, the time required to create animation has been greatly reduced through the use of computers and special graphics software. The movie industry also uses computers routinely for a variety of special effects and specialized computer programs have even made it possible to “colourize” old black-and-white films. Musicians are also taking advantage of advances in technology by using computerized electronic synthesizers to store, modify, and access a wide variety of sounds.
Homes
Our private homes represent one of the last places in our society to be significantly changed by the computer. Today, there are already computerized security systems in many homes. Some home builders have installed systems in houses that use a computer to control the lights, the heat, and even the electric appliances. In some homes, these computerized systems can be controlled by calling the house from any phone and typing in number sequences using the phone’s numbered dialing buttons.
Libraries
The computer has long been a powerful tool for libraries providing patrons access to bibliographic information on all of the materials that are available for their use. Now the greater storage capacities of CD-ROM disks are being used to give library users full-page access to such materials as journals, catalogs, and encyclopedias. Online catalogs provide constantly updated information about which books and other library resources are available and whether or not they are currently checked out.
Product Design and Manufacturing
Companies that are in the business of manufacturing products have found new ways to use computers in every aspect of product development. Many companies now use computers in the entire product development and production process, from the design stage to the manufacturing stage. Computer-aided design (CAD) software provides product designers with a way not only to develop a representation of the product, but also test the product design in a variety of simulated environments.
21. General understanding:
How were computers used in your school?
What other areas of study would benefit from the instruction of computers?
22. When you read texts like these, you don’t always need to understand every word. But there are words which you can guess from the context. Look at these words. Are they nouns (n), verbs (v) or adjectives (adj)?
|
1. instruction
|
2. data
|
3. perform
|
4. install
|
5. transaction
|
|
6. financial
|
7. store
|
8. connected
|
9. capability
|
10. communicate
|
Now find the words in the text and match them with the meanings below.
|
a
|
information
|
|
|
f
|
linked
|
|
|
b
|
execute (do)
|
|
|
g
|
put a new program into a computer
|
|
|
c
|
connected with money
|
|
|
h
|
act of buying or selling
|
|
|
d
|
keep (save)
|
|
|
i
|
detailed information on how to do or use sth
|
|
|
e
|
exchange information or ideas
|
|
|
j
|
the abilities or qualities necessary to do sth
|
|
23. Choose the statements which correspond to the contents of the text.
1. Nothing epitomised modern life better than computer. For better or worse, computers have infiltrated every aspect of our society.
2. Although there are many new developments in computers that are blurring the lines between these types, we can still place computers generally into four categories.
3. Computerized telephone switching centres play traffic cop to millions of calls and keep lines of communication untangled; and automatic teller machines let us conduct banking transactions from virtually anywhere in the world.
4. The basic job of the computer is the processing of information. Computers accept information in the form of instruction called a program and characters called data to perform mathematical and logical operations, and then give the results. The data is raw material while information is organized, processed, refined and useful for decision making. Computer is used to convert data into information. Computer is also used to store information in the digital form.
5. Today computers do much more than simply compute: supermarket scanners calculate our grocery bill while keeping store inventory.
6. The powerful capabilities of today’s high-resolution colour graphics hardware and new types of graphics programs are changing the way many artists do their work.
24. Find in the text passages about the computer usage in science and translate them into Russian.
25. Find in the text and put down 10-12 words or word combinations which can be used to speak about the computer usage in education.
26. Read the translation of the first two paragraphs given below. Compare it with the original and say if everything is right.
Наши дома представляют собой одно из последних мест в нашем обществе, которые значительно изменены компьютерами. Сегодня же во многих домах установлена компьютеризованная система охраны.
Если технологии телевидения, компьютеров и электронных игр объединить, то они обеспечат новую форму интерактивных видеоразвлечений. Они могут принять форму продолжительного телевизионного вещания, которое может сохраниться внутри компьютерного развлекательного центра, позволяя вам определять, что и когда вы хотите посмотреть.
В некоторых домах установлены системы, которые контролируют свет, тепло, и даже электрические приборы. В некоторых домах эти компьютерные системы могут контролироваться звонком с любого телефона и ввода последовательности чисел, используемых на телефонном диске.
Некоторые работники боятся, что могут быть заменены компьютерами. Но внедрение компьютеров в работу не влияет на безработицу. Многие из нас боятся изменений до тех пор, пока мы не научимся с ними работать.
27. Give the main idea of the extract “Computers in our lives” in 25 sentences.
Listening Practice
28. Listen to these people talking about how they use computers at work and write each speaker’s job in the table.
|
electrical engineer
|
secretary
|
librarian
|
composer
|
|
Speaker
|
Job
|
What they use computers for
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
3
|
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
29. Now listen again and write what each speaker uses their computer for. Note different meanings for word “to communicate”.
30. Mike Hartley is a director of the Adaptive Technology Project for the Blind in Washington, DC. Listen to this interview with him in which he discusses the needs of blind computer users and make notes.
Work he's involved in:
Minimum configuration required to meet the needs of these workers:
Processor:
RAM:
Expansion slots:
Specific technologies (input/output devices):
Companies that are developing adaptive equipment:
31. Compare your notes in pairs.
32. Listen again and complete your notes.
33. Read and translate the text.
TEXT 2B
COMPUTERS IN THE WORKPLACE
|
to be responsible - быть ответственным за ч.-л.
on the other hand - с другой стороны
phobia - страх, боязнь
|
previously - предыдущий
skill - умение
wrist pain - боль в пояснице
|
Almost everyone recognizes the presence of computers in today’s work places. What computers have often caused is a need for people to be retrained so they can fill the jobs that have been created by computers and new related technologies.
Most users find that many of the skills that were previously learned as part of their jobs can be applied to learning about the new tools made available by the computer. In most cases job-related skills rather than computer skills are found to be most important to worker productivity.
Fear of technology is known as technophobia. Many people feel that as new generations grow up with computers and learn to use them in a variety of environments they will feel more comfortable with the technology and will not suffer from the discomfort of this transitional period.
Telecommuting
Some people are working in their homes. These workers can communicate with the office and access information from the company’s computer system. If employees have to work overtime, at least they can do so in the comfort of their own home. Parents can be available for their children at home and still get some work done. By telecommuting, employees can do the work when they are most productive. As a result, because the computer never sleeps, night owls can work all night.
Worker Health
Many people are concerned about the effect of radiation from the cathode-ray tube (CRT) technology used in many computer displays. Computer display technology is being improved to reduce the amount of radiation that is emitted. There is also some evidence that spending too much time looking at a computer screen may cause headaches and vision problems. Filters have now been developed to reduce the amount of glare coming off of computer screens.
On the other hand, too much time is engaged in repetitive motion while using a computer can cause problems. For example, computer users who spend too much time sitting in one position while using a computer can develop back problems. And many people who spend long hours typing on a computer keyboard can develop wrist pain.
34. Choose a passage and read it aloud (The approximate time of reading is 1-2 minutes).
35. Look through the text again to find two facts which were quite new to you and two facts which were already known to you.
36. Give the main idea of the extract “Computers in the workplace” in 20 sentences.
Writing Practice
37. Write a letter to Mike Hartley asking for information about computers for the disabled. Make sure you include the following points.
- Begin by saying why you're writing:
I am writing to ...
- Ask for information about specific input/output equipment for deaf, blind and motor-disabled workers:
I would like to know ...
- Ask for a free handbook about how to add adaptive technology to personal computers:
I would be very grateful if...
- End the letter appropriately:
I look forward to hearing from you soon.
Yours sincerely ...
Oral Practice
38. In small groups, choose one of the areas in the diagram below and discuss what computers can do in this area.
Useful words
Formula 1: racing car, car body, design, mechanical parts, electronic components, engine speed.
Entertainment: game, music, animated image, multimedia, encyclopedia.
Factories: machinery, robot, production line, computer-aided manufacturing software.
Hospitals: patients, medical personnel, database program, records, scanner diagnose, disease, robot, surgery.
Useful constructions
Computers are used to ...
A PC can also be used for ...
|
Computers can
|
help ...
|
manage ...
|
measure ...
|
|
|
make ...
|
give …
|
test ...
|
|
|
control ...
|
perform ...
|
provide ...
|
|
|
store ...
|
keep ...
|
provide access to ...
|
39. Now write a short paragraph summarizing your discussion. Then ask one person from your group to give a summary of the group’s ideas to the rest of the class.
Examples
In the business, computers are used for financial planning, accounting and specific calculations.
In the office, computers are used to write letters and e-mails, and keep records of clients, suppliers and employees.
40. Discussion.
More and more people begin using computers in their work. Some of them cannot imagine their life without this invention of the 20th century. Children find computer games very interesting. Are computers one of the greatest or the most dangerous inventions?
Say whether you use a computer in your work or for playing computer games. Do you use your computer in any other way or for any other purposes?
a) Read the following arguments. Think of some more.
|
Computers are one of the greatest inventions
|
Computers are one of the most dangerous inventions
|
|
1. They save a lot of time.
2. They can do calculations and other things which are not interesting for people to do.
3. They help you to process information.
4. You can learn many things using a computer as a tutor.
5. You can relax playing computer games.
|
1. They are dangerous for your health.
2. People waste a lot of time playing computer games.
3. You can lose the results of your work if something goes wrong with the computer.
4. Some people live in a virtual reality not in the real world.
5. Children cannot do the simplest arithmetic sums because they rely on computers.
|
b) Discuss the problem in groups of 3-5 students in order to make decision.
UNIT 3
THE HISTORY OF COMPUTING
This unit takes you back in time and introduces you to the technological developments that have evolved over time into the complex computer systems we use today. By understanding the connections between these early developments in the history of computers, you can see insight into the processes of technological evolution that continue today. In this chapter you will learn about the following topics:
- the evolution of computers;
- next-generation computers.
Terms Concepts
Despite the fact that today’s computers are much smaller and much cheaper than their predecessors, they are far more flexible and powerful. Integrator and Calculator (ENIAC) is in now seen as the first electronic computer. The first really successful computer was produced by Mauchley and Eckert and was named the UNIVAG 1.
New methods of programming the firm generation of computers evolved with the hardware development. Fortran is generally seen as the first high-level programming language. Special-purpose microprocessors were produced in the early 1970s and in 1974 Intel produced their new 8-bit processor with 64,000 operations per second.
Language Material
1. Consult a dictionary and practise the pronunciation of the following words:
progress, importance, project, to succeed, efficiency, minuscule, artificial, versatility, feature, cumbersome, enormous, demand, sensitive, quartz, scientist, ultra-large, icon.
2. Learn by heart the following vocabulary:
|
experience
equation
efficiency
feature
onset
semiconductor
stride
trend
versatility
cumbersome
distinct
distinctive
large-scale
reliable
sophisticated to shrink
|
опыт
уравнение
эффективность, действенность
черта, особенность
начало, натиск
полупроводник
шаг, успех
тенденция, направление
разносторонность
громоздкий
отчетливый, различный
отличительный, различный
многомасштабный
надежный
сложный сужать(ся),
садиться
|
to consume
to contain
to diminish
to describe
to eliminate
to expand
to exploit
to hasten
to handle
to include
to increase
to link
to resume
to share
to succeed
to squeeze
|
потреблять, съедать
содержать
уменьшать, ослаблять
описывать
исключать, устранять
расширять
использовать
ускорять
управлять, обращаться с
включать
увеличивать
связывать(ся)
возобновлять
делить(ся)
достигать цели, удаваться
вмещать, сжимать
|
3. Read the words; translate them in writing and learn by heart:
|
sequence
missile
generation
invention
silicon
|
icon
enormous
to damage
to fit
to consist
|
to allow
to limit
to move
to replace
to remain
|
4. Match the English word combinations in the left-hand column with the Russian equivalents in the right-hand column:
|
1. machine language
2. computer function
3. computer engineering
4. the key element
5. vacuum tube
6. a general-purpose computer
7. tape storage
8. disk storage
9. stored program
10. to run program
11. to meet any number demands
12. an electronic relay computer
|
a) функция компьютера
b) компьютер с электрическим реле
c) электровакуумная лампа
d) ЭВМ
e) компьютерное проектирование / техника
f) машинный язык
g) запустить программу
h) отвечать любым требованиям
i) ленточный накопитель
j) ключевой элемент
k) дисковый накопитель
l) с хранимой программой
|
5. Consider the grammar:
to apologise to smb for - извиняться перед к-л., за ч-л.
They apologized me for what happened. Go and apologize to her. We apologized to the passengers for the late departure of this flight.
to explain sth to smb – объяснять ч-л. к-л.
Can you explain this word to me? First, I’ll explain the rules of game to you. It was difficult to explain the problem to the beginners. The government now has to explain its decision to the public.
to lead to - приводить к ч.-л.
Eating too much sugar can lead to health problems. This has led scientists to speculate on the existence of other galaxies. The situation is far worse than we had been led to believe.
to listen to – слушать ч-л.
We spend the evening listening to music. I listened carefully to her story. None of this would have happened if you’d listen to me. Why won’t listen to reason?
to talk/ speak to smb – разговаривать с к-л.
Who was that man you were talking to? Ann and Joe aren’t talking to each other right now. Talk to your doctor if you’re still worried. I’ve spoken to the manager about it. Have you talked to your parents about the problems you’re having?
to write to – писать к-л. ч.-л.
I wrote to the hotel complaining about the poor service we had received. She wrote to him in France. An error was reported when he tried to write data to the file for the first time.
6. Note additional meanings for word “to fit”.
|
to fit
|
быть в пору
|
The key does not fit the lock.
|
|
|
монтировать, устанавливать
|
They fitted a smoke alarm to the ceiling.
|
|
|
соответствовать, совпадать
|
The facts certainly fit your theory.
|
|
|
подходить
|
His experience fitted him to do the job.
|
7. Match the synonyms:
trend – direction, tendency, orientation, tenor.
intelligent - smart, clever, brilliant, bright.
to contain - to include, to incorporate, to embody, to encompass, to involve, to comprehend.
to diminish – to lessen, to reduce, to decrease, to minimize, to shorten, to cut off.
to impact on – influence on, have an influence on, affect.
to limit - to eliminate, to restrict, to confine.
to squeeze – to hold, to contain, to go into, to compress, to contract.
8. Match the antonyms:
|
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
|
to increase
to develop
to decode
part
slow
complex
powerful
reliable
small
specific
toward
|
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
g)
h)
i)
j)
k)
|
simple
massive
general / common
fast
to decrease
weak
to encode
whole
back
unreliable
to shorten
|
9. Find in each line word that is given at the beginning:
|
application
|
a) эффективность
|
b) уравнение
|
c) применение
|
d) направление
|
|
icon
|
a) полупроводник
|
b) окошечко
|
c) действенность
|
d) опыт
|
|
silicon
|
a) уравнение
|
b) натиск
|
c) успех
|
d) кремний
|
|
to damage
|
a) увеличивать
|
b) повреждать
|
c) потреблять
|
d) расширять
|
|
to resume
|
a) описывать
|
b) содержать
|
c) возобновлять
|
d) делить
|
|
large-scale
|
a) большой
|
b) сложный
|
c) крупномасштабный
|
d) громоздкий
|
|
distinctive
|
a) отличительный
|
b) отдаленный
|
c) дистанционный
|
d) длительный
|
10. Find in each line the word – synonym to the first word:
|
to increase
|
a) to expand
|
b) to handle
|
c) to raise
|
d) to diminish
|
|
to exploit
|
a) to succeed
|
b) to use
|
c) to include
|
d) to eliminate
|
|
to consist
|
a) to include
|
b) to hasten
|
c) to exploit
|
d) to diminish
|
|
missile
|
a) generation
|
b) sequence
|
c) invention
|
d) rocket
|
|
to link
|
a) to join
|
b) to consume
|
c) to eliminate
|
d) to squeeze
|
|
cumbersome
|
a) distinct
|
b) bulky
|
c) reliable
|
d) sophisticated
|
11. Find in each line the word – antonym to the first word:
|
reliable
|
a) cumbersome
|
b) distinctive
|
c) enormous
|
d) unstable
|
|
the onset
|
a) end
|
b) versatility
|
c) icon
|
d) invention
|
|
to hasten
|
a) to include
|
b) to slow
|
c) to expand
|
d) to consume
|
|
distinct
|
a) enormous
|
b) reliable
|
c) cumbersome
|
d) same
|
|
entire
|
a) part
|
b) sophisticated
|
c) large-scale
|
d) reliable
|
|
demand
|
a) onset
|
b) equation
|
c) supply
|
d) stride
|
12. Read and translate the following expressions.
|
the increasing funding
a secret code-breaking computer
in common (general) use
magnetic drum
a set of instruction
binary-coded program
quartz clock
energy-efficient
spreadsheet program
|
Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer
Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator
Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer
user-friendly software package
soldered join
great deal
solid state
integrated circuit
word processing
|
13. Give definitions to the following using the vocabulary:
generation, vacuum tube, transistor, integrated circuit, microprocessor, operating system, artificial intelligence, semiconductor.
14. Word Bingo.
Look at the list of the words given below. Write down any four words. The teacher is going to read the definitions of all the words in random order. If you hear the definition of one of the words you have chosen, cross it out. The first student to cross out all the words he or she has chosen calls out “Bingo” and reads the words to prove his/her claim.
Words: computing, history, vacuum tube, transistor, integrated circuit, microprocessor, operating system, generation, the onset, distinct, trend.
Word-building
Model 7
Основа прилагательного + -ly наречие
|
free – свободный
possible – возможный
deep – глубокий
safe – безопасный
|
freely – свободно
possibly – возможно
deeply – глубоко
safely – безопасно
|
Model 8
Основа существительного + -ic прилагательное
|
history – история
system – система
base – основа
|
historic – исторический
systematic – систематический
basic – основной
|
Model 9
Основа глагола + -ing существительное
|
to open – открывать
to break – разбивать, разрушать
to repair – ремонтировать
to measure – мерить
|
opening – открытие
breaking – разрушение
repairing – ремонт
measuring – мера
|
15. Make new words using the models 7-9.
|
accurate
to build
canon
exact
to break
parabola
legal
to help
period
simple
to process
ascent
|
applicable
to buy
magnet
fair
to engineer
diplomat
loud
to keep
philately
successful
to read
atom
|
correct
to cook
opportunist
inadequate
to develop
patriot
objective
to learn
phobia
to play
to see
electron
|
easy
to drive
pantheist
indirect
to find
pedant
real
to meet
photograph
to prove
to program
fatalist
|
16. Read the text and define the parts of speech of the words in a bold type. Name their meaning. Translate the text.
Early computing machines and inventors
|
numerical – числовой
counter – счетчик
soldered – припаянный
capability – способность
|
wire – провод
to connect – соединять
variety – разнообразие
power – мощность
|
vacuum-tube – электровакуумная лампа
to consider – рассматривать
remarkable – замечательный
|
In the late 1800s, a variety of mechanical devices were designed to carry out numerical calculations. But the first real computers came during World War II when governments needed better and faster calculating systems. The earliest computers were designed to facilitate weapons management, code breaking, and wartime recordkeeping.
In the late 1930s, Howard Aiken at Harvard University was working with a $500,000 grant from IBM to develop an automatic calculating machine. The machine, which came to be known as the Mark 1, was completed in 1944. It used electrically powered mechanical counters to store the results of arithmetic calculations. It contained 500 miles of wire, had 3 million electrical connections, and required about 6 seconds to carry out each multiplication task.
At about the same time, at Iowa State University a computing device that incorporated an advanced design was built by John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry. Although the device was not designed for large-scale processing, it was the first to be based on vacuum-tube technology and was therefore the first fully electronic computing device. Completed in 1942, it became known as Atanasoff-Berry Computer, or the ABC computer.
At the University of Pennsylvania, J. Presper Eckert and John W. Mauchley were working on a much larger device. They designed a completely electronic device that could be used for a variety of calculating tasks. They called it the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator, or ENIAC. Unveiled in 1944, it is now considered to be the first large-scale, general-purpose electronic computer. Although it was very slow and very limited in capability as compared to today’s computers, it represented a remarkable advancement in computing power for the time. The ENIAC contained 19,000 vacuum tubes and 5 million soldered electrical connections. It could perform up to 5,000 additions per second, but it consumed much power.
None of the early computers could be programmed. In the midle1940, John von Neumann joined Eckert and Mauchley. His ideas for designing a programmable computer were to form the basis for the types of stored-program computers we still use today. These stored programs are now known as software (in contrast to the computer’s physical devices, known as hardware).
Reading Practice
17. Read the text. Try to understand it and be ready to answer the questions.
FIVE GENERATIONS OF MODERN COMPUTERS
As important as computers are to today’s businesses, hospitals, and educational institutions, they haven't been in general use very long.
The computer is often described as having gone through five distinct generations. Each of these generations is based on the type of technology used during the period.
First Generation (1945-1956)
With the onset of the Second World War, governments sought to develop computers to exploit their potential strategic importance. This increased funding for computer development projects hastened technical progress. By 1941 German engineer Konrad Zuse had developed a computer, the Z3, to design airplanes and missiles. The Allied forces, however, made greater strides in developing powerful computers. In 1943, the British completed a secret code-breaking computer called Colossus to decode German messages. The Colossus impacts on the development of the computer industry. Colossus was not a general-purpose computer; it was only designed to decode secret messages. American Howard H. Aiken (1900-1973) succeeded in producing an all-electronic calculator by 1944. The Harvard-IBM Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator, or Mark I for short, was an electronic relay computer. It used electromagnetic signals to move mechanical parts. The machine was slow (taking 3-5 seconds per calculation) and inflexible (in that sequences of calculations could not change); but it could perform basic arithmetic as well as more complex equations. Another computer development was the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), consisting of 18,000 vacuum tubes, 70,000 resistors and 5 million soldered joints, the computer was such a massive piece of machinery that it consumed 160 kilowatts of electrical power. Developed by John Presper Eckert (1919-1995) and John W. Mauchly (1907-1980), ENIAC, unlike the Colossus and Mark I, was a general-purpose computer that computed at speeds 1,000 times faster than Mark I. Integrator and Calculator (ENIAC) are in now seen as the first electronic computer.
In the mid-1940s John von Neumann (1903-1957) joined the University of Pennsylvania team, initiating concepts in computer design that remained central to computer engineering for the next 40 years. Von Neumann designed the Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer (EDVAC) in 1945 with a memory to hold both a stored program as well as data. This “stored memory” technique allowed the computer to be stopped at any point and then resumed, allowed for greater versatility in computer programming. The key element to the von Neumann architecture was the central processing unit which allowed all computer functions to be coordinated through a single source. In 1951 the UNIVAC I (Universal Automatic Computer), built by Remington Rand, became one of the first commercially available computers to take advantage of these advances.
First generation computers were characterized by the fact that operating instructions were made-to-order for the specific task for which the computer was to be used. Each computer had a different binary-coded program called a machine language that told it how to operate. This made the computer difficult to program and limited its versatility and speed. Other distinctive features of first generation computers were the use of vacuum tubes and magnetic drums for data storage.
Second Generation Computers (1956-1963)
The invention of the transistor greatly changed the computer’s development. The transistor replaced the large cumbersome vacuum tube in televisions, radios and computers. As a result, the size of electronic machinery has been shrinking ever since. The transistor was at work in the computer by 1956. Coupled with early advances in magnetic-core memory, transistors led to second generation computers that were smaller, faster, more reliable and more energy-efficient than their predecessors. The first large-scale machines taken advantage of this transistor technology were early supercomputers, produced by IBM and LARC by Sperry-Rand. These computers could handle an enormous amount of data, a capability much in demand by atomic scientists. Second generation computers replaced machine language with assembly language, allowing abbreviated programming codes to replace long, difficult binary codes. These second generation computers (Burroughs, Control Data, Honeywell, IBM, Sperry-Rand) were also of solid state design, and contained transistors in place of vacuum tubes. They also contained printers, tape storage, disk storage, memory, operating systems, and stored programs. One important example was the IBM 1401. The stored program concept meant that instructions to run a computer were held inside the computer's memory, and could quickly be replaced by a different set of instructions for a different function. More sophisticated high-level languages such as COBOL (Common Business-Oriented Language) and FORTRAN (Formula Translator) came into common use during this time. New types of careers (programmer, analyst, and computer systems expert) and the entire software industry began with second generation computers.
Third Generation Computers (1964-1971)
Transistors still generated a great deal of heat which damaged the computer's sensitive internal parts. The quartz clock eliminated this problem. Jack Kilby, an engineer with Texas Instruments, developed the integrated circuit (IC) in 1958. The IC combined three electronic components onto a small silicon disk which was made from quartz. Scientists later managed to fit even more components on a single chip called a semiconductor. As a result, computers became ever smaller as more components were squeezed onto the chip. Another third-generation development included the use of an operating system that allowed machines to run many different programs at once with a central program that monitored and coordinated the computer's memory.
Fourth Generation (1971 - Present)
After the integrated circuits, the only place to go was down - in size, that is, large scale integration (LSI) could fit hundreds of components onto one chip. By the 1980s very large scale integration (VLSI) squeezed hundreds of thousands of components onto a chip. Ultra-large scale integration (ULSI) increased that number into the millions. The ability to fit so much helped diminish the size and price of computers. It also increased their power, efficiency and reliability. The Intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, took the integrated circuit one step further by locating all the components of a computer (central processing unit, memory, and input and output controls) on a minuscule chip. Now one microprocessor could be manufactured and then programmed to meet any number of demands. These minicomputers came complete with user-friendly software packages most popularly word processing and spreadsheet programs. In 1981, IBM introduced its personal computer (PC) for use in the homes, offices and schools. Computers continued their trend toward a smaller size, working their way down from desktop to laptop computers to palmtop. In direct competition with IBM’s PC was Apple’s Macintosh line, introduced in 1984. The Macintosh offered an operating system that allowed users to move screen icons instead of typing instructions. Users controlled the screen cursor using a mouse, a device that mimicked the movement of one's hand on the computer screen. As smaller computers became more powerful, they could be linked together, or networked, to share memory space, software, information and communicate with each other. As opposed to a mainframe computer which was one powerful computer that shared time with many terminals for many applications, networked computers allowed individual computers to form electronic co-ops. A global web of computer circuitry, for example, the Internet links computers worldwide into a single network of information.
Fifth Generation (Present and Beyond)
Computers have come from nowhere 50 years ago and are rapidly catching in capability with the human brain. We can expect human machine equivalence by about 2015. But after this, computers will get smarter. There is a noticeable positive feedback loop in technology development with each generation of improved computers giving us more assistance in the design and development of the next.
Ultimately, they will design their offspring with little or no human involvement. This technology development will push every field of knowledge forwards, not just computing.
But we will never get far unless we can solve the interface problem. In the near future we may have electronic pets, with video camera eyes and microphone ears, linked by radio to the family computer. With voice and language recognition we will have easy access to all that the Internet can provide. We can tell the pet what we want and it will sort it out of us. It will be impossible to be technophobic about such an interface, and the only IT skill needs will be to speak any major language.
However, new computer programs and new methods of programming computers will have to be design and put into operation before we can be said to be fully engaged in this latest generation of computing.
18. General understanding:
1. What is the relationship between devices like EDVAC and the device that is the modern computer?
2. What was the name of the first electronic computer and what computing principles did it introduce?
3. On what electronic component was based the first generation of computers? Name a computer that reprimands this generation.
4. What new methods of programming were introduced with the first generation of computers?
5. What new invention is associated with the second generation of computers?
6. Contrast the second and third generations of computers by describing hardware and software development that emerged during each period.
7. Contrast how microcomputers are used with the way second and third generation computers?
8. What are some of the names used to refer to a small computer, a microprocessor?
19. Choose the correct answer. Watch this section and tick the right answers below.
|
1. The history of computing has gone through …
|
a) four distinctive generations of modern computers;
b) five distinct generations, based on the type of technology;
c) three main characteristic generations.
|
|
2. First generation computers were characterized …
|
a) by the use of vacuum tubes and magnetic drums for data storage;
b) by designing to decode secret messages;
c) performing basic arithmetic equations.
|
|
3. Second generation computers contained …
|
a) vacuum tubes;
b) printers, tape storage, disk storage, memory, operating systems, and stored programs;
c) long difficult binary codes.
|
|
4. Third generation development included …
|
a) the quartz clock, integrated circuit;
b) the use of an operating system to run many different programs;
c) a) and b).
|
|
5. The fourth generation computers managed …
|
a) to squeeze hundreds of thousands of components onto a chip;
b) to increase power, efficiency and reliability of a computer;
c) a) and b)
|
|
6. The main characteristic feature of the fifth generation computers is …
|
a) artificial intelligent;
b) the use of visual input;
c) the ability to translate a foreign languages.
|
20. Try and complete the following crossword.
1. ………
2. On this component was based the first generation of computers.
3. All the events that happened in the past.
4. A chip, or integrated circuit, that process the instructions provided by the software.
5. A set of programs that controls the way a computer works and runs other programs.
6. This computer became one of the first commercially available computers to take advantage of these advances.
7. A small electronic device used in computers, radios, televisions, etc. for controlling an electric current as it passes along a circuit.
8. An area of study concerned with making computers copy intelligent human behavior.
9. A small microchip that contains a large number of electrical connections and performs the same function as larger circuit made from separate parts.
10. A stage in development of a technical product.
21. Find in the text passages about the first generation computers and translate them into Russian.
22. Choose a passage from those you’ve translated and read it aloud (the approximate time of reading is 2-3 minutes).
23. Find in the text and put down 10-12 words or word combinations which can be used to speak about the second generation computers.
24. What do you know about the computers of the third generation? Read the statements given below and if you think the statement is true agree to it saying “That’s right” If you think it is not true, disagree saying “That’s wrong” and make the necessary corrections.
1. The computers of the third generation did not generate a great deal of heat.
2. An engineer Jack Kilby developed the integrated circuit (IC) in 1958.
3. The IC combined three electronic components onto a small silicon disk which was made from silicon.
4. Scientists managed to fit more components on a semiconductor.
5. The ability to translate a foreign language is also moderately possible with third generation computers.
6. Another third-generation development included the use of an operating system.
25. Read the translation of the paragraph given below. Compare it with the original and say if everything is right.
Чип Intel 4004, разработанный в 1981 году, продвинул интегральные схемы на шаг вперед, вместив все компоненты компьютера (CPU, память, устройства ввода и вывода данных) на один небольшой чип. Сейчас любой микропроцессор может быть сконструирован и запрограммирован так, чтобы отвечать любым требованиям. Эти миникомпьютеры были выпущены в комплекте с дружественным пользовательским интерфейсом, особенно популярным текстовым редактором и электронными таблицами. В 1971 году фирма IBM представила свой персональный компьютер для использования дома, в офисе и школах. Компьютеры продолжали свое движение по уменьшению размера, разрабатывая от настольного компьютера к лэптопам, а затем и к палмтопам. В тесной конкуренции с компанией IBM, Макинтош представил свою линию компьютеров в 1984 году.
26. Look through the text again to find two facts which were quite new to you and two facts which were already known to you.
27. Answer the following questions. If necessary, look through the text again.
- What will be the difference between computers and humans after 2015?
- What does “positive feedback loop” mean in computer development?
- Why will knowledge of a major language be the only IT skill needed?
28. Give the main idea of extract “Five Generations of Modern Computers” in 25-30 sentences.
Listening Practice
29. Listen to the text “The first computers” and answer if these sentences are true (T) or false (F)?
- In the 1940s and 1950s, computers were very small.
- It was not easy for the Sumerians to do calculations.
- The word “computer” used to mean “a person who does calculations”.
- In the 1820s, a British mathematician called Charles Babbage invented a machine that did very difficult calculations automatically.
- Babbage wrote programs for his machines by making holes in old cinema film.
- In 1979 a modern computer programming language was named Zl.
- Ada Lovelace was still the first computer programmer in the world.
- Lord Byron, a famous English writer, was an excellent mathematician and understood Babbage’s ideas.
- Babbage’s Difference Engine is still in the museum today.
- Ada Lovelace never finished anything - she always had a better idea and started working on something new.
30. Put the sentences in the right order.
1. who, did, the, the people, the books, calculations, called, and, wrote, were, computers.
2. in the 1820s, called Charles Babbage, a machine, a British mathematician, invented, that, difficult calculations, automatically, did, very.
3. programs, old, for, Zuse, making, machines, wrote, film, his, by, holes, in, cinema.
4. in, built, 1938, he, machine, parents’, his, Berlin, living, first, the Zl, in, in, his, room.
5. not, Babbage, making, did, finish, the, Difference, Engine.
6. work, on, a, started, called, an, Babbage, machine, Analytical, Engine.
31. Think the arguments for and against this statement.
Computers will catch up with the power and speed of the human brain by 2050. Some time after that the computing will start outstripping us and taking over from us.
32. Choose one side only – for or against the statement. Now listen to the recording and note down any points in support of your side.
33. Using your notes and your own ideas, try to persuade the rest of your group to accept your views on the statement in task 30.
Writing Practice
34. Summarise the views of Pearson and of the experts you heard on the Future of Information Technology. Give your own comments on their views. Write about 250 words.
35. Skim the text; write a summary in English about what it is.
Классификация ЭВМ по этапам создания
По этапам создания и используемой элементной базе ЭВМ условно делятся на поколения:
1-е поколение, 50-е гг.: ЭВМ на электронных вакуумных лампах, быстродействие - до нескольких десятков тысяч операций в секунду. Первые запоминающие устройства (перфокарты, перфолента);
2-е поколение, 60-е гг.: ЭВМ на дискретных полупроводниковых приборах (транзисторах); быстродействие - до 1-2 млн. операций в секунду;
3-е поколение, 70-е гг.: ЭВМ на полупроводниковых интегральных схемах с малой и средней степенью интеграции (сотни - тысячи транзисторов в одном корпусе), быстродействие – до 300 млн. операций в секунду, микро-ЭВМ, предназначенные для работы с одним пользователем;
4-е поколение, 80-е гг.: ЭВМ на больших и сверхбольших интегральных схемах-микропроцессорах (десятки тысяч - миллионы транзисторов в одном кристалле), быстродействие - миллиарды операций в секунду. Персональные ЭВМ. Готовые прикладные программы, графический интерфейс, использование технологии мультимедиа. Глобальные компьютерные сети.
5-е поколение, 90-е гг.: ЭВМ со многими десятками параллельно работающих микропроцессоров, позволяющих строить эффективные системы обработки знаний; ЭВМ на сверхсложных микропроцессорах с параллельно-векторной структурой, одновременно выполняющих десятки последовательных команд программы;
6-е и последующие поколения: оптоэлектронные ЭВМ с массовым параллелизмом и нейронной структурой 2-с распределенной сетью большого числа (десятки тысяч) несложных микропроцессоров, моделирующих архитектуру нейронных биологических систем.
Каждое следующее поколение ЭВМ имеет по сравнению с предшествующим существенно лучшие характеристики. Так, производительность ЭВМ и емкость всех запоминающих устройств увеличиваются, как правило, больше чем на порядок.
UNIT 4
TYPES OF COMPUTER
Unit 4 will give you an overview of the kinds of computers we use today. You will also learn some of the basic issues, definitions, and concepts related to computers and their use. In this chapter, you will learn about the following topics:
- defining the computer;
- how computers are used;
- computer types.
Terms Concepts
There are four main types of computers: mainframes (large, expensive computers, often referred to as host computers), supercomputers, minicomputers (smaller and less powerful, but also used as host computers), and microcomputers (desktop-sized, personal computers).
Microcomputers are based on a microprocessor (a single chip with numerous miniaturized circuits) generally manufactured by a third side (someone other than the maker or the user of the computer).
Language Material
1. Consult a dictionary and practise the pronunciation of the following words:
essential, era, automation, design, to vary, variety, various, entire, research, to attach, to process, to accept, specified, due, manufacturing, generally, often, essentially, fundamental, significantly, agency, board, thought.
2. Learn by heart the following vocabulary:
|
desktop PC
handheld
inception
laptop
mainframe
microcomputer
microprocessor notebook
proximity workstation
host
portable
significant
|
настольный компьютер
карманный компьютер
начало
портативный компьютер
универсальная ЭВМ
микрокомпьютер
микропроцессор
компьютер-блокнот
близость
рабочая станция
главный, хост
переносной, портативный
значительный
|
powerful
regardless
due to
despite
to attach
to allow
to communicate
to include
to input
to output
to process
to referred to as
to serve
|
мощный
безотносительно
благодаря, из-за
несмотря на
прикреплять, присоединять
позволять
общаться
включать
вводить
выводить
обрабатывать
называться
служить
|
3. Match the English word combinations in the left-hand column with the Russian equivalents in the right-hand column:
|
1. mainframe
2. to execute
3. to obtain
4. set of instructions
5. a single chip
6. circuit
7. to input data
8. to output data
9. specific computer task
10. binary system
11. operating system
12. printed board
13. to serve the needs
14. PDA
|
a. цепь, схема
b. получать данные на выходе
c. печатная плата
d. служить нуждам
e. операционная система
f. набор инструкций
g. исполнять (команду)
h. определенная компьютерная задача
i. получить, добиться
j. (универсальная) вычислительная машина
k. вводить данные
l. отдельный чип
m. личный цифровой секретарь
n. двоичная система
|
4. Translate into Russian words internationals:
computer, class, microcomputer, supercomputer, notebook, electronic, system, processor, limit, instruction, information, program, disk, era, graphics, design.
5. Match these names to different types of computer.
|
1. mainframe
2. communicator
3. notebook
4. handheld
|
5. PDA
6. minicomputer (server)
7. supercomputer
|
8. pen-based computer
9 smart phone
10. workstation
|
|

a) ...............................
|

b) ...........................
|
|

c) ......................................
|
 d)........................................ d)........................................
|
|

e) .....................................
|

f).......................................
|
|

g) .......................................
|
h) ......................................
|
|
i) ......................................
|

j) ............................................
|
Who uses these types of computer?
- computer Salesperson
- hardware Engineer
- software Designer
- secretary
- politician
|
- housewife
- schoolboy
- student
- plumber
- pilot
|
- systems Support Person
- businessman
- operator
- book-keeper
- mathematician
|
- system Analyst
- technical Sales Manager
- network Support Person
- scientist
- cosmonaut
|
Where do they use them? Make a list.
|
... is/are used in ...
|
... is/are used for ... -ing
|
Using ..., you can ...
|
You can use ... to ...
|
6. Find in each line word that is given at the beginning.
|
to provide
|
a) исполнять
|
b) получать
|
c) вводить
|
d) обеспечивать
|
|
palmtop
|
a) рабочая станция
|
b) карманный компьютер
|
c) компьютер-блокнот
|
d) универсальная ЭВМ
|
|
to obtain
|
a) обеспечивать
|
b) получать
|
c) выполнять
|
d) использовать
|
|
portable
|
a) переносной
|
b) мощный
|
c) значительный
|
d) главный
|
|
to process
|
a) обрабатывать
|
b) присоединять
|
c) позволять
|
d) получать
|
|
inception
|
a) близость
|
b) начало
|
c) множество
|
d) использование
|
|
significant
|
a) совместимый
|
b) значительный
|
c) мощный
|
d) отдельный
|
7. Give definitions to the following using the vocabulary.
computer, host computer, microcomputer, minicomputer, mainframe, supercomputer, microprocessor, notebook, desktop PC, workstation, handheld, PDA.
8. Note different meanings for word “to communicate”.
|
to communicate
|
сообщаться, связываться
|
One computer system is set up to communicate with another computer system.
|
|
|
обмениваться, общаться
|
They communicated in sign language.
|
|
|
передавать
|
The disease is communicated through dirty drinking water.
|
|
|
понимать
|
The novel is about a family who can’t communicate with each other.
|
9. Consider the grammar:
to base sth. on /upon sth. – основывать, базировать, опираться на ч.-л.
What are you basing this theory on?
to concentrate on – сосредоточивать(ся), концентрировать(ся) на ч.-л.
Don’t look out of the window. Concentrate on your work.
to insist on – настаивать на ч.-.л.
I wanted to go alone, but some friends of mine insisted on coming with me.
10. Match the synonyms:
capacity – volume, size, expanse, magnitude, content, faculty, ability, skill, genius.
cost – spending, expenditure, expenses, outlay, outgoings.
inception – beginning, start, origin, initiation, opening, onset.
speed – swiftness, quickness, urgency, haste, expedition, dispatch, hurry, rapidity.
type – symbol, emblem, figure, character, letter, sign, sort, kind, form, class, copy, shape.
11. Match the antonyms:
- cheap
- possible
- high
- different
- main
- to attach
- output
- often
- powerful
- fast
- large
- complex
|
- input
- seldom
- weak
- slow
- small
- simple
- expensive
- low
- similar
- additional
- impracticable
- to unfasten
|
12. Match the English words with them from what they are built.
user, microprocessor, printer, information, computer, electronic, processing, specified, development, communication, mainly, manufacturing, inception, significantly, traditionally, workstation, generally, usually, building, location, basic, institution, calculation, department, specific, basically, managing, instruction, operating.
13. Find in each line the word – synonym to the first word.
|
to obtain
|
a) to allow
|
b) to attach
|
c) to acquire
|
d) to process
|
|
to provide
|
a) to include
|
b) to stipulate
|
c) to contain
|
d) to serve
|
|
host
|
a) main
|
b) regard
|
c) proximity
|
d) board
|
|
powerful
|
a) portable
|
b) forceful
|
c) regardless
|
d) single
|
|
significant
|
a) due to
|
b) regardless
|
c) despite
|
d) important
|
14. Find noun in each line.
|
1.
|
a) allow
|
b) powerful
|
c) portable
|
d) inception
|
e) cheap
|
|
2.
|
a) handheld
|
b) due to
|
c) significant
|
d) specific
|
e) fast
|
|
3.
|
a) include
|
b) attach
|
c) regard
|
d) print
|
e) complex
|
|
4.
|
a) regardless
|
b) refer
|
c) execute
|
d) serve
|
e) proximity
|
|
5.
|
a) despite
|
b) circuit
|
c) obtain
|
d) possible
|
e) main
|
15. Read and translate the following expressions.
|
processing hardware
a single printed board
storage device
|
for that reason
binary data
in closer proximity
|
to access the site
data processing device
the computer’s response time
|
16. Complete this crossword by using the terms from the vocabulary. Then write the word in the puzzle.
1. Smaller than a mainframe, powerful, multi-user, multi-tasking.
2. A very small computer that you can carry with you and use anywhere.
3. A smaller computer that can be held in the palm of one hand.
4. A smaller computer that can work with a battery and be easily carried.
5. These devices aren’t quite as big as notebooks. Can fit into a jacket pocket.
6. Most powerful type of desktop, used for graphic design, etc.
7. Small enough to be held in the hand while being used.
8. These devices can be used as a tiny notebook.
9. … … .
17. Word Bingo.
Look at the list of the words given below. Write down any four words. The teacher is going to read the definitions of all the words in random order. If you hear the definition of one of the words you have chosen, cross it out. The first student to cross out all the words he or she has chosen calls out “Bingo” and reads the words to prove his/her claim.
Words: way, laptop, microprocessor, capability, microcomputer, to obtain, circuit, to contain, workstation, mainframe, minicomputer, data.
Word-building
Model 10
Основа прилагательного + (i)ty существительное
|
regular – регулярный
similar – сходный
popular – популярный
stable – стабильный
|
regularity – регулярность
similarity – схожесть
popularity – популярность
stability – стабильность
|
Model 11
Основа существительного + al прилагательное
|
center – центр
culture – культура
form – форма
intellect – интеллект
option – выбор, предмет выбора
|
central – центральный
cultural – культурный
formal – формальный
intellectual – интеллектуальный
optional – необязательный, факультативный
|
18. Make new words using the models 10-11.
|
accessible
ordinary education
regular
politic
|
component patient economic
resistive
post
|
acute
globe
responsible
region
mobile
|
cruel
industry
valid
advisable
similar
|
curious
probable music
capable
stupid
|
rational
orbit
notion
robber material
|
Reading Practice
19. Read the text. Try to understand it and be ready to answer the questions.
TEXT 4A
COMPUTERS
Computer is an electronic device that can accept data in a certain form, process the data and give the results of the processing in a specified format as information.
The modern world of high technology is possible mainly due to the development of the computer. Computers have opened up a new era in manufacturing by means of automation and they have enhanced modern communication systems.
Essentially all of the computers in use today are based on the same fundamental design. Despite their size, speed, or cost, almost all of the computers we use today are based on a design that includes the following elements:
Computers process data using some kind of central processing system.
Computers provide some method of storing data.
Computer systems include specialized devices that humans can use to communicate with the processing hardware.
Computers have been designed in this way since their inception. But different types of computers can vary significantly in their size and processing capacity, cost, and speed. Computers traditionally have been categorized as being one of four main types – microcomputers (desktop PC, workstation, portable - laptop, notebook, subnotebook, handheld - palmtop, PDA, communicator), minicomputers (server), mainframes and supercomputers.
Supercomputers are the most powerful and expensive computers. They are often grouped together with the mainframes. Although they are similar in basic design to the mainframes, they can process data faster than any other type of computer. Supercomputers generally are used by very large companies and research institutions to process complex mathematical calculations.
The large and powerful computers are known as mainframes. They generally cost hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars and they usually are used as central data processing and storage devices by large businesses or government agencies. An organization's computer users can usually access the mainframe from many different offices that can be in different buildings or even in different cities. Many people can be in contact with the mainframe at the same time and at any one moment the mainframe can be processing several different programs for several different users. For that reason, mainframes are often referred to as host computers. They are host to many users in many different locations. Many printers and a variety of storage devices may be attached to the mainframe computer.
A minicomputer is a computer manufactured on a single printed board which contains one or more chips. At present these computers have become so powerful that they are used as CAD/CAM systems.
Minicomputers are smaller and less expensive than mainframes. Although they may be accessed by a number of different users just as mainframes are, there are usually fewer access sites and the access sites are usually located in closer proximity to the minicomputer. Because they are designed to serve the needs of many different users, they are also referred to as host computers, but, because of their more limited capacity and speed when many users are in communicate with the minicomputer, the computer’s response time may be noticeably slower.
Minicomputers are generally thought of as medium sized computers. While the mainframe may do the data processing and data storage for the widespread offices of an entire large company, minicomputers are generally limited to data processing and storage in one location (often for one department or for a smaller company).
Microcomputers come in many different sizes and they offer users a number of different capabilities. Regardless of their size and appearance, all microcomputers are, basically, “personal”; that is, they are designed to be used by one person at a time. Personal computers are also called home computer. The most compact are called handheld. They are portable and work on built in batteries. Unlike mainframes and minicomputers, microcomputers generally do not have devices attached that allow them to be “host” to several users at the same time. And microcomputers are not only personal, generally they are local. The computer’s input devices, output devices, and storage devices are all designed to be used by one person in the same location as the computer with that one person managing the data input, output, and storage.
Microcomputers are based on a microprocessor. A microprocessor is a single chip that includes a large number of miniaturized circuits that are designed to carry out specific computing tasks. It’s the microprocessor that does all of the data processing in a personal computer. Microprocessors can obtain from memory and execute a limited set of instructions in order to perform addition or subtraction on a binary system and to input or output binary data.
Workstations are microcomputers because they are based on a microprocessor. And like other microcomputers, they are designed to be used by one person at a time. However workstations are usually faster than desktop PCs, often have more storage than PCs, and may use more complex and powerful operating systems than PCs. Workstations are often used for scientific tasks or for managing detailed design and graphics tasks. Often they are used as multiprocessing machines: that is, because they are fast and use a powerful operating system, they can be used to carry out more than one type of data processing task at the same time.
20. Choose the phrases on the right which complete the sentences on the left.
|
l. A microcomputer is ... .
|
a) based on a microprocessor and which can perform addition or subtraction on a binary word;
b) a computer manufactured on a single printed board which contains one or more chips;
c) a very small device that can obtain from memory and execute a limited set of instructions.
|
|
2. A microprocessor is ... .
|
a) a device which can perform logical operations;
b) a computer manufactured on a single printed board which contains one or more chips;
c) a single chip that includes a large number of miniaturized circuits that are designed to carry out specific computing tasks.
|
|
3. A minicomputer is … .
|
a) a computer which does not have devices attached that allow them to be “host” to several users at the same time;
b) often used for scientific tasks or for managing detailed design and graphics tasks;
c) a computer manufactured on a single printed board which contains one or more chips.
|
|
4. A mainframe is ... .
|
a) based on a microprocessor;
b) often referred to as host computers and used as central data processing and storage devices by large businesses or government agencies;
c) generally limited to data processing and storage in one location (often for one department or for a smaller company).
|
|
5. A supercomputer is ... .
|
a) even more powerful and expensive than most mainframes and it can process data faster than any other type of computers;
b) basically “personal”; that is, it is designed to be used by one person at a time;
c) device which may do the data processing and data storage for the widespread offices of an entire large company.
|
|
6. Workstation is … .
|
a) generally limited to data processing and storage in one location;
b) powerful microcomputer that has taken over some of the more complex data management tasks that formerly are reserved for mainframes and minicomputers;
c) mostly used on individual desks in homes and in small businesses.
|
|
7. A laptop is … .
|
a) a small computer that can work with a battery and be easily carried;
b) a large powerful computer, usually the center of network and shared by many users;
c) a computer that is smaller and slower than mainframe but larger and faster than a microcomputer.
|
|
8. A notebook is …
|
a) a very small computer that you can carry with you and use anywhere;
b) mostly used on individual desks in homes and in small businesses;
c) small enough to be held in the hand while being used.
|
|
9. A handheld is … .
|
a) the desk and computer at which a person works; one computer that is part of a computer network;
b) small enough to be held in the hand while being used;
c) medium sized computer.
|
|
10. A palmtop is …
|
a) a smaller computer that can be held in the palm of one hand;
b) a very small computer that is used for storing personal information and creating documents and that may include other functions such as telephone, fax, connection to the Internet;
c) mostly used on individual desks in homes and in small businesses.
|
|
11. A PDA is …
|
a) a computer manufactured on a single printed board which contains one or more chips;
b) the desk and computer at which a person works; one computer that is part of a computer network;
c) a very small computer that is used for storing personal information an creating documents and that may include other functions such as telephone, fax, connection to the Internet.
|
21. Find in the text passages about mainframes and translate them into Russian.
22. Choose a passage from those you’ve translated and read it aloud (The approximate time of reading is 1-2 minutes).
23. What do you know about microcomputers? Read the statements given below and if you think the statement is true agree to it saying “That’s right”. If you think it is not true, disagree saying “That’s wrong” and make the necessary corrections.
Personal computers are designed for use at homes, schools, and offices. At home they can be used for home management (balancing the family finances, for example) and for playing computer games, watching films or listening to music. Schoolchildren can use computers for doing their homework and many schools now have computers for independent learning and computer-literacy studies. In the office personal computers may be used for word processing, book-keeping, storage and handling of necessary information.
Microprocessors are now used as control devices inside appliances like microwave ovens and stereo systems. They are used to control the complex switching and regulating tasks used in modern appliances. In more complex devices such as automobiles and copy machines, these embedded microprocessors may have a self-diagnostic function that results in the output of information that can be used by humans.
24. Find in the text and put down 10-12 words or word combinations which can be used to speak about minicomputers.
25. General understanding:
- What are the four main types of computers and how do they differ from each other in terms of size, speed, and processing power?
- What is the difference between a host computer and a file server?
- Which type of computer is:
- the most common?
- small enough for a pocket?
- the most common portable?
- used by many people at the same time?
- used like mainframes?
- also called a handheld computer?
- the most powerful?
- not suitable for a lot of typing?
26. Reread the text and write a summary in English.
TEXT 4B
HOW TO READ A COMPUTER AD.
27. Now study the text below to find this information:
1. What is the memory size of this PC?
2. Which input devices are supplied?
3. What size is the monitor?
4. How fast is the processor?
5. What is the capacity of the hard drive?
6. Which operating system does it use?
7. What multimedia features does the computer have?
|
1. Intel Pentium IV 5,5 GHz Processor
2. Mini Tower Chassis
3. 2 GB Rambus RDRAM
4. 1 TB Hard Drive
5. Embedded Intel 3D Direct AGP video
6. 64-voice wavetable sound
7. 48 X GD-ROM Drive
8. 19" (17.9" VIS) Colour SVGA monitor
9. Microsoft Windows XP
10. 1.44MB 3.5" Floppy Drive
11. Microsoft Intellimouse
12. 105-key keyboard
|

|
TEXT 4C
A DIGITAL PEN
28. Read this text and fill in the blanks with words in the box.
|
sends
|
cables
|
computer
|
chip
|
digital
|
data
|
Internet
|
Anoto is a (1) … pen that allows you to store and transmit anything you write or draw on paper to any (2) … .
The components of Anoto are: (i) a digital camera, which scans the patterned paper, (ii) an image processor, (iii) a memory (3) …, which can store several written pages, and (iv) a Bluetooth radio transceiver, which (4) … the information to your PC, mobile phone or handheld computer. It also contains an ink cartridge so that you can actually see the characters and pictures that you are making.
As you write or draw on the Anoto patterned paper, the digital pen converts your notes and diagrams into digital (5) … which is stored and then transmitted to your computer or, by using a Bluetooth device such as a mobile phone, to another PC, database or the (6) … . Bluetooth is a wireless technology which doesn't need (7) … in order to send and receive information.
Oral Practice
29. Questions for group discussion:
1. Almost all of today's computers are based on the same design. Describe the three main elements of that design and list the four main types of computers in use today.
2. Computers based on a microprocessor are known as microcomputers. There are now several different types of microcomputers in use. Describe them.
3. In pairs, decide what sort of computer is best for each of these users.
- John Wilmott is a salesperson and he spends a lot of time visiting customers. He wants a computer to carry with him so he can access data about his customers and record his sales.
- Pat Nye is a personnel officer. She needs a computer to keep staff records and to keep a diary of appointments. She also needs a computer for writing letters.
- The University of the North needs a computer to look after its accounts, its network, the records of all students and staff, and to help with scientific research.
- The James family want a computer for entertainment, writing letters, the Internet, and for calculating tax.
30. Look at these sentences and match them with the language functions a-g.
|
1. Good morning. Can I help you?
2. Can I have a look at those pocket PCs?
3. It has a processor running at 3 GHz.
4. What about RAM?
5. Does it have a DVD?
6. Which one would you recommend?
7. How much does it cost?
8. Well, you can pay by cheque, credit card or in cash.
|
a. asking the price
b. describing a computer
c. asking to see some computers
d. greeting customers and offering help
e. asking about technical specifications
f. explaining different ways of paying
g. asking for advice
|
31. Role play. Work with a partner. One of you wants to buy a computer; the other is the sales assistant. Put and answer questions, using the information and instructions below to help you.
|
Products available
|
Processor Speed
|
Minimum/ Maximum RAM
|
Hard disk
|
Disk drives
|
Monitor
|
Price
|
|
Explora 700 Net PC
|
Mips R4700
900 MHz
|
128 MB expandable to 512
|
20 GB
|
Optional 3.5" drive
|
Super VGA compatible
|
Ј 499
|
|
Toshiba portable
|
Pentium 4 1.5 GHz
|
256 MB expandable to 512
|
40 GB
|
3.5" drive DVD/ CD-RW
|
colour LCD
|
Ј 609
|
|
IBM
|
Pentium 4 1. 8 GHz
|
256 MB expandable to 512
|
70 GB
|
DVD/ CD-RW
|
XGA
|
Ј 749
|
|
Polywell
|
AMD Athlon
1.6 GHz
|
512 Mb expandable to 2 GB
|
80 GB
|
3.5" drive DVD/ CD-RW
|
SuperVGA
|
Ј 900
|
|
Dell
|
Pentium 4 2 GHz
|
256 MB expandable to 1GB
|
60 GB
|
DVD/ CD-RW
|
XGA
|
Ј 1,010
|
|
DEPO Race 625
|
Pentium 4
3 GHz
|
1 Gb
up to 4 GB
|
160 GB
|
DVD/ CD-RW
|
XGA
|
Ј 1,250
|
Shop assistant Customer
Greet the customer and offer help.
Ask to see some computers.
Show the customer some models.
Ask for details: processor, RAM, etc.
Describe the speed in megahertz and the main memory.
Ask about the hard disk.
Give explanations (GB storage capacity, etc.).
Ask about the monitor and other features.
Give the required information.
Ask the price.
Give the price and explain different ways of paying.
Decide to buy one/to think about it.
Thank the shop assistant and leave the shop.
Listening Practice
32. Before listening, answer these questions.
- Have you got a computer at home, school or work? What kind is it?
- How often do you use it? What do you use it for?
- What are the main components and features (the configuration) of your computer system?
33. Listen to Part 1 of this conversation between a shop assistant and customer. Tick () the correct answers to these questions.
|
1. The customer wants a computer for:
|
2. A multimedia computer provides:
|
|
|
writing
|
|
Internet
|
|
sound
|
|
telephone
|
|
|
graphics
|
|
video
|
|
graphics
|
|
video
|
|
|
games
|
|
|
|
animation
|
|
|
34. Listen to Part 2 of the conversation. In column A, tick the hardware items named. In column B, tick the items the assistant recommends.
|
A
|
|
B
|
Device
|
A
|
|
B
|
Device
|
|
|
|
|
multimedia computer
|
|
|
|
handheld
|
|
|
|
|
multimedia notebook
|
|
|
|
printer
|
|
|
|
|
subnotebook
|
|
|
|
monitor
|
|
|
|
|
laptop
|
|
|
|
modem
|
Writing Practice
35. Complete the text below with the words in the box.
Minis and micros
|
systems
|
memory
|
task
|
terminals
|
desktop
|
CAD
|
applications
|
The first microcomputers, also known as (1) “...” PCs were for single users only, and this clearly distinguished them from minicomputers. Another important difference was that “minis” were much more powerful than “micros”: they hold execute more than one (2) ... simultaneously and were used as file servers for (3) ... and workstations. However, modern microcomputers have operating (4) ... and network facilities that can support many simultaneous users. Today, most personal computers have enough (5) ... to be used for word processing and business (6) ... . Some PCs can even handle multitasking and (7) ... applications. As a result, the division between “minis” and “micros” is now disappearing.
36. Put the words in brackets into the correct form to make an accurate description of sizes of computers.
There are different types of computer. The (large) ... and (powerful) ... are mainframe computers. Minicomputers are (small) ... than mainframes but are still very powerful. Microcomputers are small enough to sit on a desk. They are the (common) ... type of computer. They are usually (powerful) ... than minicomputers.
Portable computers are (small) ... than desktops. The (large) ... portable is a laptop. (Small) ... portables, about the size of a piece of writing paper, are called notebook computers. Subnotebooks are (small) ... than notebooks. You can hold the (small) ... computers in one hand. They are called handheld computers or palmtop computers.
UNIT 5
COMPUTER ESSENTIALS
This chapter introduces the various types of hardware and software that comprise today's computer systems. In this chapter you will learn about computer hardware components, and understand the basic structure of a computer in use. By the end of this unit, you should be better at: matching pictures of components to their English names and functions listening for specific detail. You should know and be able to use these words and abbreviations: byte, kilobyte, megabyte, gigabyte, megahertz, motherboard, port, RAM, ROM, cache memory, expansion card.
Terms Concepts
A computer system is composed of a set of interrelated devices with interrelated functions, including the central processing unit or CPU (the computer's main processing device), main memory, input devices (used to get information into the computer), output devices (used to get information out of the computer in a form usable by humans), and secondary storage system (used for long-term data storage).
Language Material
1. Consult a dictionary and practise the pronunciation of the following words:
procedure, to process, processing, variety, circuit, microscopic, keyboard, to direct, capability, capacity, durable, result, specified, screen, to accept, character, raw, to convert, board, facility, expansion, supply, removable, design.
2. Learn by heart the following vocabulary:
|
character
connector
contents
CPU
to incorporate
software
hardware
instruction
driver
drive
display
keyboard
main memory
memory board
RAM
ROM
peripherals
power supply
|
символ
соединитель, разъем
содержание
микропроцессор
объединять, включать, присоединять
программное обеспечение
оборудование
команда
программа управления устройствами
дисковод
экран; выставлять, показывать
клавиатура
оперативная (основная) память
плата памяти
оперативная память (ОЗУ)
постоянная память (ПЗУ)
периферия
источник питания
|
procedure
pointer
compatible
durable
flexible
raw
to accept
to connect
to convert
to create
to evolve
to house
to perform
to plug
to refine
to respond
to retrieve to set up
|
процедура, операция
указатель, курсор
совместимый
длительный, прочный
гибкий
необработанный, сырой
принимать, допускать
соединять
преобразовывать
создавать
развивать(ся)
размещать
выполнять
подключать, вставлять
очищать
отвечать
извлекать устанавливать
|
3. Match the English word combinations in the left-hand column with the Russian equivalents in the right-hand column:
|
1. term
2. useful
3. combination
4. despite
5. activity
6. capability
7. to retrieve
8. silicon
9. to rotate
10. to insert
11. pointer
12. button
13. to type
14. screen
15. system board
16. chip
17. capacity
18. to make decision
|
a. деятельность
b. вставлять
c. указатель
d. полезный
e. термин
f. кремний
g. чип
h. печатать
i. экран
j. извлекать
k. несмотря на
l. комбинация, сочетание
m. вращать(ся)
n. способность, мощность
o. кнопка
q. способность
r. системная плата
s. принимать решение
|
4. Which of the listed below terms have Russian equivalents?
computer, circuit, diskette, metal, activity, processor, display, scanner, information, data, microphones, contents, printer, modem, screen, Internet, monitor, motherboard, video, icon, component, graphics, electronics, adapter, stereo, contract, letter, instruction, disk, command, application, format, megabyte, specialize, photo, combination.
5. Find 12 words about a computer system and its parts. They go down and across.
|
D
|
R
|
I
|
V
|
E
|
B
|
R
|
A
|
M
|
F
|
H
|
P
|
|
L
|
S
|
O
|
I
|
R
|
A
|
H
|
M
|
E
|
I
|
A
|
L
|
|
O
|
R
|
S
|
C
|
A
|
N
|
N
|
E
|
R
|
D
|
R
|
M
|
|
W
|
L
|
P
|
X
|
Y
|
I
|
O
|
M
|
O
|
C
|
D
|
O
|
|
E
|
O
|
M
|
M
|
F
|
A
|
E
|
B
|
L
|
A
|
W
|
D
|
|
P
|
R
|
O
|
C
|
E
|
S
|
S
|
O
|
R
|
L
|
A
|
E
|
|
R
|
C
|
U
|
G
|
P
|
A
|
M
|
B
|
L
|
Z
|
R
|
M
|
|
I
|
D
|
S
|
D
|
R
|
R
|
O
|
M
|
I
|
R
|
E
|
Y
|
|
N
|
C
|
E
|
I
|
E
|
B
|
I
|
G
|
U
|
E
|
V
|
Z
|
|
T
|
R
|
I
|
S
|
E
|
M
|
O
|
N
|
I
|
T
|
O
|
R
|
|
E
|
R
|
S
|
K
|
X
|
Q
|
O
|
Z
|
X
|
Y
|
A
|
Z
|
|
R
|
R
|
E
|
T
|
S
|
O
|
F
|
T
|
W
|
A
|
R
|
E
|
6. Find in each line word that is given at the beginning.
|
1. программное обеспечение
|
a) hardware
|
b) command
|
с) instruction
|
d) software
|
|
2. обрабатывать
|
a) to access
|
b) to process
|
c) to reduce
|
d) to adjust
|
|
3. символ
|
a) letter
|
b) figure
|
c) character
|
d) key
|
|
4. применение
|
a) software
|
b) resolution
|
c) application
|
d) sharpness
|
|
5. устанавливать
|
a) to install
|
b) to type
|
c) to access
|
d) to plug
|
|
6. совместимый
|
a) compatible
|
b) convenient
|
c) suitable
|
d) floppy
|
|
7. ссылаться
|
a) to display
|
b) to process
|
c) to refer
|
d) to point
|
|
8. дисковод
|
a) driver
|
b) arrow
|
c) screen saver
|
d) drive
|
7. Find in each line word that is given at the beginning.
|
1. term
|
a) диск
|
b) термин
|
c) операция
|
d) устройство
|
|
2. instruction
|
a) команда
|
b) конструкция
|
c) дисковод
|
d) курсор
|
|
3. slot
|
a) дисковод
|
b) символ
|
c) разъем
|
d) периферия
|
|
4. to describe
|
a) обрабатывать
|
b) принимать
|
c) описывать
|
d) дискета
|
|
5. to set up
|
a) устанавливать
|
b) падать
|
c) садить
|
d) размещать
|
|
6. to upgrade
|
a) модернизировать
|
b) размещать
|
c) выполнять
|
d) извлекать
|
|
7. digital
|
a) необработанный
|
b) подвижный
|
c) значимый
|
d) цифровой
|
|
8. useful
|
a) бесполезный
|
b) полезный
|
c) полный
|
d) сырой
|
8. Work in pairs. Study these pictures of inside of a computer. Can you label these components? Compare your answers with other students in your group.
|

a) …………
|

b) …………
|
|
c)………..
|

d) ……….
|
|

e) …………
|

f) …………
|
|

g) …………
|

h) …………
|
|
1. hard disk drive
2. mother board
|
3. memory chips
4. power supply
|
5. processor
6. sound card
|
7. video card
8. chain
|
9. Read the following sentences; find out parts of the speech of the words in bold,; translate them.
1. a) There were a lot of files on the desk.
b) It took operator some time to find the necessary file.
2. a) You can use only floppy disks with this computer.
b) This hard disk holds more information than 100 floppies.
c) This floppy drive is usually referred to as drive A.
3. a) Drivers are one of the components of a computer.
b) Drivers do their best to reduce the car body wear.
c) The drives can read and write on diskettes.
4. a) According to the readings of the instrument a considerable amount of fuel was stored in the tank.
b) A computer is a device used to manage the great amount of world’s information.
5. a) Computers can be used to access the Internet, teach courses such as computer-aided design, language learning, programming, mathematics.
b) You can get access to a great amount of information with the help of CD-ROM.
c) The access to the mountain village was extremely difficult because of many rapid rivers.
6. a) This computer is not IBM-compatible.
b) The account section has been completely computerized.
c) My friend is a specialist in computer hardware.
d) You can buy a computer and the necessary software as well.
7. a) Women were afraid that there might be mice in the house.
b) Usually it takes some time to learn to use a mouse.
8. a) Press the button to switch on the device.
b) Nobody expected that the application of this device is so wide.
9. a) Hоw many letter keys are there on the computer keyboard?
b) I’ve written a letter to my grandmother.
10. Note additional meanings for word “to make up”.
|
to make up
|
пополнять, возмещать
|
Can I leave this afternoon and make up the time tomorrow?
|
|
|
компенсировать
|
Nothing can make up for the loss of a child.
|
|
|
составлять, комплектовать, собирать
|
The term computer is used to describe a device made up of a combination of electronic and electromechanical components.
|
|
|
гримировать, подкрасить
|
She made up herself to prepare for an appearance in the theatre.
|
|
|
выдумывать
|
I told the kids a story, making it up as I went along.
|
|
|
мириться
|
Has he made it up with her yet?
|
|
|
подходить, приближаться
|
We just managed to make up the deadline.
|
11. Consider the grammar:
to break into - взламывать(ся), разрываться смехом, прервать
Our system was broken into, but nothing was stolen.
to convert into – превращать, переделывать в
Computer is used to convert data into information.
to divide into – делить, подразделяться на
The book is divided into three parts.
to translate into – переводить на
All computer languages must be translated into binary commands.
12. Match the synonyms.
combination – union, association, alliance, league, confederacy, cabal, conspiracy, plot, faction.
manner – habit, custom, behavior, appearance, aspect, look, way, style, mood, expression, description, character, stamp, means, method, fashion, approach.
to connect - to join, to link, to unite, to put through, to combine.
to accept – to receive, to take, to acquire, to admit, to get, to gain, to assent, to concur.
to perform – to do, to act, to play, to achieve, to execute, to accomplish, to fulfill, to complete.
to respond - to reply, to react.
13. Match the antonyms.
basic – additional, supplementary, extra, subsidiary, complementary.
part – whole, all, total, aggregate, sum, entirety, entireness, completeness, bulk, mass, totality, amount, gross, combination, unity, integration, stock.
raw – mature, ripe, adult, seasoned.
useful – useless, worthless, unserviceable, valueless, unproductive, ineffectual, idle, fruitless.
14. Name all possible word expressions with following verbs and nouns:
|
to process
|
characters
|
to display
|
to set up
|
|
to install
|
a computer
|
a keyboard
|
data
|
|
information
|
to type
|
a floppy disk
|
to house
|
|
a mouse
|
instruction
|
input
|
procedure
|
|
to perform
|
device
|
to store
|
output
|
15. Complete the sentences with suitable compounds from this list.
|
expansion slots
magnification software
|
database
voice recognition
screen reader
|
websites
word processor
|
1. …. can enlarge text appearing on the screen by up to 16 times.
2. Blind users can't use a typical … to write letters or faxes. They need Braille and a speech-synthesis system.
3. A … allows blind users to hear the text from the screen.
4. … interprets human speech, transforming the words into digitized text.
5. … let users install expansion boards (modems, graphics boards, etc.) to improve the computer system.
6. A … contains a set of structured data.
7. There are … which give information about assistive technologies for the disabled.
16. Read and translate the following expressions.
|
hardware pieces
to produce hardware
to process information
word processor
a disk drive
to type a letter
to press any key
to read a manual carefully
to produce the software
a screen of the display
a long pointer
3-inch diskette
temporary storage system
spinning platters
hard disk
|
to communicate with a computer
to display a character
to put all the files on the table
a floppy disk
to refer to the experimental data
a great amount of information (data)
the access to this important information
to access the main highway
to be compatible with most computers
the compatibility of computers
nonmagnetic technology
a pointing device
display monitor (screen)
two inches square
diskette drive
|
17. Match the following:
- процессор
- модем
|
- клавиатура
- «винчестер»
|
- мышь
- экран
|
- дискета
- ПЗУ
|
- ОЗУ
- память
|
a) nonvolatile, nonmodifiable computer memory, used to hold programmed instructions to the system.
b) the part of a television or computer on which a picture is formed or information is displayed.
c) rigid disk coated with magnetic material, for storing computer programs and relatively large amounts of data.
d) an electronic device that makes possible the transmission of data to or from computer via telephone or other communication lines.
e) a set of keys, usually arranged in tiers for operating a typewriter, typesetting machine, computer terminal, or the like.
f) volatile computer memory, used for creating, loading, and running programs and for manipulating and temporarily storing data; main memory.
g) central processing unit: the key component of a computer system, containing the circuitry necessary to interpret and execute program instructions.
h) a palm-sized device equipped with one or more buttons, used to point at and select items on a computer display screen and for controlling the cursor by means of analogous movement on a nearby surface.
i) a thin, usually flexible plastic disk coated with magnetic material, for storing computer data and programs.
g) the system of the computer component in which information is stored.
18. Try to complete the following crossword.
1. The device, which function is to execute program instruction and coordinate the activities of all other units.
2. A CRT device which displays the computer output.
3. The process of keeping information on a computer.
4. The section which holds the instructions and data currently being processed.
5. Disks made of a flexible plastic material upon which data is stored on magnetic tracks.
6. A small input device with a ball underneath that is rolled by the user to specify the position of the cursor or to make choices from the menu.
7. The component in the processor or other chip which holds the instruction from the memory while it is being executed.
8. An object or a piece of equipment that has been designed to do a particular job.
9. An output device which converts data into printed form.
Word-building
Model 12
|
Prefix
|
Meaning
|
Examples
|
|
deci-
hexadeci-
kilo-
mega-
giga-
mini-
micro-
bi-
tri-
multi-
mono-
|
ten
sixteen
one thousand (1,000) (1,024 in binary: 210)
large; one million
very large; one thousand million
small
very small
two
three
many
one
|
decimal, decimalize, decibel
hexadecimal
kilocycle, kilogram(me), kilowatt
megahertz, megalith, megaton
gigantic, gigabyte, gigahertz
minibus, minimum, minimize
microfilm, microphone, microwave
bidirectional, bidimensional, binary
tripartite, tricycle, trilingual
multi-racial, multi-user, multitasking
monologue, monosyllable, monolingual
|
Model 13
Compound adjectives
|
battery-powered systems
|
hands-free operations
|
waist-mounted computer
|
head-mounted display
|
voice-activated device
|
19. Explain these expressions, taking into account the prefixes and root word, using the model 12.
Example: the binary system - the binary system is a notation which uses two digits, 0 and 1.
|
1. a minicomputer
2. a microcomputer
3. the decimal system
4. the hexadecimal system
5. a multi-user configuration
|
6. a bidimensional chessboard
7. a tricycle
8. a monochrome computer
9. a CPU with 256 MB of RAM
10. a document of 3 kilobytes
|
20. Prefixes are commonly used in computer science. With the help of a dictionary, find two additional examples for each prefix.
super- more than super-computer
hyper- extremely hyper-media
mini- small mini-computer
micro- very small micro-computer
semi- partly, half semi-conductor
ultra- beyond ultra-modern
uni- one…………… unilateral
mono- one…………… monochromatic
kilo- thousand…….. kilobit
21. Think of suitable compound nouns for these definitions.
Example: A device which displays or prints the output - An output device.
- A secret word used to receive e-mail - ………………………………….
- A pool that we swim in - ………………………………………………..
- A book which has cheques - …………………………………………….
- A room where you eat meals - …………………………………………..
- Lights used to control the traffic - ……………………………………….
- A card used instead of coins to make phone calls - ……………………...
22. Making wordwebs will help you to organize and remember vocabulary. Use the words in the box to make three different wordwebs with compounds.
|
floppy
optical
soft
|
error
free
designer
|
mail
firm
hard
|
share
pal
directory
|
word
site
drive
|
page
compact
server
|
23. Find the expression from the model 13 in the text and explain their meaning.
Wearable computers, aren’t they chic?
Can you imagine wearing a PC on your belt and getting e-mail on your eyeglasses? Wearable computers are battery-powered systems worn on the user’s body on a belt, backpack or vest and are designed for mobile or hands-free operations, often incorporating a microphone and a head-mounted display.
Some devices are waist-mounted, equipped with a wireless modem, a keypad and small screen. Others are voice-activated, worn like a scarf and access e-mail or voice mail.
Users of wearable technology consider themselves “cyborgs”. This term comes from “cybernetic organism”, referring to a being that is part robot, part human.
Reading Practice
24. Read the text. Try to understand it and be ready to answer the questions.
TEXT 5A
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
The term “computer” is used to describe a device which can accept the data in a certain form, process it and give the results of the processing in a specified format as information. Computer doesn’t have intelligence by itself and is referred to as hardware. A computer system is a combination of five elements:
• hardware;
• software;
• people;
• procedures;
• data/information.
The electronic, magnetic, electrical and mechanical parts that make up a computer system are called hardware. Computer hardware refers to the computer’s machinery, its electronic devices and its circuits. A computer is actually a system, a combination of parts that work together. Computer hardware can be divided into four categories:
1) input hardware (keyboard, mouse, etc.);
2) processing hardware (CPU, main memory);
3) storage hardware (fixed-disk drive, diskette drive, magnetic tape drive, etc.);
4) output hardware (display monitor, printer, etc.).
The hardware is designed to work hand-in-hand with computer programs that are often designed specifically for use with one type of hardware. Software is the term used to describe the instructions that tell the hardware how to perform a task. People however are the most important component of the computer system: they create the computer software instructions and respond to the procedures that those instructions present.
The basic job of the computer is the processing of information. Three basic steps are involved in the process. First, data is fed into the computer’s memory. Then, when the program is run, the computer performs a set of instructions and processes the data. Finally, we can see the results (the output) on the screen or in printed form. Computers accept information in the form of instruction called a program and characters called data to perform mathematical and logical operations and then give the results. The data is raw material while information is organized, processed, refined and useful for decision making. Computer is used to convert data into information. Computer is also used to store information in the digital form.
PROCESSING HARDWARE
The Central Processing Unit
Today’s computers are designed around a single large-scale processing chip known as the central processing unit (CPU). At the microscopic level, many circuits and processing capabilities are incorporated into one chip that may only be one or two inches square. The CPU can be thought of as the "brains" of the computer. Its function is to execute program instructions and coordinate the activities of all the other units. The Control Unit, the ALU and the registers make up the CPU of a computer. Each new generation of CPUs has added new processing capabilities and yet, despite this increased capability, each new generation processes information faster. Today’s CPUs are complex devices composed of many different components and circuits that carry out a great variety of functions.
Main Memory
The main memory holds the instructions and data which are currently being processed by the CPU. In today’s computers, the CPU acts on instructions that are retrieved from a storage system known as main memory. The CPU also uses this main memory to store data temporarily as it carries out processing tasks. This temporary storage system is based on sets of silicon chips. Each chip is actually made up of millions of circuits that store data in a coded format. RAM is the volatile computer memory, used for creating loading and running programs and for manipulating and temporarily storing data. This information is lost when the computer is turned off. ROM is nonvolatile nonmodifiable computer memory used to hold programmed instructions to the system. ROM contains permanently stored information such as the instructions that are needed for the computer’s operation.
Power is a function of both speed and capacity. The power of a computer depends on the combination of all the components. When buying a computer, often can be chosen between different components, in particular between different processor speeds, amounts of memory and hard disk sizes. Units of measurement commonly used in computing are shown below.
|
Unit
|
Symbol
|
Meaning
|
Measurement
|
|
hertz
|
Hz
|
cycles per second
|
frequency
|
|
byte
|
B
|
space for one character, i.e. one letter, number, punctuation mark, symbol or even a space
|
capacity
|
Hertz are measured using the decimal system but bytes are measured using the binary system. The values of the unit prefixes vary in these two systems as shown in the table below.
|
Unit
|
Symbol
|
Decimal System
|
Binary System
|
|
kilo
|
K
|
103 = 1000
|
210=1024
|
|
mega
|
M
|
106 = 1000000
|
220= 1048576
|
|
giga
|
G
|
109 = 1000000000
|
230 = 1073741824
|
SECONDARY STORAGE SYSTEMS
Hard Disk Drive
Hard disks (also known as fixed disks) are very similar to diskettes but they are fixed permanently inside the computer. Hard disks use one or more spinning platters that are very much like diskettes, but they can hold far greater amounts of data.
Floppy
Diskettes (also known as floppy disks) are a form of storage that can be inserted into a computer that has a compatible disk drive. Earlier personal computers used a 5 1/4-inch diskette housed inside a flexible plastic jacket; however, now it is used smaller 3 1/2-inch diskettes enclosed in a hard plastic case. Both types of diskettes use the same thin, flexible disk inside, but their capacities can vary from 360,000 bytes to more than 2 million bytes.
Flash
It is another type of hard drive, known as “removable”, allows you to record data on “cartridges” which can be removed and stored off-line for security purposes. Some systems allow to back up entire PC on one disk.
Optical Disk Drive
Optical disks can store information at much higher densities than magnetic disks. Some storage devices use a nonmagnetic technology that is based on optical disks. Optical disks are far more durable and they can be used to store significantly more information. There are various types of optical drives: CD-ROM; CD-Recorders in two different forms: CD-R and CD-RW; DVD (digital versatile disk); magneto-optical (MO) drives.
THE PERIPHERALS
The peripherals are the physical units attached to the computer. They include storage devices and input/output devices.
Input Devices
Devices that are used to get information into the computer are known as input devices. Input devices are used to convert information from a form used by humans into a form that is useable by computers. Today, there are many different ways to get information into the computer, but the keyboard is still one of the most common input devices.
The computer mouse is another input device. It is referred to as a pointing device. A pointing device is used to move a pointer around on the display screen. Another input devices are trackerball, joystick, touchscreen, microphone, barcode reader, scanner, camera, modem, etc.
Output Devices
Output devices are used to get information out of the computer in a form useable by humans. The display monitor and the printer have long been the computer’s primary output devices. But the type and variety of both monitors and printers are in constant change.
25. General understanding:
1) What does the term «computer» describe?
2) Is computer intelligent?
3) What are five components of computer system?
5) What is software? What's the difference between hardware and software?
6) Why people are the most important component of a computer system?
7) In what way do terms “data” and “information” differ?
8) How does computer convert data into information?
9) Why can the central processing unit be thought as the “brains” of computer? Name the CPU’s three different components and describe what they do.
10) What is the main memory? How does it work?
11) Without what parts computer is unable to work?
12) What is the most expensive part of the hardware?
13) Describe the role of input devices and describe how they are changing because of new methods now being used to interact with computers.
14) Today’s computers use secondary storage systems to store data that is not currently being processed. Name and describe three different types of storage systems that use disks.
26. Find in the text passages about the central processing unit and translate them into Russian.
27. Choose a passage from those you’ve translated and read it aloud (The approximate time of reading is 1-2 minutes).
28. Find in the text and put down 10-12 words or word combinations which can be used to speak about secondary storage system.
29. Use the information in the text to help you match the terms in the box with appropriate explanation or definition below.
|
a. software
|
b. peripheral devices
|
c. monitor
|
d. floppy disk
|
e. hardware
|
|
f. input
|
g. central processing unit
|
h. output
|
i. port
|
j. mouse
|
- The brain of the computer
|
|
- Physical parts that make up a computer system
|
|
- Programs which can be used on a particular computer system
|
|
- The information which is presented to the computer
|
|
- Results produced by a computer
|
|
- Hardware equipment attached to the computer
|
|
- Visual display unit
|
|
- Small device used to store information. Same as “diskette”
|
|
- Any socket or channel in a computer system into which an input/output device may be connected
|
|
- A handheld device connected (or not) to the computer by small cable
|
|
30. Give definitions to the following words and expressions using the vocabulary:
|
computer
CPU
ROM
|
hardware
main memory
printer
|
software
floppy disk
modem
|
procedure
hard disk drive
motherboard
|
data
scanner
keyboard
|
information
CD-ROM
sound-card
|
31. Match the following:
|
a) program
b) information
|
c) processing of information
d) software
|
f) computer
g) people
|
1) ... doesn't come to life until it is connected to other parts of a system.
2) ... is the term used to describe the instructions that tell the hardware how to perform a task.
3) ... create the computer software instructions and respond to the procedures that those instructions present.
4) Information in the form of instruction is called a ... .
5) ... is organized, processed and useful for decision making.
6) The basic job of the computer is the ... .
32. Read these slogans or quotations, and say what computer elements they refer to.
|
1.
|
a
b
|
“Point and click here for power.”
“Obeys every impulse as if it were an extension of your hand.”
|
....................
|
|
2.
|
a
b
|
“Displays your ideas with the perfect brilliance.”
“See the difference – sharp images and a fantastic range of colours.”
|
....................
|
|
3.
|
a
b
|
“I love his drive. It’s quiet and fast.”
“With this it’s easy to back up your data before it’s too late.”
|
....................
|
|
4.
|
a
b
|
“Power and speed on the inside.”
“Let your computer’s brain do the work.”
|
....................
|
|
5.
|
a
b
|
“... a big impact on the production of the text and graphics.”
“Your choice: a laser powerhouse.”
|
....................
|
33. Match each item in column A with its function in column B. Then describe its function in two ways: using the Present Simple, or constructions used to - Infinite, used for + ing form.
|
A Item
|
|
B Function
|
|
RAM
processor
mouse
clock
3,5" floppy drive
monitor
keyboard
DVD-ROM drive
cache
ROM
|
|
controls the cursor
inputs data through keys like a typewriter
displays the output from a computer on a screen
reads DVD-ROMs
reads and writes to removable magnetic disks
holds instructions which are needed to start up the computer
holds data read or written to it by the processor
provides extremely fast access for sections of a program and its data
controls the timing of signals in the computer
controls all the operations in a computer
|
34. Describe the functions of these items:
|
1. scanner
|
3. ATM
|
5. hard disk drive
|
7. mainframe computer
|
9. swipe card
|
|
2. printer
|
4. PDA
|
6. supercomputer
|
8. barcode
|
10. memory
|
35. Name the main parts of the computer and fill in the chart.
|
The part
|
Its function
|
|
mouse
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36. Read these sentences and identify all classifying patterns. Then put them into the correct column.
1. There are two classes of personal computers: (a) desktop PCs and (b) portable PCs.
2. A computer system consists of two parts: hardware and software.
3. The basic structure of a PC is made up of three hardware sections: the CPU, the main memory and the peripherals.
4. The Control Unit, the ALU and the registers make up the CPU of a computer.
5. The RAM and ROM constitute the main memory.
6. A DVD is a type of disk.
7. A hub is a component of a computer network.
|
From general to specific
|
From specific to general
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
|
……………………………………………………….
|
|
………………………………………………….
|
………………………………………………………
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
|
……………………………………………………….
|
|
………………………………………………….
|
………………………………………………………
|
37. Designing vocabulary trees or networks can help you build up your own mental «maps» of vocabulary areas. Look at the list of terms in the box and put each one in an appropriate place on the vocabulary tree below. The first one has been done for you.
|
processor
megahertz
RAM
DVD
mouse
megabyte
|
kilobyte
SIMMs
computer brain
clock speed
gigahertz
floppy disk
|
expandable memory
hard disk
byte
keyboard
CD-ROM
registers
|
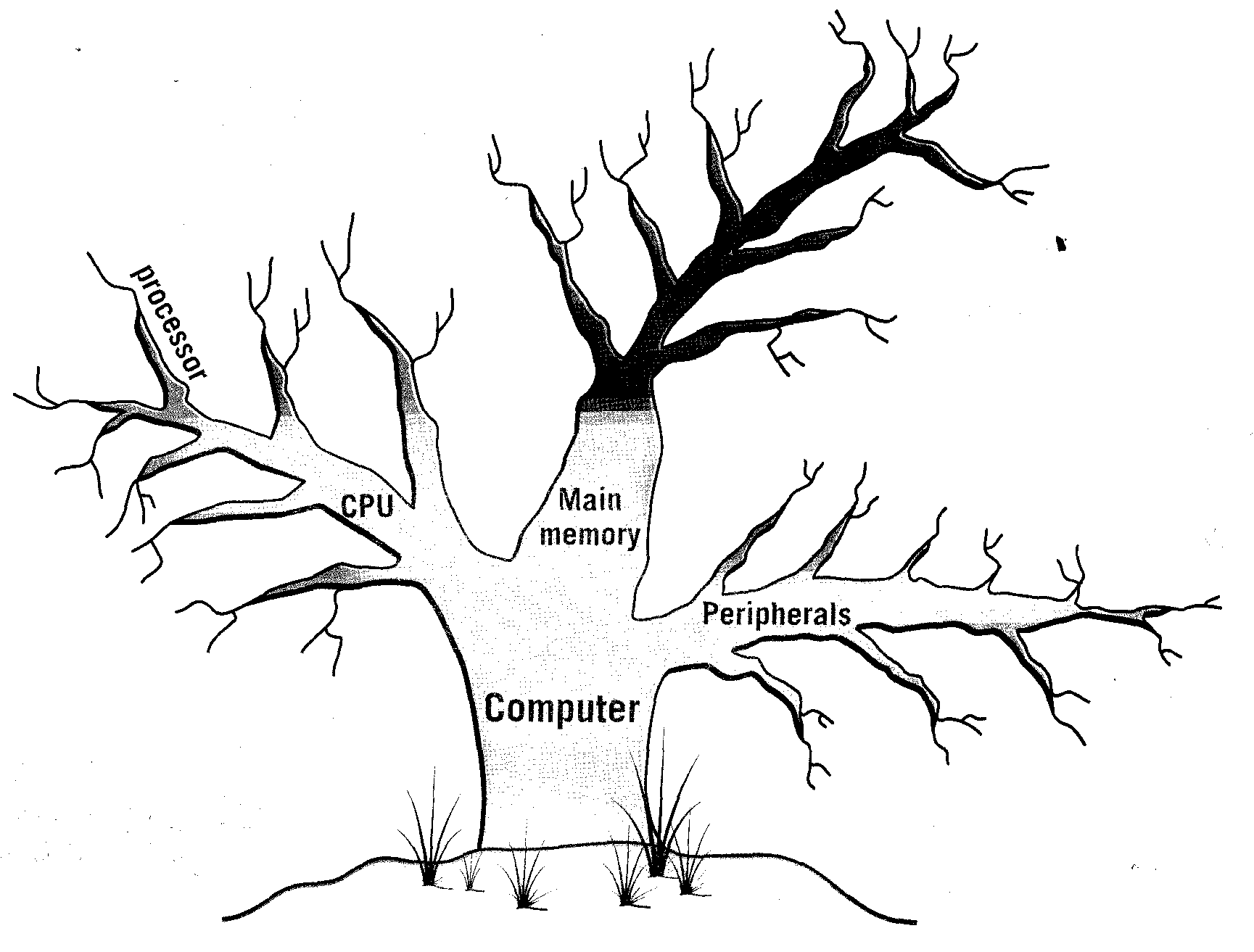
38. Give the main idea of extract “COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE” in 25-30 sentences.
Listening practice
39. Label this diagram with the correct terms.
40. Compare your answers with the partner.
41. Listen and check your answers.
Buying a computer
42. You are going to hear two people making enquiries in a Macintosh computer shop. The shop assistant is telling them about the two models below. Listen and fill in the missing information.
|
iBook
Processor speed ……………………….
RAM standard ………………………..
Hard disk capacity…………………...
Price ...………………………….1,207
DVD and Mac OS included? …………
|
iMac
Processor speed ………………….…..1 GHz
RAM standard ……………………………...
Hard disk capacity ………………………...
Price ………………………………………...
DVD and Mac OS included? ………………..
|
43. Now listen again and fill in the gaps below.
Assistant: Do you need any help?
Paul: Um yes, we’re looking for a personal computer. Have you got any fairly basic ones?
Assistant: Yes, sure. If you’d like to come over here ... .
Paul: What different (1) … are there?
Assistant: At the moment we’ve got these two models: The iMac, which is a desktop computer with a (2) … operating at 1 gigahertz, and the portable iBook, which has a processor (3) … at 700 megahertz.
Sue: So the iMac is the (4) … one. And which one has the most memory? I mean - which has the most RAM?
Assistant: Well, the iMac has 256 megabytes of (5) …, which can be (6) … up to 1 gigabyte, and the iBook has 128 megabytes which can be expanded up to (7) … . It all depends on your needs. The iMac is suitable for home users and small offices. The iBook is ideal for students and for people who travel.
Reading Practice
TEXT 5B
THE MOTHERBOARD
The main parts of a desktop computer are enclosed in a box known as the system unit. This contains an electronic board called the motherboard that holds and connects together the main electronic components. These are shown in the table below.
|
Processor
|
controls the system (microprocessor)
and processes the data
|
|
ROM (Read Only Memory)
|
stores the program instructions the computer needs to start up
|
|
RAM (Random Access Memory)
|
stores the data being processed
|
|
Cache memory
|
speeds up the processing
|
The motherboard usually has empty electronic connectors, called expansion slots, into which additional electronic boards (sometimes called expansion cards) can be plugged. This allows extra electronic components to be added. For example, more memory can be added by plugging memory boards (e.g. SIMMS) into the memory slots. Sound facilities can be added by plugging a sound card into an expansion slot. This is one way of upgrading a computer. Another way is to replace the motherboard with a newer and better one. The system unit usually also contains a small speaker (or loudspeaker), the power supply, and some storage devices. These often include: a hard disk drive with a fixed disk that can store a very large amount of data; a floppy disk drive that uses removable floppy disks (diskettes); a CD-ROM or DVD drive that is used for reading CD-ROM or DVD drive disks (particularly in multimedia computers). Some other devices may be included in the system unit but most input and output devices are plugged into the back of the system unit using connectors known as ports.
44. Study this photo of a PC motherboard. Match the components to their descriptions. If you need help, use the Glossary.
1. These are memory chips. The more you have the more work you can do at a time. Empty memory slots mean you can add more memory.
2. This is the «brain» of the computer.
3. It is part of the memory store. It has extremely fast access. It's faster than normal RAM. It can speed up the computer.
4. These let you add features such as sound or a modem to your computer.
5. This kind of memory contains all the instructions your computer needs to activate itself when you switch on. Unlike RAM its contents are retained when you switch off.

45. Study these instructions for formatting a disk in Microsoft Windows. Write the instructions in the correct order (1-6), using sequence words. You will have to use one of the words more than once.
|
a) Select “OK” to start formatting the disk.
b) Choose “Format” from the drop-down menu.
c) Click the “Start” button.
|
d) Put the disk into the drive.
e) Choose the formatting options you require.
f) Click the “OK” button when formatting is complete.
|
TEXT 5C
A PORTABLE COMPUTER
46. Complete the text about a portable computer with the words in the box.
|
notebook
CD
keyboard
|
microphone
peripherals
|
drive
anti-virus
|
display
performance
|
The Toshiba Satellite only weighs eight pounds but it provides the power, (1) … and multimedia functions of a desktop PC in a new mobile design. Packed with 3 GHz and 512 MB of RAM, the Satellite (2) … is the perfect solution for those customers that want a multimedia portable computer at an affordable price.
Its 60 GB hard disk (3) … is large enough to hold all the applications that you're likely to need. You also get a 3.5" internal floppy disk drive and a DVD/CD-RW unit compatible with most DVD and (4) … formats.
It features a large 14.1" TFT active matrix (5) … supporting up to 16 million colours at 1024 x 768 pixel resolution.
The Satellite comes with Windows XP pre-installed and additional software including Lotus SmartSuite, Adobe Acrobat Reader, Internet Explorer and an (6) … program.
Its (7) … has 85 full-sized keys with 12 function keys, and a touch pad pointing device acts as a mouse. The sound capabilities comprise a SoundBlaster card, built-in stereo speakers, and an external (8) … port, so you can digitally record, edit and play back speech.
To get online, the Satellite has a 56k modem and an Ethernet connector. It can be connected to a wide range of (9) … and network devices.
It runs on rechargeable Lithium batteries.
47. Read the text again and complete these notes with the most relevant information.
|
Microprocessor: …
RAM: …
Hard disk: …
Screen: …
Operating system: ....
|
Other software:
Other peripherals:
Power supply: …
|
Oral Practice
48. Work in pairs. Study this diagram. It shows the ports at the back of a desktop PC. With the help of the text below, match these labels to the correct ports.
|
keyboard
|
parallel port
|
serial ports
|
USB port
|
COM 1
|
video port
|
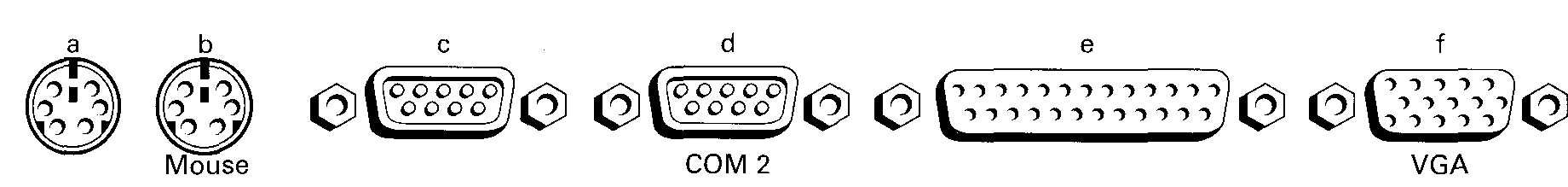
Desktop PC ports and connectors
External devices connect to ports at the back of the computer. Different types of port are used for each device. Most computers have: 1 keyboard port, 1 video port, 2 serial ports, 1 parallel port. Some also have a mouse port and one or more USB ports.
The mouse port and the keyboard port look exactly the same but they have labels to avoid confusion. If there is no mouse port, a serial mouse can be used. This connects with one of the serial ports. You can use the other one for a modem. The serial ports often have the labels COM1 and COM2.
The monitor connects to the video (VGA) port. The printer uses the larger parallel port. A variety of peripherals can be connected through the USB ports.
49. Work in pairs, A and B. Find out as much as you can about your partner’s computer and complete this table.
|
Feature
|
|
A
|
|
B
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
processor type
processor speed
bus speed
memory (RAM)
memory type
hard disk capacity
hard disk type
monitor size
monitor resolution
CD-ROM drive speed
|
|
|
|
|
Student A - Your conversion is on page 139.
Student B - Your conversion is on page 140.
Writing Practice
50. A friend has written to you asking you to recommend a computer that suits their needs. Write a letter in reply, describing its technical features and saying why you recommend it.
51. Complete this description of the motherboard shown on page 65 by adding the definitions from the reading text 5 B in the correct places.
The most important electronic part of a computer is the motherboard. The largest chip is the processor. The board also contains plug-in chips. One type contains ROM. A number of chips are mounted on memory boards. A third type of memory is cache memory. The board also has expansion slots.
UNIT 6
PROCESSING HARDWARE
This unit introduces the various hardware components that make up a computer system. By the end of this unit you should be better at reading for specific information, understanding computer advertisements. In this unit you will learn about the following topics:
- processing hardware;
- main memory.
Terms Concepts
Hardware comes in many configurations, depending on what the computer system is designed to do. Processing is controlled by the central processing unit which consists of a control unit that directs the transfer of data and arithmetic/logic unit that performs mathematical and logical calculations. The smallest unit of data that a computer can deal with is a single binary unit called a bit. Generally, computers deal with bits in groups of eight (called bytes) and computer storage capabilities are measured in bytes or kilobytes (K-bytes). Other common symbols are M (megabytes or millions of bytes), and G (gigabytes or billions of bytes).
Language material
1. Consult a dictionary and practise the pronunciation of the following words:
design, area, processing, temporarily, to direct, instruction, execution, internal, architecture, to couple, to interpret, tiny, circuit, to coordinate, register, although, extremely, counter, which, to synchronize, high-resolution, currently, to determine.
2. Learn by heart the following vocabulary:
|
adapter
CPU
CD-ROM
RAM
ROM
expansion slot
microprocessor
performance
processing hardware
unit
to relate
|
адаптер
центральный процессор, ЦП
накопитель на компакт-дисках
ОЗУ
ПЗУ
гнездо платы расширения
микропроцессор
быстродействие, эффективность
устройство обработки данных
блок, устройство
устанавливать связь, относиться
|
sophisticated
tiny
to couple
to deliver
to determine
to evolve
to execute
to handle
to interpret
to refer
to retrieve
|
сложный
крошечный
соединять
снабжать, поставлять
определять
развивать(ся)
выполнять
управлять
переводить
относиться, ссылаться
извлекать
|
3. Match the English word combinations in the left-hand column with the Russian equivalents in the right-hand column:
- computer’s machinery
- hand-in-hand
- key component
- memory register
- two-state binary system
- date encoding system
- hard disk
- internal clock
- clock speed
- arithmetic/logic unit
- instruction register
- program counter
- arithmetic computation
- control unit
|
- регистр команд
- два положения двоичной системы
- система кодирования данных
- арифметическое вычисление
- внутренний таймер
- программный счетчик
- тактовая частота
- компьютерное оборудование
- рука об руку, совместно
- ключевой компонент
- жесткий диск, “винчестер”
- арифметико-логическое устройство
- устройство управления
- регистр памяти
|
4. What's the meaning of these abbreviations?
|
CPU ………….
ALU ………….
GHz …………
ASCII ……….
|
RAM ………..
ROM ………
DIMM ………
EBCDIC ……
|
PC ………
CU ………
IR ………
MR ……..
|
5. Find in each line word that is given at the beginning.
|
activity
|
a) устройство
|
b) блок
|
c) адаптер
|
d) деятельность
|
|
circuit
|
a) блок
|
b) плата
|
c) схема
|
d) устройство
|
|
to determine
|
a) определять
|
b) извлекать
|
c) ссылаться
|
d) выполнять
|
|
to cause
|
a) управлять
|
b) причинять
|
c) переводить
|
d) поставлять
|
|
to emit
|
a) испускать
|
b) соединять
|
c) развивать
|
d) управлять
|
|
frequency
|
a) извлекать
|
b) ссылаться
|
c) излучать
|
d) частота
|
6. Note different meanings for words “to manage”, “to hold”.
|
to manage
|
руководить, управлять
|
The pension funds are managed by commercial banks.
|
|
|
уметь обращаться
|
The questionnaire was managed by trained interviewers.
|
|
|
применять, накладывать
|
The teacher has the authority to manage punishment.
|
|
|
справляться, ухитряться
|
She managed to persuade the child to give an injection.
|
|
|
принимать
|
Police believe his wife could not have managed the poison.
|
|
|
|
|
|
to hold
|
держать
|
He was holding the baby in his arms.
|
|
|
владеть
|
Employees hold 30% of the shares.
|
|
|
удерживать (позицию)
|
Hold this position for a count of 10.
|
|
|
вмещать, содержать в себе
|
The plane holds about 300 passengers.
|
|
|
держать (в тюрьме)
|
Police are holding two men in connection with last Thursday’s bank raid.
|
|
|
держаться
|
How long will the fine weather hold?
If their luck holds, they could still win the championship.
|
|
|
удерживать
|
Who holds the world record for the long jump? She held the title of world champion for three years.
|
|
|
полагать, считать
|
He holds strange views on education. She is held in high regard by her students.
|
|
|
проводить (собрание, разговор)
|
The meeting will be held in the community centre. It’s impossible to hold a conversation with all this noise.
|
|
|
подождать (телефон)
|
That extension is busy right now. Can you hold?
She asked me to hold the line.
|
|
|
останавливать, сдерживать
|
Hold your fire! Hold the front page! Give me a hot dog, but hold the mustard.
|
7. Match the synonyms.
instruction – direction, order, control, command, management.
to manage – to regulate, to govern, to direct, to control, to administer, to dominate, to rule.
to provide – to ensure, to secure, to assure, to meet the requirements.
to hold – to have, to hold on, to retain, to keep, to own, to occupy, to contain, to maintain.
to measure – to plumb, to evaluate, to estimate.
8. Match the antonyms.
|
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
|
temporally
software
less
simple
next
fixed
to differ
able
|
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
g)
h)
|
more
previous
complex
flexible
constantly
unable
to resemble
hardware
|
9. Find in each line the word – synonym to the first word:
|
performance
|
a) component
|
b) computation
|
c) productivity
|
d) unit
|
|
unit
|
a) device
|
b) design
|
c) instruction
|
d) speed
|
|
to execute
|
a) to increase
|
b) to perform
|
c) to resume
|
d) to include
|
|
to relate
|
a) to expand
|
b) to succeed
|
c) to bear
|
d) to squeeze
|
|
to handle
|
a) to allow
|
b) to communicate
|
c) to contain
|
d) to use
|
10. Find in each line the word – antonym to the first word:
|
to evolve
|
a) to determine
|
b) to couple
|
c) to lessen
|
d) to deliver
|
|
to couple
|
a) to unfasten
|
b) to relate
|
c) to execute
|
d) to handle
|
|
hardware
|
a) clock speed
|
b) performance
|
c) execution
|
d) software
|
|
complex
|
a) tiny
|
b) simple
|
c) basic
|
d) small
|
|
subtraction
|
a) division
|
b) multiplication
|
c) addition
|
d) comparison
|
11. Find in each line noun:
|
1.
|
a) sophisticated
|
b) direct
|
c) design
|
d) retrieve
|
e) central
|
|
2.
|
a) during
|
b) perform
|
c) sort
|
d) examine
|
e) through
|
|
3.
|
a) temporally
|
b) instruction
|
c) logical
|
d) main
|
e) involve
|
|
4.
|
a) combine
|
b) contain
|
c) temporary
|
d) comparison
|
e) internal
|
|
5.
|
a) provide
|
b) refer
|
c) enable
|
d) partly
|
e) example
|
12. Give definitions to the following using the vocabulary:
CPU, hardware, microprocessor, software, memory, instruction, data, chip, control unit, speed, information, internal clock.
13. Try and complete the following crossword:
CLUES ACROSS
1. The part of a computer where information is stored; the amount of space in a computer for storing information.
2. The physical units which make up a computer system.
3. The component in the processor or other chip which holds the instructions of the screen.
4. A tiny piece of silicon containing complex electronic circuits; is used to make the hardware components of a computer.
5. The “brain of the computer”. Its function is to execute programs stored in the main memory by fetching their instructions, examining them and then executing them one after another.
6. The set of electronic circuits used to control the timing of signals and synchronise different parts of a computer system.
7. A series of actions that a computer performs on data to produce an output.
10. Abbreviation for a component of the CPU which performs the actual arithmetic and logical operations asked for by a program.
CLUES DOWN
1. Equipment with moving parts that is designed to do a particular job.
8. A chip, or integrated circuit, that processes the instructions provided by the software.
9. A small electronic device used in computers, radios, televisions, etc. for controlling an electric current as it passes along a circuit.
|
1.
|
|
8.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Word-building
Model 14
Основа глагола + -ance/-ence существительное
-ant/ - ent прилагательное
|
to differ – различаться
to insist – настаивать
to resist – сопротивляться
to depend – зависеть
|
difference – различие
insistence – настойчивость
resistance – сопротивление
dependence – зависимость
|
different – различный
insistent – настойчивый
resistant – сопротивляющийся, стойкий
dependent – зависимый
|
Model 15
Основа глагола + ive прилагательное
|
to communicate – общаться
to regulate – регулировать
to illustrate – иллюстрировать
to demonstrate – демонстрировать
|
communicative – общительный
regulative – регулярный
illustrative – иллюстративный
demonstrative – демонстративный
|
14. Make new words using the models 14-15.
|
to correspond
to attract
to neglect
to impress
to confine
to negate
|
to assist
to create
to observe
to incise
to obsolesce
to nominate
|
to signify
to imitate
to perform
to legislate
to consent
to restrict
|
to coexist
to progress
to acquaint
to select
to excel
to operate
|
to ignore
to imagine
to compete
to offend
to import
to connect
|
Reading Practice
15. Read the advertisement and translate the technical specifications into Russian.
|
Ulysses XT
|
- Pentium 4 microprocessor at 5,5 GHz (5,500 MHz)
- 2 gigabytes of RAM, upgradable to 4 GB
- 1 TB hard disk
- comes with Microsoft Windows
|
16. Try to answer these questions.
- Without what parts is computer unable to work?
- What is the main function of a microprocessor?
- What unit of frequency is used to measure processor speed?
- What is the most expensive part of the hardware?
- What other hardware devices do you know? What are they for? Do you know how to use them?
17. Read the text below and then sentences 1 to 8 on page 73. Decide if the sentences are true (T) or false (F), and rewrite the false ones to make them true.
Text 6A
PROCESSING HARDWARE
Almost all of today’s computers, large and small, are based on a design that couples some sort of central processing device with a memory area that is used to temporarily hold instructions and data that can be used during processing. The purpose of processing hardware is retrieve, interpret and direct the execution of software instructions provided to the computer.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The central processing unit is the most complex of the computer's hardware components. The CPU is just a tiny microprocessor chip but it holds more than forty million transistors and functions as the nerve centre of the entire computer. The CPU can be thought of as the "brains" of the computer.
The power and performance of a computer is partly determined by the speed of its microprocessor. A clock provides pulses at fixed intervals to measure and synchronize circuits and units. The clock speed is measured in MHz (megahertz) or GHz (gigahertz) and refers to the frequency at which pulses are emitted. For example, a CPU running at 1.6 MHz (1,600 million cycles per second) will enable the computer to handle the most demanding applications.
One area where microprocessors differ is in the amount of data – the number of bits – they can work with at a time. There are 16, 32 and 64-byt processors. The computer’s internal architecture is evolving so quickly that the new 64-bit processors are able to address 4 billion times more information than a 32-bit system.
The two main manufacturers of microprocessor chips are Intel and Motorola.
1. The Intel 80x86 chips were used in the first IBM PCs and compatibles. In 1993 Intel Corporation introduced the Pentium processor which was 150 times faster than the speediest 80 x 86. Now most PCs have Intel Pentium 4 or AMD chips, delivering high performance for multimedia, Internet communications and 3-D applications.
2. The Motorola 680x0 chips were used in the first Macintosh, Atari ST and Amiga computers. In 1993 the alliance of IBM, Apple and Motorola created the PowerPC, a new 64-bit processor that could handle more information than 32-bit processors. Today, Macs have a PowerPC G3 or G4 processor, with high-performance multimedia extensions and faster clock speeds.
Its functions are following: (1) interpretation of instructions and direction the processing, (2) performance arithmetic operations and making comparisons, and (3) temporarily storage data during processing (main memory).
The CPU is composed of following key components: a control unit, arithmetic/logic unit, a clock and some memory registers.
The Control Unit examines the instructions and causes the circuits and the rest of the components, e.g. controls and coordinates all of the CPUs activities. Acting on instructions that it retrieves one by one from main memory, the control unit interprets each instruction and carries it out. In addition, it controls input and output devices and transfers data between the arithmetic/logic unit and main memory.
The Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU) performs arithmetic computations and logical operations. The arithmetic operations include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The logical operations involve comparisons such as less than, greater than, or equal to. Although these may seem like simple operations, the ALU can carry out extremely complex tasks by combining these functions. The speed of the ALU determines the speed of the computer.
Both the control unit and the ALU contain Registers, which are high-speed units of memory used to control information. They are temporary storage locations for managing instructions and data as they are being processed. One of these registers is the program counter (PC) which keeps track of the next instruction to be performed in the main memory. Another is the instruction register (IR) which holds the instruction that is currently being executed.
The CPU has an Internal Clock that synchronizes all of the operations in the cycle and the clock speed helps to determine the speed at which operations are carried out.
The Central Processing Unit performs the following four steps for each instruction:
- The control unit fetches (gets) the instruction from memory.
- The control unit decodes the instruction and directs that the necessary data be moved from memory to arithmetic/logic unit. These first two steps together are called instruction time, or I-time.
- The arithmetic/logic unit executes the arithmetic or logical instruction. That is the ALU is given control and performs the actual operation on data.
- The arithmetic/logic unit stores the results of this operation in memory or in a register.
Steps 3 and 4 together are called execution time, or E-time. The control unit eventually directs memory to realise the result to an output device or a secondary storage device. The combination of I-time and E-time is called the machine cycle.
Computers use a data encoding system that is based on a two-state binary system. Information in this system is represented through the use of ones and zeros. The digit 1 stands for on (the presence of an electronic signal), and the digit 0 stands for off (the absence of an electronic signal). When using magnetic media such as disks and tapes, these two states are indicated through the use of one or two magnetic polarities. When computers store data in a binary representation, each letter, number, and special character is stored based on a coding system. The two most commonly used coding systems are American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII), and the Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC) which is usually used only on large mainframe computers. The smallest unit of data that a computer can deal with is known as a bit, but generally computers deal with bits in groups of eight, referred to as a byte. As a result data management and storage capacities are usually measured in bytes.
- The CPU directs and coordinates the activities taking place within the computer system.
- The arithmetic logic unit performs calculations on the data.
- 32-bit processors can handle more information than 64-bit processors.
- A chip is an electronic device composed of silicon elements containing a set of integrated circuits.
- Information cannot be processed by the microprocessor if it is not loaded into the main memory.
- The speed of the microprocessor is measured in gigahertz or megahertz. One GHz is equivalent to one thousand MHz. One MHz is equivalent to one million cycles per second.
- Computer is an electronic device therefore hardware is a system of electronic devices.
- The purpose of processing hardware is to retrieve, interpret and direct the execution of software instructions provided to the computer.
- CPU reads and interprets software and prints the results on paper.
- User is unable to change the contents of ROM.
18. Which of the following is Processing Hardware:
|
program
modem
keyboard
|
mouse
command
character
|
CPU
port
RAM
|
printer
cursor or the pointer
ROM
|
19. Label this diagram of a computer system with these terms.
|
storage
|
input
|
output
|
processor
|
ROM
|
CPU
For example: For example:
keyboard, mouse, monitor, printer,
lightpen, scanner plotter, speaker, motor
For example: hard disk, floppy disk, CD-ROM
20. Work in pairs. What other examples of output devices, input devices, and storage devices can you add to the diagram?
21. General understanding:
- What is the definition of the hardware?
- What are the main parts of the CPU?
- What is processing hardware?
- What is the typical unit used to measure RAM memory and storage memory?
- What is a megahertz?
- What is the ALU? What does it do? Where does the ALU store the results of its operations?
- What is the abbreviation for “binary digit”?
- What must be put into memory before an instruction can be executed?
- Where will the data be stored temporarily?
- What operation does the control unit perform on the data?
- What happens to the results eventually?
- What is the machine cycle?
22. Study this diagram of a machine cycle. Answer these questions.
- How many steps are there in the machine cycle?
- What are the Fetch and Decode steps together called?
- Which steps together are called E-time?
- Where does the Decode step happen?
|
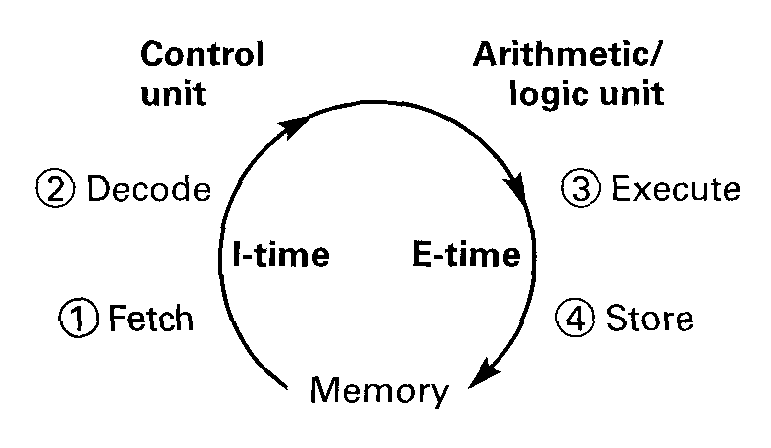
|
Text 6B
MAIN MEMORY
23. Read the text below and then sentences, decide if the sentences are true (T) or false (F).
|
temporary – временный, рабочий
solid-state – твердотельный
|
to modify - модифицировать
volatile memory – энергозависимая память
|
Memory is the system of components of the computer in which information is stored. Computers act on instructions provided by computer programs. These instructions are temporarily stored in a special data storage area referred to as main memory which is based on sets of silicon chips. Before the CPU can act, it must retrieve instructions from main memory (also known as temporary or internal storage). The CPU may also store data in main memory temporarily as it carries out processing tasks. Each chip contains millions of miniature circuits and each of those circuits can be in one of two states. This system is known as a binary system. The word “binary” refers to two distinct states, on or off, present or absent. Data is stored in these chips in grouped, coded patterns using this binary method. By setting some circuits to on and others to off, the computer can store many different kinds of data. In fact, all the different types of data that can be used on computers can be stored using complex combinations of this simple on/off binary coding system.
There are two types of solid-state, chip-based memory: RAM (random-access memory) and ROM (read-only memory). The computer uses random-access memory (RAM) to temporarily store program and processing information. This information is lost when the computer is turned off. Without power the circuits in the chips change back to their normal off-state and all the data is lost. For that reason this type of memory is known as volatile. It is contrasted to more permanent types of storage systems that are known as non-volatile. However, the term “random” may not be the best way to refer to this type of memory. While almost all of today’s computers use some random-access method of storing data (that is, the computer can retrieve data from wherever it is stored, randomly), the term “RAM” is reserved for the computer’s primary, chip-based memory system.
Read-only Memory (ROM) is another storage system that also uses silicon chips, but with this type of storage the data is not lost when the computer’s power is turned off. ROM is nonvolatile, nonmodifiable computer memory, used to hold programmed instructions to the system. ROM contains permanently stored information such as the instructions that are needed for the computer’s operation. This type of memory is known as “read-only memory” because the computer cannot store data to ROM but data can be read from ROM as often as needed. Computer makers use this type of chip-based storage system to permanently store data that is needed for the computer’s operation.
- “Permanent” storage of information is provided by RAM.
- ROM is nonvolatile, nonmodifiable computer memory.
- RAM, ROM and secondary storage are the components of the main memory.
- Main memory provides a way to pass files to and from the hard drive or to and from another computer.
- A chip is an electronic integrated circuit in a small package.
- RAM is volatile computer memory, used for creating, loading, and running programs and for manipulating and temporarily storing data.
- ROM is used to hold programmed instructions to the system.
- A binary system is a notation system in which the base for each digital position is 2.
24. As we have seen, there are three types of the memory used by computers: RAM, ROM and secondary storage. Look through this list of features and decide which type of memory they refer to.
- Any section of the main memory can be read with equal speed and ease.
- It is available in magnetic, optical and video disks.
- A certain amount of this memory can be designated as “cache” memory to store information in applications that are used very frequently.
- It stores basic operating instructions, needed by the CPU to function correctly.
- Memory which can be expanded by adding SIMMs of 8 MB, 16 MB, 32 MB or other major increments.
- Information is permanent and cannot be deleted.
- You can save and store your documents and applications.
25. With a partner try to answer these questions.
- Can a PC-user change the ROM? Who records the information in ROM?
- What is storage hardware? What is CD-ROM used for? Can a user record his or her data on a CD? What kind of storage hardware can contain more information: CD-ROM, RAM or ROM?
- What are the basic types of memory used in a PC?
- What memory section is permanent and consists instructions needed by the CPU?
- What is the meaning of the acronym SIMM?
- How can we store data and programs permanently?
- How many digits does a binary system use? What is a “bit”?
- What is the difference between binary notation and the decimal system? Give some examples.
- What is a collection of eight bits called?
- One kilobyte (1 Kb) equals 1,024 bytes. Can you work out the value of these units?
1 megabyte = bytes/1,024 kilobytes
1 gigabyte = bytes/1,024 megabytes
11. What does the acronym ASCII stand for? What is the purpose of this code?
Text 6C
UNITS OF MEMORY
26. Now read the text to check your answers or to find the correct answer.
Bits - basic units of memory
Information is processed and stored in computers as electrical signals. A computer contains thousands of electronic circuits connected by switches that can only be in one of two possible states: ON (the current is flowing through the wire) or OFF (the current is not flowing through the wire). To represent these two conditions we use binary notation in which 1 means ON and 0 means OFF. This is the only way a computer can “understand” anything. Everything about computers is based upon this binary process. Each 1 or 0 is called a binary digit or bit.
Bytes and characters
1s and 0s are grouped into eight-digit codes that typically represent characters (letters, numbers and symbols). Eight bits together are called a byte. Thus, each character in a keyboard has its own arrangement of eight bits. For example, 01000001 for the letter A, 01000010 for B and 01000011 for C.
The ASCII code
The majority of computers use a standard system for the binary representation of characters. This is the American Standard Code for Information Interchange, known popularly as “ASCII” (pronounced “ask-key”). There are 256 different ways of combining 0 and 1 bits in a byte. So they can give us 256 different signals. However, the ASCII code only uses 128 bytes to represent characters. The rest of the bytes are used for other purposes.
The first 32 codes are reserved for characters such as the Return key Tab, Escape, etc. Each letter of the alphabet, and many symbols (such as punctuation marks), as well as the ten numbers, have ASCII representations. What makes this system powerful is that these codes are standard.
Kilobytes, megabytes and gigabytes
In order to avoid astronomical figures and sums in the calculation of bytes, we use units such as kilobytes, megabytes and gigabytes. One kilobyte is 1,024 bytes (210) and it is represented as KB, or more informally as K. One megabyte is equivalent to 1,024 KB, and one gigabyte is 1,024 MB.
We use these units (KB, MB, GB, and TB) to describe the RAM memory, the storage capacity of disks and the size of any application or document.
27. Look at the illustrations and the captions below. Then fill in the blanks with the correct unit of memory.
|
nglish
|
|

|

|
|
1. One … represents one character.
|
2. One … represents 1,024 characters (about a small page of text).
|
3. One … represents 1,000,000 characters (about the text of this book).
|
4. One … represents 1,000,000,000 characters (about 1,000 books in a library).
|
28. Put these units of measurement in the correct place.
|
terabyte
|
megabyte
|
gigabyte
|
bit
|
byte
|
kilobyte
|
|
Units of memory
|
Equivalence
|
|
1. ……………………..
2. ……………………..
3. ……………………..
4. ……………………..
5. ……………………..
6. ……………………...
|
binary digit (0 or 1)
8 bits
1,024 bytes
1,024 kilobytes
1,024 megabytes
1,024 gigabytes
|
29. The quotations 1-7 below are typical in computing. Read them and find:
1. the unit of measurement that represents ASCII characters;
2. the abbreviation for “megabyte”;
3. the size of the text file;
4. the acronym for “random access memory”;
5. the speed of a conventional modem;
6. the maximum storage capacity of a DVD;
7. the reason why you can't download an audio file.
|

A conventional modem transmits data at 56 kilobits per second.
|
This text file occupies 3 kilobytes.
|

I’ve got a Pentium computer with 5,5 GHz (5,500 MHz) and 2 gigabytes of RAM and 1 TB of hard disk space Windows.
|
|
|

|

|
|
A CD can hold 650 megabytes of data. However, a DVD can store up to 17 gigabytes.
|
You can’t download this audio file. You need 3 MB of additional space on your disk.
|
This Windows program runs best with 256 MB or more of memory.
|
|
A, z, 7
Bytes are used to represent individual characters – a letter, a number, or even a space.
|
Listening Practice
30. Study this diagram of the Central Processing Unit. Answer the questions:
|
1. What does ALU mean?
|
Registers
|
Address Bus
|
|
2. What is a register?
|
ALU
|
Data Bus
|
|
3. What does the control unit do?
|
Control Unit
|
Control Bus
|
Listen to the recording. Check your answer to exercise.
31. Listen again to find the answers to these questions.
- What sort of functions does the ALU perform?
- Name a logic operation performed by the ALU.
- Which part of the CPU controls printers?
- What is the difference between registers and main memory?
Oral Practice
32. Make notes about the features of the computer that you would like to have.
|
CPU ....
Minimum/maximum RAM ....
Hard disk: …….
|
Speed ....
|
Optical disk drives ....
Monitor ...
Software .....
|
33. Now describe it to your partner.
Useful expressions
- It has got ...
- It’s very fast. It runs at ...
- The standard RAM memory .... and it is expandable ...
- The hard disk can hold ....
- I need SuperVGA monitor because ....
- As for the Internet .....
34. Work in pairs, A and B. Explain to your partner how to convert a number from one system to another. You can write down the steps and show them to your partner, but you must explain each step in English.
Student A - Your conversion is on page 139.
Student B - Your conversion is on page 140.
Writing Practice
35. Read the text and complete it with the phrases in the box.
|
All the information stored in the RAM is temporary
|
|
Microcomputers make use of two types of main memory
|
|
ROM chips have “constant” information
|
|
the size of RAM is very important
|
Main memory: RAM and ROM
The main memory of a computer is also called the “immediate” access store, as distinct from any storage memory available on the disks. (1) ...: RAM and ROM, both contained in electronic chips connected to the main board of the computer.
RAM stands for “random access memory” and is the working area of the computer, that is, the basic location where the microprocessor stores the required information. It is called “random access” because the processor can find information in any cell or memory address with equal speed, instead of looking for data in sequential order.
(2) ..., so it is lost when the machine is turned off. Therefore, if we want to use this information later on, we have to save it and store it on a disk. When running an application, the microprocessor finds its location in the storage device (the floppy or hard disk) and transfers a temporary copy of an application to the RAM area. Consequently, (3) ... if we what to increase the performance of a computer when several applications are open at the same time or when a document is very complex.
The RAM capacity can sometimes be expanded by adding extra chips. There are usually contained in single in-line memory modules or SIMMs which are installed in the motherboard of the computer.
We can designate a certain amount of a RAM space as a cache in order to stare information that an application uses repeatedly. A RAM cache may speed up our work, but it means that we need enough internal memory or a special cache card.
ROM is an acronym for “read only memory” which implies that the processor can read and use the information stored in the ROM chip, but cannot put information into it. (4) ..., including instructions and routines for the basic operations of the CPU. These instructions are used to start up the computer, to read the information from the keyboard, to send characters to the screen, etc. They cannot be changed and are not erased when the power is turned off. For this reason, the ROM section is also referred to as firmware.
UNIT 7
SECONDARY STORAGE SYSTEM
The term secondary storage refers to devices that are used to store data and program files for long periods of time. There are many different types of secondary storage devices including diskette drives, fixed disk drives, and magnetic tape drives.
Terms Concepts
Today’s storage systems generally are based on magnetic disks or magnetic tape. One such storage system uses a diskette (also known as a floppy disk) which is available in a 3.5 inch size. Fixed disks, also known as hard disks, use the same magnetic media, but they can store a great deal more data and they are permanently sealed in a case. Magnetic tape is often used to store backup copies of programs and data. Optical disks are high-capacity, nonmagnetic storage devices that are based on laser technology.
Language material
1. Consult a dictionary and practise the pronunciation of the following words:
purpose, relatively, permanent, basic, function, except, capacity, surface, circle, catalogue, head, toward, measure, millisecond, mechanism, microdrive, multimedia, through, various, digitized, archive, version, rewritable, language, limitation, suitable.
2. Learn by heart the following vocabulary:
|
average
cartridge
density
entry
off-line
purpose
shareware
surface
track
corporate
empty
flexible
permanent
random
rigid
secure
relatively
tightly
|
среднее число, средний
патрон, картридж
плотность, компактность
вход, проход
автономный режим
намерение, цель, назначение
условно-бесплатное ПО
поверхность
дорожка, след, курс
корпоративный, общий
пустой
гибкий
постоянный, долговременный
случайный, наугад
жесткий, твердый, негибкий
безопасный, надежный
относительно, сравнительно
тесно, туго, плотно, крепко
|
as soon as
therefore
while
to back up
to clamp
to coat
to discover
to distinguish
to distribute
to duplicate
to erase
to format
to initialize
to occupy
to record
to share
to spin
to stack
|
как только, не позже
следовательно
в то время как, пока
поддерживать
фиксировать, захватывать
покрывать, облицовывать
обнаруживать, открывать
различать, отличать
распределять
дублировать, делать копию
стирать, вычеркивать
размечать, форматировать
инициализировать
занимать
записывать данные на носитель
делиться, участвовать
вращаться
записывать в стек
|
3. Match the English word combinations in the left-hand column with the Russian equivalents in the right-hand column:
|
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
|
office filing system
electromagnetic signal
floppy disk
concentric circle
a blank disk
read/write head
access time
at full speed
seek time
data transfer rate
sealed case
at the same rate
animation program
optical disk
digital versatile disk
magneto-optical disk
magnetic tape
removable disk
track density
|
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
k.
l.
m.
n.
o.
p.
q.
r.
s.
|
полным ходом
магнитооптический диск, магнитооптика
магнитная лента
головка чтения/записи
время поиска, позиционирования
скорость передачи данных
дискета, гибкий (магнитный) диск
офисная файловая система
пустой диск
электромагнитный сигнал
концентрический круг
с такой же скоростью
анимационная программа
съемный диск
поперечная плотность записи
время доступа
закрытый корпус
оптический диск
цифровой многофункциональный диск
|
4. Look at the illustrations and find out:
- the size (dimensions) of a floppy disks;
- the name of a hard drive on a PC platform;
- the storage capacity of external DVD ;
- the system that can hold 10 GB tapes;
- the meaning of the abbreviations “DS”, “DD”, “HD”;
- the external features of double density and high density disks.
|

|

|

|
|
3.5-inch diskette
A high-density (HD) floppy disk can store 1.44 MB of information. A floppy drive uses 3.5-inch disks and it's called drive A.
|
Hard disk
Most PCs have one hard drive, called drive C. It's used to keep software and files organized in a convenient way. A hard disk can hold several gigabytes of data.
|
Removable hard drive
Hard drive, which can be taken off from the computer and easily carried.
|
|

|

|

|
|
External DVD
External DVD is used for reading and recording data on removable DV disks. It comes up to 8 GB.
|
Pocket-sized drive
Ultra portable drives are used with mobile computers. They hold 40 MB disks. The Peerless system can hold 20 GB disks.
|
Microdrive
A Microdrive is the smallest external hard drive for PC. It comes in 10 GB and 30 GB capacities
|
5. Find in each line word that is given at the beginning.
|
application
|
a) приложение
|
b) плотность
|
c) корпус
|
d) намерение
|
|
platter
|
a) цель
|
b) лента
|
c) проход
|
d) тарелка диска
|
|
to allow
|
a) расширять
|
b) позволять
|
c) отличать
|
d) вычеркивать
|
|
to replace
|
a) замещать
|
b) делиться
|
c) занимать
|
d) поддерживать
|
|
to retrieve
|
a) форматировать
|
b) вращаться
|
c) извлекать
|
d) размечать
|
|
to seal
|
a) инициализировать
|
b) запаивать
|
c) покрывать
|
d) открывать
|
|
common
|
a) общий
|
b) гибкий
|
c) пустой
|
d) надежный
|
|
thus
|
a) относительно
|
b) сравнительно
|
c) тесно
|
d) таким образом
|
6. Note additional meanings for words “to pass”, “to mean”.
|
to pass
|
проходить мимо
|
Several people were passing but nobody offered to help. There was a truck behind that was trying to pass me.
|
|
|
передавать, давать
|
Pass the salt, please. Pass that book over. Pass me over that book.
|
|
|
переходить (после смерти)
|
On his death, the title passed to his eldest son.
|
|
|
превышать
|
Unemployment has now passed the three million mark.
|
|
|
проходить, проводить (о времени)
|
Six months passed and we still had no news of them. We sang songs to pass the time. How did you pass the evening?
|
|
|
заканчиваться
|
They waited for the storm to pass.
|
|
|
сдавать (экзамены)
|
She hasn’t passed her driving test yet. The examiners passed all the candidates.
|
|
|
|
|
|
to mean
|
значить, означать, иметь значение
|
What is meant by “batch processing”? The flashing light means you must stop.
|
|
|
иметь в виду
|
What do you mean, you thought I wouldn’t mind? Did he mean he was dissatisfied with our service?
|
|
|
подразумевать
|
What did she mean by leaving so early? Don’t be upset - I’m sure she meant it as a compliment.
|
|
|
собираться, намереваться
|
His father meant him to be a systems support person.
|
|
|
означать
|
Spending too much now will mean a shortage of cash next year. This new order will mean working overtime.
|
|
|
значить, быть важным
|
$20 means a lot when you live on $100 a week. Her children mean the world to her.
|
7. Consider the grammar:
to insert into – вставлять в
When you insert a blank disk into a disk drive, it must be “initialized”, or formatted, before information can be recorded onto it.
to pass into sth – превращаться в, переходить в, делаться
Many foreign words have passed into the English language.
to read into – вчитываться в
The operating system looks for its entry in the directory, moves the read/write heads to the correct sectors, and reads the file into the RAM area.
to seal into – скреплять с
There are “internal” and “external” drives which are both rigid disks sealed into the drive unit, either within or attached to the computer.
8. Match the synonyms:
|
1.
2.
3.
4.
5
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
|
to occupy
to affect
to clamp
to back up
hard
area
common
secure
entry
purpose
|
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
|
rigid
field
to take up
to influence
to fix
reliable
entrance
aim
to maintain
usual
|
9. Match the antonyms:
|
1.
2.
3.
4.
5
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
|
often
common
empty
secure
removable
entry
off-line
permanent
rigid
random
|
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
|
exit
on-line
premeditated full
unreliable
fixed
temporal
flexible
seldom
rare
|
10. Find in each line the word – synonym to the first word:
|
to transfer
|
a) to back up
|
b) to discover
|
c) to transmit
|
d) to coat
|
|
to consist
|
a) to include
|
b) to clamp
|
c) to distribute
|
d) to share
|
|
to start
|
a) to duplicate
|
b) to erase
|
c) to occupy
|
d) to begin
|
|
information
|
a) application
|
b) image
|
c) data
|
d) driver
|
|
type
|
a) kind
|
b) track
|
c) surface
|
d) density
|
|
way
|
a) ware
|
b) method
|
c) purpose
|
d) average
|
11. Find in each line the word – antonym to the first word:
|
fast
|
a) high
|
b) cheap
|
c) slow
|
d) also
|
|
special
|
a) large
|
b) ordinary
|
c) expensive
|
d) ideal
|
|
towards
|
a) inside
|
b) out
|
c) with
|
d) back
|
|
top
|
a) bottom
|
b) version
|
c) memory
|
d) case
|
|
to write
|
a) to damage
|
b) to erase
|
c) to create
|
d) to archive
|
|
to create
|
a) to involve
|
b) to ruin
|
c) to carry out
|
d) to enhance
|
12. Find in each line noun:
|
1.
|
a) transmit
|
b) processor
|
c) retrieve
|
d) occupy
|
e) digital
|
|
2.
|
a) various
|
b) storage
|
c) optical
|
d) distribute
|
e) which
|
|
3.
|
a) area
|
b) while
|
c) divided
|
d) modern
|
e) create
|
|
4.
|
a) secure
|
b) lot
|
c) represent
|
d) reason
|
e) both
|
|
5.
|
a) stable
|
b) held
|
c) duplicate
|
d) erase
|
e) access
|
|
6.
|
a) fixed
|
b) versatile
|
c) just
|
d) device
|
e) electromagnet
|
13. What’s the meaning of these abbreviations?
|
DVD-ROM
|
DVD
|
CD-ROM
|
HDD
|
CD-RW
|
|
CD
|
CD-MO
|
WORM
|
CD+G
|
DVD-RAM
|
|
FD
|
DVD-E
|
CD-R
|
DIVX
|
CD-DA
|
14. Read the clues and complete the crossword.
|
|
1.
|
|
|
2.
|
|
|
|
|
3.
|
|
4.
|
5.
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.
|
|
|
7.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.
|
|
9.
|
|
10.
|
|
|
|
11.
|
|
12.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.
|
|
|
|
17.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.
|
|
|
|
20.
|
|
21.
|
|
22.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Across
1. Acronym for “light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation”.
4. A microcomputer.
6. To write information on a disk, magnetic tape or film.
10. To record and keep for future use.
12. Abbreviation of “binary digit”.
14. Thousandth of a second.
15. The type of computer with a 286 processor introduced by IBM in 1984.
17. Concentric ring marked on the surface of a disk when the disk is formatted.
18. Prefix meaning “very large” or “one thousand million”.
20. Read only memory.
22. The physical mechanism that accepts, reads and writes data on a disk.
Down
1. Acronym for “local area network”.
2. Opposite of “indelible”.
3. Abbreviation of “high density” or “hard disk”.
5. Way of storing a lot of information in a removable form.
7. Abbreviation of “optical character recognition”.
8. All disks must be “initialized” or … when used for the first time.
9. Indelible optical storage device: “write once, read many”.
11. Not cheap.
13. A flat, circular surface used to hold computer data.
16. Opposite of “soft”.
19. Disk that holds music.
21. A thousand kilobytes.
Word-building
Model 16
Основа существительного + -ous прилагательное
|
courage - смелость
danger - опасность
fame - слава, известность
glory - слава
|
courageous - смелый
dangerous - опасный
famous - знаменитый, известный
glorious - славный
|
Model 17
Основа прилагательного + -ness существительное
|
black – черный
bitter – горький
cold – холодный
dark – темный
|
blackness – чернота
bitterness – горечь
coldness – холод
darkness – темнота
|
15. Look at the groups of words and decide what class each word belongs to: noun, verb, adjective or adverb. Complete the sentences.
|
magnet
|
magnetic
|
magnetically
|
magnetism
|
magnetize
|
magnetized
|
- … is the science of magnetic phenomena and properties.
- Floppy and hard disks are considered as … storage devices.
- Data is recorded on a disk in the form of … spots called bits.
|
record
|
recorder
|
recording
|
recorded
|
- All disks must be initialized before information can be … onto them.
- The … heads follow the tracks and magnetize the coating along each track.
- A disk drive works very much like a tape … that can both play and record.
|
fragment
|
fragmentation
|
defragmenter
|
fragmented
|
- After you create, delete and modify a lot of files the hard disk becomes ... with bits and pieces spread all over the disk.
- ... slows down the speed at which data is accessed because the disk drive has to work harder to find the parts of a file stored in many different locations.
- To reorganize your hard disk, you can use a disk optimizer or …, this will reorder your files into contiguous clusters.
Reading Practice
16. There are many different kinds of storage device for computers and developments are taking place all the time. List the storage devices mentioned in this unit so far. List any other storage devices you know.
17. Work in groups of three. Read following text and complete your sections of the table.
|
Medium
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
|
|
|
|
Floppy disk
|
|
|
|
Fixed hard disk
|
|
|
|
Removable hard disk
|
|
|
|
CD-ROM disk
|
|
|
|
Magneto-optical disk
|
|
|
|
Magnetic tape
|
|
|
Text 7 A
STORAGE HARDWARE
18. Read the text. Try to understand it and be ready to answer the questions.
The purpose of storage hardware is to store computer instructions and data in a form that is relatively permanent and retrieve when needed for processing. Storage hardware serves the same basic functions as do office filing systems except that it stores data as electromagnetic signals. The most common ways of storing data are hard disk, floppy disk and CD-ROM.
The floppy drive
Floppy disks are so called because they consist of flexible plastic material which has a magnetizable surface. Floppy drives provide a way to pass files to and from the hard drive or to and from another computer. They are also very cheap, but they are slow and have a limited capacity.
The surface of a disk is divided into concentric circles or “tracks”, which are then divided into “sectors”. When you insert a blank disk into a disk drive, it must be “initialized”, or formatted, before information can be recorded onto it.
This means that magnetic areas are created for each track and sector, along with a catalogue or “directory” which will record the specific location of files.
When you save a file, the operating system moves the read/write heads of the disk drive towards empty sectors, records the data and writes an entry for the directory. Later on, when you open that file, the operating system looks for its entry in the directory, moves the read/write heads to the correct sectors, and reads the file into the RAM area.
Hard Disks
Almost all desktop computers have hard disks. Hard disk, often referred to as fixed disks, is a rigid disk coated with magnetic material for storing programs and relatively large amounts of data. Hard disks work in the same way as floppies. But they have important advantages: they can hold much more data and spin at higher speed, so you can store and retrieve information 25 much faster than with floppies. The speed at which a hard drive finds data is called “access time” - or seek time. The average access time is measured in milliseconds (ms). Most hard drives have an access time of 8 to 14 ms.
You have to distinguish between access time (e.g. 9 ms) and “data transfer rate” (the average speed required to transmit data from a disk system to the RAM, e.g. at 10 megabits per second). The transfer rate depends also on the power of your PC.
Fixed disks often use several magnetically coated disks stacked one on top of the other. All of these disk platters inside the sealed case spin at the same rate, but each disk has its own set of read/write heads. While the diskette drive's mechanism clamps onto the diskette and starts it spinning after it is placed in the drive, fixed disks start spinning as soon as the computer is turned on. And since fixed disks spin very fast inside a tightly sealed case, they can provide faster rates of data transfer to the processor.
If you only use word-processing programs, you will need less storage capacity than if you use CAD, sound and animation programs. If you need an extra hard drive, you should consider the type of mechanism. There are “internal” and “external” drives which are both rigid disks sealed into the drive unit, either within or attached to the computer.
Another type of hard drive, known as “removable”, allows you to record data on “cartridges”, which can be removed and stored off-line for security purposes. Some systems allow you to back up your entire PC on one disk. Laptops use pocket-sized drives. Digital cameras and music players use microdrives with special cards.
Optical disks and drives
Optical disks can store information at much higher densities than magnetic disks. Thus, they are ideal for multimedia applications where images, animation and sound occupy a lot of disk space. Besides, they are not affected by magnetic fields. This means that they are secure and stable, e.g. they can be transported through airport metal detectors without damaging the data. However, optical drives are slower than hard drives. While there are hard drives with an average access time of 8 ms, most CD-ROM drives have an access time of 150 to 200 ms.
There are various types of optical drives:
CD-ROM (compact disk read only memory) is a compact disk on which a large amount of digitized read-only data can be stored. They are removable and can hold about 650MB.They are also cheap to make. However, they are usually read-only. You cannot change the information on them. They are also slow compared to hard disks.
CD-ROM systems offer everything, from shareware programs to dictionaries and encyclopedias, from multimedia databases to 3-D games. A lot of institutions have discovered that CD-ROM is the most economical way of sharing information. In fact, one CD-ROM disk can replace 300,000 pages of text (about 500 floppies), which represents a lot of savings in distributing materials and corporate databases. In addition, CD-ROM drives can play music CDs while you work.
CD-Recorders come in two different forms: CD-R and CD-RW. CD-R machines record on CD-R (write-once) disks, allowing you to create and duplicate CDs. They are used to back up hard disks or to distribute and archive information. In fact, these systems are the modern version of old WORM (write once, read many) disks. CD-RW (rewritable) disks can be erased and re-used, just as you would do with a hard disk.
The future of optical storage is called DVD (digital versatile disk). A DVD-ROM can hold 17 GB, about 25 times an ordinary CD-ROM. For this reason, it can store a large amount of multimedia software and complete Hollywood movies in different languages. They can also play music CDs and CD-ROMs. However, DVD-ROMs are “read-only” devices. To avoid this limitation, companies also produce DVD-R and DVD rewritable disks.
19. Now exchange information with the other students in your group to complete all the sections of the table. Ask questions like these.
- What are the advantages of floppy disks?
- What are the disadvantages of a magnetic tape?
- Do CD-ROMs conform to a standard?
- What is input hardware? What are the examples of input hardware?
- What is mouse designed for? What is a light pen?
- What is modem used for? Can PC-user communicate with other people without a modem?
- Today's computers use secondary storage systems to store data that is not currently being processed. Name and describe three different types of storage systems that use disks.
20. Now read these sentences and decide if they are true (T) or false (F).
- Hard drives are faster than floppy drives.
- Access time refers to the average time required for the recording heads to move and access data.
- Access time and data transfer rate mean the same.
- Hard disks use rigid rotating disks.
- A hard drive is about 20 times faster than a floppy disk drive.
- If you use multimedia applications you need the same storage capacity as required for word processors.
- Removable cartridges are not transportable.
21. Read the text and match the terms on the left with the explanations on the right.
- backing store
- floppies
- disk drive
- formatting
- directory
- read/write heads
|
a) a catalogue of where each piece of data is stored and how to find it
b) recording heads
c) secondary memory
d) diskettes
e) initializing; setting tracks and sectors on magnetic disks
f) a device which spins disks and contains a read/write head
|
22. Read the text again and summarize in the table the most relevant information.
|
|
Technical specifications
|
Use
|
|
CD-ROM
|
|
|
|
CD-Recorder
|
|
|
|
DVD
|
|
|
|
Magneto-optical disk
|
|
|
23. Read these sentences and clauses and look back to find out what the words in bold refer to.
1. ... they are secure and stable ...
2. ... which represents a lot of savings in distributing materials ...
3. ... you cannot write anything onto a CD-ROM disk.
4. You can only “read” it ...
Writing Practice
24. Read the text match these headings to the correct paragraphs.
|
DVD formats
DVDs versus CDs
|
What's a DVD?
Configurations of data layers
|
|
Looking forward
|
1...........................
DVD stands for digital versatile disk. It’s essentially a new type of compact disk which can hold several gigabytes of multimedia elements - video, audio and computer data. DVD uses MPEG-2 to compress video.
2.............................
At first sight a DVD is similar to a CD. Both disks are 120 mm in diameter and 1.2 mm thick. They also use a laser beam to read data. However, they are very different in infernal structure and data capacity. In a DVD the tracks are very close in space, thus allowing more tracks per disk. The distance between each track is 0.74 micron, whereas in a CD the track pitch is 1.6 micron. In addition, the pits in which data is stored are smaller, so there are more pits per track. Furthermore, DVDs can be double-sided, which doubles their potential storage capacity.
3...................................
A DVD-ROM holds computer data and is read by a DVD-ROM drive in a computer. DVD-ROM drives are backward-compatible, so they can also play old CD-ROMS, video CDs and CD-R disks.
A DVD-Video disk is the best storage medium for full-length movies. It can support eight different languages, 52 subtitles, and various audio formats. DVD-Video players are connected to TV sets.
A DVD-Audio disk contains sound files, supporting PCM digital audio, Dolby Digital and DTS, a high-quality audio Format used in theatres.
Recordable DVDs come in various formats: DVD-R disks are similar in concept to CD-R (Recordable), i.e. they can record data only once, while the rewritable formats (e.g. DVD-RAM and DVD+RW) can be erased and reused many times. They can all record any kind of information - data files, video and TV programmes.
DIVX means digital video express, a new format promoted by the film industry in America. It’s like a pay-per-view DVD allowing you to rent or buy a DIVX disk at low price and view its contents within a limited period of time, DIVX players come with a modem which connects to the phone lines to communicate with the central server.
4.............................................
The basic pattern is a single-sided, single layer disk with a capacity of 4.7 GB. The single-sided, dual layer disk can hold up to 8.5 GB. The double-sided, single layer disk offers a capacity of 9.4 GB. As the contents are on both sides, the disks must be used in a DVD player capable of reading the two sides. Finally, the double-sided dual layer disk increases the storage capacity up to 17 GB with 8.5 GB on each side.
5.....................................
There are still too many formats and specifications, but in the near future DVD drives are expected to be compatible with all existing CD and DVD formats. DVDs will gradually replace audio CDs, CD-ROMs and video cassettes.
PC users and movie addicts are waiting with excitement for a universal drive that can play any type of optical disk.
25. Join the sentences with the words in brackets.
1. A virus entered the computer. Many files have been destroyed. (as a result)
2. DVDs and CDs are physically similar in size. Their data structure is very different. (although)
3. Colour, animation and 3D graphics are essential in many applications. They're used in art, graphic design and engineering. (for example)
4. In computers, RAM memory is temporary. The ROM section is permanent. (however)
26. Summarize the technical specifications and uses of these DVD formats.
27. Read the text again and find:
1. the compression format used by DVD-video technology;
2. two similarities between CDs and DVDs;
3. two differences between CDs and DVDs;
4. the storage capacity of a basic DVD disk;
5. the storage capacity of a double-sided dual layer DVD.
28. Look at the expressions in italics in these sentences and clauses.
1. Thus, they are ideal for multimedia applications ... .
2. Besides, they are not affected by magnetic fields.
3. However, optical drives are slower than hard drives.
4. In addition, CD-ROM drives can play music CDs while you work.
5. Yet CD-ROM technology has one disadvantage: ... .
6. For this reason, it can store a large amount of multimedia software ... .
29. Give the main idea of extract “STORAGE HARDWARE” in 25-30 sentences.
30. Match the instructions to the pictures “Protect your data”.
- Protect your floppies against high temperatures.
- Check for viruses before opening files you receive from the Web or via e-mail.
- Keep back-ups (spare copies) of your data.
- Don't write on the discs.
- Keep disks away from water and humidity.
- When handling CDs or DVDs, hold the disks around the edge.
31. In pairs, tell each other what you must or mustn’t do to protect your disk.
Example – You mustn’t leave them on the top of your computer.
- in a protective case;
- into a disk drive very carefully;
- near strong magnetic fields; they can damage the information stored on them;
- update your anti-virus program regularly since new viruses are created everyday;
- password and security devices to protect confidential information;
- at a temperature of between 10 C and 52 C;
- bend or fold the disk.
32. Study these rules for CD-ROM and floppy disk care. Tick () things to do and cross (X) things not to do. Then compare your choice with a partner.
|
1.
|
|
Hold a CD-ROM by the edges.
|
|
2.
|
|
Keep the optical/silver side of a CD-ROM clean.
|
|
3.
|
|
Smoke when you use your CD-ROM drive.
|
|
4.
|
|
Put floppy disks near a magnet.
|
|
5.
|
|
Keep disks away from the sun and excessive heat.
|
|
6.
|
|
Write the contents on the label on your floppy disk.
|
|
7.
|
|
Put extra labels on floppy disks.
|
|
8.
|
|
Remove by force a disk stuck in the drive.
|
|
9.
|
|
Remove a disk when the drive light is on.
|
Listening practice
33. Sue is in a shop. Listen to the conversation and answer these questions.
- What type of drive does Sue want to buy?
- How much information can be stored on a Jaz disk?
- What’s the storage capacity of a Zip disk?
- How much is a Jaz drive?
- How much is a Zip drive?
- What is the storage capacity of high density disks?
- What type of disk is a good substitute for diskettes?
- Which system is ideal to store MP3 music and videos – the Jaz or the Peerless?
34. Role play. Work with a partner. One of you wants to buy a removable hard drive; another is a sales assistant.
Storage devices
35. Study this diagram of a hard disk drive. Match the labels to the diagram.
|
1.
|
|
drive motor
|
a b
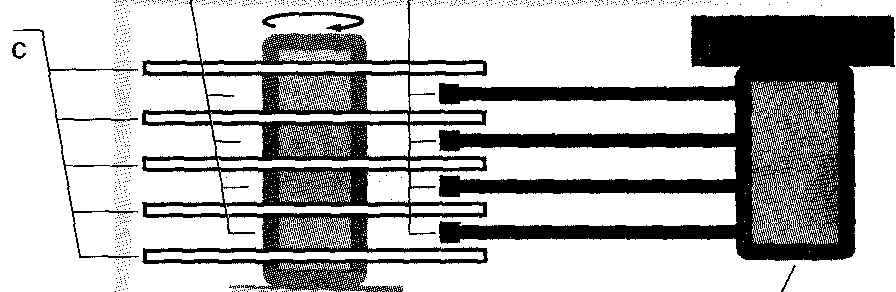
d e f
|
|
2.
|
|
sealed case
|
|
|
3.
|
|
disks
|
|
|
4.
|
|
read/write heads
|
|
|
5.
|
|
head motor
|
|
|
6.
|
|
gap between disks
|
|
Listen to Part 1 of this description of a hard disk drive to check your answers.
36. Study this diagram. Answer these questions.
1. What sort of things can damage a hard disk?
2. How big is the gap between the read/write heads and the disk?
3. How can we protect a disk drive from damage?
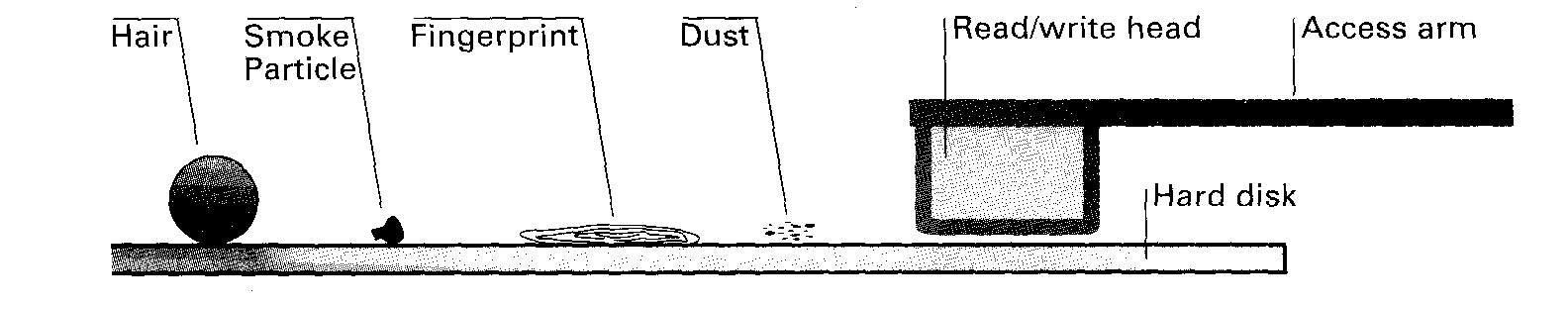
Now listen to Part 2 of the description to check your answers.
Oral Practice
37. Which of the products on the next page would be most suitable for the purposes below? Discuss the pros and cons with a partner.
1. To store data and programs at home.
2. To hold large amounts of information in a big company.
3. To store an illustrated encyclopedia for children.
4. To hold historical records in the National Library.
5. To store high-quality audio and video, and hold several movies in different languages.
Useful Expressions
|
For personal use, I would recommend .., because...
In a big company, it would be a good idea to ...
However, ... is good for an encyclopedia because...
|
I agree/disagree with you. CD-ROMs …
Besides, ...
Well, that depends on ...
|
PRODUCTS AVAILABLE
Hard disk drive.
Superfast 8 ms hard drive. Capacity ranges from 6 GB to 1 TB.
Iomega’s removable drives.
The Zip series uses 100 MB and 250 MB disks. In the nearer future it can replace the floppy disk as the portable storage medium.
The Jaz series can hold 2 GB cartridges. Ideal to back up hard disks.
CD-ROM drive.
Each CD disk holds 650 MB.
CD-Recordable drive.
Makes it possible to write data to CDs as well as read it.
Magneto-optical (MO) disk systems.
Erasable optical-magnetic 5.25" cartridges with 5.2 GB of storage capacity. Can be erased and written on like a hard disk.
Rewritable 3.5" floptical disks with a storage capacity of 1.3 GB.
DAT Data tape drive.
Digital audio tape drives to store computer data. Used for back-up purposes. Slow access. Huge amounts of information (about 10 GB).
Digital Video Disk-ROM drive.
Each DVD-ROM disk has a capacity of up to 17 GB, and can hold various full-screen movies. The drive can also read your CD-ROMs.
38. Notice how these terms are used in computing.
bit (b) a 0 or a 1 in the binary system
byte(B) a group of eight bits, e.g. 10101110
kilo (K) 210 (approximately a thousand)
mega (M) 220 (approximately a million)
giga (G) 230 (approximately a thousand million)
39. Now work in pairs, A and B. Fill in the gaps in this table as your partner dictates. Ask your partner to repeat if necessary.
|
Storage device
|
Capacity
|
Storage device
|
Capacity
|
|
DVD
High density floppy Average hard disk
|
………………
………………
………………
|
CD-ROM
Large hard disk
Tape
|
………………….
………………….
………………….
|
Student A - Your data is on page 139.
Student B - Your data is on page 140.
Text 7 B
CACHE MEMORY
40. Find the answers to questions in the following text.
1. What is one of the main causes of a PC not running at its highest potential speed?
2. What word in the text is used instead of “buffer”?
3. What device looks after cache coherency?
4. What is the main alternative to “write-through cache”?
5. When does a write-back cache write its contents back to main memory?
6. When is data marked as “dirty” in a write-back cache?
7. What determines that data is replaced in a disk cache?
41. Skim the text, trying to understand what it is about. Time your reading. It is good if you can read it for minutes (70 words per minute).
cache coherency – непротиворечивость, синхронизация
cache controller – контролер кэш-памяти
cache hit – “попадание”, наличие нужных данных
cache miss – “непопадание”, отсутствие нужных данных
write-through cache – кэш с прямой записью
write back cache – кэш с обратной записью
chunk – участок памяти, часть данных
disk caching – кэширование диска
cache line – строка данных кэша
to request – запрашивать, требовать
adjacent – смежный, примыкающий
anticipation - ожидание
vice versa – наоборот
“dirty” - недействительный, измененный
Most PCs are held back not by the speed of their main processor, but by the time it takes to move data in and out of memory. One of the most important techniques for getting around this bottleneck is the memory cache.
The idea is to use a small number of very fast memory chips as a buffer or cache between main memory and the processor. Whenever the processor needs to read data it looks in this cache area first. If it finds the data in the cache then this counts as a “cache hit” and the processor need not go through the more laborious process of reading data from the main to memory. Only if the data is not in the cache does it need to access main memory, but in the process it copies whatever it finds into the cache so that it is there ready for the next time it is needed. The whole process is controlled by a group of logic circuits called the cache controller.
One of the cache controller’s main jobs is to look after “cache coherency” which means ensuring that any changes written to main memory are reflected within the cache and vice versa. There are several techniques for achieving this, the most obvious being for the processor to write directly to both the cache and main memory at the same time. This is known as a “write-through” cache and is the safest solution, but also the slowest.
The main alternative is the “write-back” cache which allows the processor to write changes only to the cache and not to main memory. Cache entries that have changed are flagged as “dirty”, telling the cache controller to write their contents back to main memory before using the space to cache new data. A write-back cache speeds up the write process, but does require a more intelligent cache controller.
Most cache controllers move a “line” of data rather than just a single item each time they need to transfer data between main memory and the cache. This tends to improve the chance of a cache hit as most programs spend their time stepping through instructions stored sequentially in memory, rather than jumping about from one area to another. The amount of data transferred each time is known as the “line size”.
Disk caching works in essentially the same way whether you have a cache on your disk controller or you are using a software-based solution. The CPU requests specific data from the cache. In some cases, the information will already be there and the request can be met without accessing the hard disk.
If the requested information isn’t in the cache, the data is read from the disk along with a large chunk of adjacent information. The cache then makes room for the new data by replacing old. Depending on the algorithm that is being applied, this may be the information that has been in the cache the longest, or the information that is the least recently used. The CPU's request can then be met, and the cache already has the adjacent data loaded in anticipation of that information being requested next.
42. Match the terms in Table A with the statements in Table B.
|
Table A
|
|
Table B
|
|
|
|
|
- Cache hit
- Cache controller
- Cache coherency
- Write-through cache
- Write-back cache
- Line size
|
|
- The process of writing changes only to the cache and not to main memory unless the space is used to cache new data.
- The amount of data transferred to the cache at any one time.
- The process of writing directly to both the cache and main memory at the same time.
- The processor is successful in finding the data in the cache.
- Ensuring that any changes written to main memory are reflected within the cache and vice versa.
- The logic circuits used to control the cache process.
|
43. Mark the following as True or False:
- Cache memory is faster than RAM.
- The processor looks for data in the main memory first.
- Write-through cache is faster than write-back cache.
- Write-back cache requires a more intelligent cache controller.
- Most programs use instructions that are stored in sequence in memory.
- Most cache controllers transfer one item of data at a time.
- Hardware and software disk caches work in much the same way.
44. Study this data about storage devices. Then complete the blanks in the following sentences comparing and contrasting the different types.
|
Device
|
Read/Write
|
Speed
|
Media Capacity
|
Media Removable
|
Cost
|
|
Floppy disk
|
Read and write
|
Slow
|
Very low
|
Yes
|
Low
|
|
Fixed hard disk
|
Read and write
|
Fast
|
Very high
|
No
|
Medium
|
|
Removable hard disk
|
Read and write
|
Medium to fast
|
High
|
Yes
|
Medium
|
|
CD-ROM
|
Read only
|
Medium
|
High
|
Yes
|
Low
|
|
CD-R
|
Recordable
|
Slow
|
High
|
Yes
|
Medium
|
|
CD-RW
|
Read and write
|
Medium
|
High
|
Yes
|
Medium
|
|
CD-MO
|
Read and write
|
Medium
|
High
|
Yes
|
High
|
|
DVD-ROM
|
Read only
|
Medium
|
High
|
Yes
|
Medium
|
|
DVD-RAM
|
Read and write
|
Medium
|
Very high
|
Yes
|
High
|
|
Magnetic Tape
|
Read and write
|
Very slow
|
High
|
Yes
|
Medium
|
1. You can write to hard disks .......... optical disks.
2. Floppy disks have a .......... capacity ............. other devices.
3. CD-ROMs and floppy disks are ........... low priced.
4. DVD-RAM has a .......... capacity ........... other optical disks.
5. CD-ROMs cannot be re-recorded .......... some other optical disks can be.
6. ......... hard disks, you can read from and write to CD-MO drives.
7. ......... CD-ROMs, CD-Rs are recordable.
8. Magnetic tape is much ..... other devices.
9. ....... DVD-RAM and fixed hard disks have very high media capacity.
10. Floppy disks are cheap ...... DVD-RAM is expensive.
Text 7C
READY FOR THE BAZILLON-BYTE DRIVE
45. Find the answers to these questions in the following text.
1. What is Currie Munce’s main aim?
2. How quickly did the possible areal density of hard disks increase in the 1990s?
3. How long does Munce think magnetic recording technology will continue to make, rapid advances in capacity?
4. What problem does he predict for magnetic storage?
5. What is the predicted limit for discrete bit magnetic storage capacity?
6. What storage technologies might replace current magnetic systems?
7. What is the advantage of holographic storage being three-dimensional?
8. What improvements are predicted due to the fast access rates and transfer times of holographic storage?
9. What is predicted to be the most important high capacity removable storage media in the next 10 years?
10. What method of software distribution is likely to replace optical disks?
Thinking about writing your memoirs - putting your life story down on paper for all eternity? Why not skip the repetitive strain injury and just capture your whole life on full-motion video, putting it all in a device the size of a sugar cube? It might not be as far off as you think.
Currie Munce, director of IBM’s Advanced HDD Technology Storage Systems Division, has one avowed goal: Build bigger storage. Recently Munce and his fellow Ph.Ds restored Big Blue's lead in the disk space race with a new world record for areal (bit) density: 35.3 gigabits per square inch - roughly three times as dense as any drive shipping at press time.
During the 1990s, areal density doubled every 18 months, keeping pace with the transistor density gains predicted by Moore’s Law. But increasingly daunting technical challenges face those who would push the storage envelope further. “I think magnetic recording technology has another good 5 to 10 years,” says Munce. “After that, we’ll see substantial difficulties with further advances at the pace people are accustomed to.”
From here on, a phenomenon called superparamagnetism threatens to make densely-packed bits unstable. Provided that new developments continue to thwart superparamagnetic corruption, scientists speculate that the theoretical limit for discrete bit so recording is 10 terabits per square inch (1 terabit = 1,000 gigabits).
Approaching this limit will require new technologies. Two possible contenders are atomic force microscopy (AFM) and holographic storage. AFM would use a spinning plastic disk, perhaps inside a wristwatch, and a tiny, 10-micron cantilever with a 40-angstrom tip (an angstrom represents the approximate radius of an atom) to write data. In theory, AFM will allow densities of 300 to 400 gigabits per square inch.
While AFM is still in the lab, holographic storage is closer to reality. According to Rusty Rosenberger, optical program manager for Imation, “We are targeting a 5-inch disk with 125GB of storage and a 40MB-per-second transfer rate.” Future iterations of holographic systems should improve substantially.
The three-dimensional nature of holography makes it an appealing storage medium because so “pages” of data can be superimposed on a single volume - imagine transferring a whole page of text at once as opposed to reading each letter in sequence. Hans Coufal, manager of IBM's New Directions in Science and Technology Research division, predicts that the fast access rates and transfer times of holographic storage will lead to improved network searches, video on demand, high-end servers, enterprise computing, and supercomputing.
Meanwhile, also-ran technologies are thriving. Tape, first used for data storage in 1951 with the UNIVAC I, has been revitalized by the corporate hunger for affordable archiving solutions. In the consumer arena, says Dataquest analyst Mary Craig, recordable CD-ROMs and DVDs will remain the dominant high-capacity removable storage media for the next decade. Despite their failure to match the areal density gains of hard disks, optical disks are cheap to produce, making them ideal for software distribution (until a mature digital rights management system facilitates online delivery). Finally, solid state options such as flash cards can’t yet match the pricing of hard disks at high capacities.
Further out, scientists salivate over the prospect of data manipulation and storage on an atomic level. Because consumer demand for capacity is lagging behind what technology can deliver, bringing new storage options to the masses will depend on seeing the need for more space.
46. Re-read the text to find the answers to those questions. Match the terms in Table A with the statements in Table B.
|
Table A
|
Table B
|
|
1. Big Blue
2. Areal density
3. Moore's Law
4. Superparamagnetis
5. Terabit
6. AFM
7. Angstrom
|
a. Atomic force microscopy;
b. The approximate radius of an atom;
c. IBM;
d. The data capacity of a storage device measured in bits per square inch;
e. Prediction that the number of transistors j that can be incorporated into a processor chip will double every 18 months;
f. A phenomenon that threatens to make densely packed bits unstable in magnetic storage devices;
g. One thousand gigabits.
|
47. Mark the following statements as True or False:
1. The development of AFM is more advanced than holographic storage.
2. The predicted maximum storage density of AFM is 400 gigabits per square inch.
3. Holography works in 3D.
4. UNIVAC I was the first computer to use tape storage devices.
5. Users want higher capacity storage devices than technology can provide.
UNIT 8
INPUT HARDWARE
Input devices are the pieces of hardware which allow us to enter information into the computer. The most common are the keyboard and the mouse. We can also interact with a computer by using one of these: a light pen, a scanner, a trackball, a graphics tablet, a joystick or a voice recognition device.
Terms Concepts
Input devices are used to transfer data from its human-readable form into machine-readable form. In the early days paper tapes and punched paper cards were used to get information into the computer. As the human-computer interface has evolved from a character-based or command-line interface to a graphical interface, input devices such as the mouse, graphics tablets, light pens, trackballs, touch screens, and touch pads have become much more important.
Digitizing technologies, such as image scanners (sometimes referred to as graphics scanners), optical character recognition (OCR), and voice input technologies have evolved to give computer users a way to input different types of information into the computer.
Language Material
1. Consult a dictionary and practise the pronunciation of the following words:
peripheral, equipment, to manage, consideration, since, keyboard, switch, pressure, row, column, routine, continuing, instead, to convert, readable, although, cursor, to push, to identify, manufacturer, to specify, register, thus, receipt, supply, beneath, image, measurement, to rotate, appropriate, to view, via.
2. Learn by heart the following vocabulary:
|
camcorder
consideration
effort
layout
order
switch
typewriter
despite
instead
via
|
записывающая видеокамера
рассмотрение, обсуждение
усилие, попытка
схема размещения
порядок, предписание
коммутатор, переключатель
пишущая машинка
не смотря на
вместо, взамен
через
|
to arrange
to device
to display
to feed
to improve
to relate
to sense
to touch
to transmit
hardwired
current
|
располагать, устраивать
устраивать
выводить на экран
загружать, снабжать
улучшать(ся), совершенствовать
относиться
ощущать, понимать
притрагиваться, волновать
предавать, отправлять
не модифицирующийся
текущий, современный
|
3. Match the English word combinations in the left-hand column with the Russian equivalents in the right-hand column:
- graphics tablet
- light pen
- trackball
- touch screen
- touch pad
- a software routine
- the needs of humans
- hand-operated device
- voice recognition
- mouse pad
- flatbed scanner
- voice-recognition software
|
- системная программа
- графический планшет
- световое перо
- шаровой манипулятор, трекбол-мышь
- сенсорный экран
- сенсорная панель
- потребности человечества
- ручное устройство
- планшетный сканнер
- распознавание голоса
- коврик для мыши
- программные средства распознавания голоса
|
4. Read and translate the following expressions.
|
the other way around
light sensitive
checkout counter
|
the brand name
rotating lamp
the desired location
|
a paper receipt
data-entry method
human-readable character
|
5. Match these pictures of input devices with their names. In pairs, try to list the uses of these devices.
|
joystick
tracker ball
lightpen
|
barcode reader
scanner
mouse
|
graphics tablet
touch screen
keyboard
|
digital earner
microphone
voice recognition device
|
|
a) ....
|
b) ....
|
c) ...
|
|
d) ...
|
e) ...
|

f) ...
|
|

g) ...
|
h) ...
|

i) ...
|
|
j) ...
|
k) ...
|
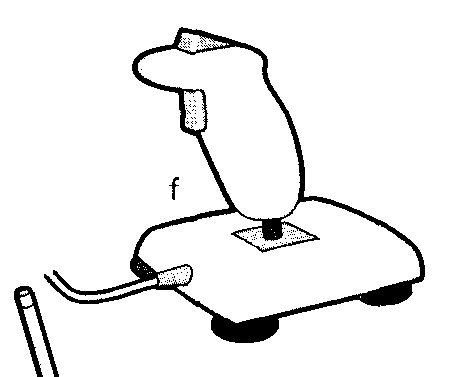
l) ...
|
6. Find in each line word that is given at the beginning:
|
оборудование
|
a) measure
|
b) location
|
c) equipment
|
d) calculation
|
|
вычисления
|
a) computation
|
b) pressure
|
c) instruction
|
d) package
|
|
матрица
|
a) code
|
b) matrix
|
c) image
|
d) screen
|
|
определять
|
a) to arrange
|
b) to check
|
c) to activate
|
d) to detect
|
|
присоединять
|
a) to convert
|
b) to relate
|
c) to attach
|
d) to connect
|
7. Find in each line the translation to the first word:
|
switch
|
a) переключатель
|
b) планшет
|
c) предписание
|
d) усилие
|
|
step
|
a) схема
|
b) обсуждение
|
c) шаг
|
d) потребности
|
|
row
|
a) оборудование
|
b) перо
|
c) панель
|
d) ряд
|
|
to convert
|
a) преобразовывать
|
b) определять
|
c) загружать
|
d) относиться
|
|
although
|
a) вместо
|
b) хотя
|
c) через
|
d) взамен
|
8. Find in each line the word – antonym to the first word:
|
to arrange
|
a) to convert
|
b) to discompose
|
c) to activate
|
d) to detect
|
|
to attach
|
a) to arrange
|
b) to improve
|
c) to touch
|
d) to unconnect
|
|
to convert
|
a) to touch
|
b) to pervert
|
c) to feed
|
d) to display
|
|
to hasten
|
a) to display
|
b) to sense
|
c) to delay
|
d) to transmit
|
|
order
|
a) disorder
|
b) layout
|
c) switch
|
d) step
|
9. Find in each line noun:
|
1.
|
a) accept
|
b) individual
|
c) column
|
d) magnetize
|
e) specific
|
|
2.
|
a) simplify
|
b) carry
|
c) mathematical
|
d) character
|
e) usually
|
|
3.
|
a) activate
|
b) location
|
c) designed
|
d) since
|
e) most
|
|
4.
|
a) transmit
|
b) editing
|
c) electronically
|
d) connected
|
e) measurement
|
|
5.
|
a) convert
|
b) create
|
c) security
|
d) sensitive
|
e) normal
|
|
6.
|
a) before
|
b) stored
|
c) also
|
d) assistance
|
e) easier
|
10. Consider the grammar:
to work out – заниматься, быть успешным
Rachel works out at the gym three times a week.
Good luck for the future. I hope everything works out well for you.
to carry out – выполнять ч.-л.
Early computers were “hardwired” to carry out specific tasks, usually mathematical calculations.
to fall out with smb – ссорится с к.-л.
They used to be very good friends. I’m surprised to hear that they have fallen out.
David fell out with his father and left home.
to find out – выяснять, обнаруживать ч.-л.
The police found out who committed the computer theft.
I called the tourist office to find out about hotels in the town.
to point sth out to smb – указывать на ч.-л. к.-л.
As we drove through the city, our guide pointed out all the sights.
I didn’t realize I’d made a mistake until somebody pointed it out to me.
to run out of sth – истощить запас ч.-л.
We run out of petrol on the motorway.
to turn out – оказываться
The weather wasn’t so good in the morning, but it turned out nice later.
to try out sth – испытывать ч.л.
The company is trying out a new computer system at the moment.
11. A great many words in English have more than one meaning.
|
to control
|
управлять, распоряжаться
|
By the age of 21 he controlled the company. The whole territory is now controlled by the army.
|
|
|
ограничивать
|
Many biological processes are controlled by hormones. Parents should control what their kids watch on television. She was given drugs to control the pain.
|
|
|
регулировать
|
This knob controls the volume. The traffic lights are controlled by a central computer.
|
|
|
сдерживать
|
I was so furious I couldn’t control myself and I hit him. He was finding it difficult to control his feelings.
|
|
|
|
|
|
space
|
пустое пространство, расстояние
|
That desk takes up too much space. How much disk space will it take up? Put it in the space between the table and the wall.
|
|
|
космос
|
When the sun’s rays hit the earth, a lot of the heat is reflected back into the space.
|
|
|
интервал, промежуток времени
|
They had achieved a lot in a short space of time. Leave a space of two weeks between appointments.
|
|
|
промежуток
|
Don’t waste space by leaving a wide margin. There was not enough space to print all the letters we received. Leave a space after the comma.
|
|
|
свобода
|
She was upset and needed space. You have to give teenagers plenty of space.
|
|
to touch
|
дотрагиваться, прикасаться
|
Can you touch your toes? I touched him lightly on the arm. He has hardly touched the ball all game.
|
|
|
соприкасаться
|
Make sure the wires don’t touch. Don’t let your coat touch the wet paint. His coat was so long it was almost touching the floor.
|
|
|
притрагиваться к еде, деньгам
|
You’ve hardly touched your food. He hasn’t touched the money his aunt left him.
|
|
|
трогать, волновать
|
Her story touched us all deeply. These are issues that touch us all.
|
|
|
сравниться
|
No one can touch him when it comes to interior design.
|
|
|
достичь уровня
|
The speedometer was touching 90.
|
|
|
касаться, иметь отношение
|
Everything she touches turns to disaster. His last two movies have been complete flops and now no studio will touch him.
|
12. Match the synonyms:
to relate – to recount, to tell, to recite, to describe, to report, to state.
to rotate – to spin, to turn, to circulate, to circle, to wheel, to revolve.
sensitive – predisposed, perceptive, prone, impressionable, liable, tender.
13. Match the antonyms:
to include – to exclude, to eliminate, to debar, to omit.
to improve – to degrade, to damage, to injure, to decline, to droop, to sink, to weaken.
to influence – to lack, to power, to be of no importance, to produce no effect, to get no result.
to join – to separate, to sever, to sunder, to detach.
- Try and complete the following crossword:
1. A device that is used for recording sounds or for making your voice louder when you are speaking or singing to an audience;
2. The main electronic input device; the set of keys for operating a computer similar layout to a typewriter;
3. An optical input device that uses the reflection of a light beam to read barcode labels;
4. A video camera that records pictures and sound and that can be carried around;
5. A piece of input equipment for taking photographs, moving pictures or television pictures; It has an electronic lends and uses electronics for storing the images rather than chemical film;
6. An optical input device which copies pictures and documents so that they can be stored on a computer;
7. A common cursor control input device that is moved by hand across a surface to control the movement of the cursor on a computer screen. It commonly has two or three button switches on top and a ball underneath;
8. This device uses a light sensitive photoelectric cell to signal screen position to the computer;
9. …
10. …
Word-building
Model 18
re- + oснова глагола глагол, обозначающий повторное действие
|
to read – читать
to appear – появляться
to consider – рассматривать
to construct – строить
|
to reread – перечитывать
to reappear – снова появляться
to reconsider – пересмотреть
to reconstruct – перестроить
|
Model 19
dis-, non- + основа отрицательное значение или противоположное действие
|
to approve – одобрять
to like – любить
essential – существенный
conductor – проводник
|
to disapprove – не одобрять
to dislike – не любить
non-essential – не существенный
non-conductor – не проводник
|
- Make new words using the models 18-19.
|
to calculate
to appear
to establish
ferrous
to open
to believe
to write
|
to cover
to arm
to install
to obey
to sell
charge
to mark
|
to do
to connect
to form
appointment
to use
to claim
to elect
|
to connect
honest
to export
to approve
to unite
comfort
to introduce
|
Reading Practice
Text 8A
16. Read the text. Try to understand it and be ready to answer the questions.
INPUT HARDWARE
The microcomputer has to communicate with the outside world, so that programs and data can be entered into its memory and processed information can be displayed or transmitted in some form to the microcomputer user. There are various types of input peripheral equipment that may be attached to microcomputers including keyboards, mouse, graphics tablets, light pens, trackballs, touch screens and touch pads for input.
When people first began to use computers to manage data, they used data input devices that were related more to the design of the early computers than to the needs of humans. Early computers were "hardwired" to carry out specific tasks, usually mathematical calculations. When newer computers were designed to be “programmed” to carry out a number of different tasks, the input of instructions and data became a very important consideration. Since most of the early computers were used mainly for mathematical computations, the main input task in those days was to feed numbers into the computer.
The most common input device is a keyboard. It looks very much like a typewriter. With it, you type instructions and commands for the computer, and information to be processed and stored. A keyboard consists of a number of switches which are activated by pressure or simply by touching them. The keys are arranged as a matrix, so that the depression of any key can be detected by scanning the rows and columns of the matrix. Hardware may be used to sense which key has been pressed or this may be carried out by a software routine.
Despite the fact that today's computers can accept input faster than we can enter it, most computer keyboards still use that same inefficient key layout. The computer keyboard limits input to the single letters, numbers, and special typing characters found on the keyboard's keys. The early punched paper cards and the later use of keyboards represent the first steps in a continuing effort to adapt computers to human needs instead of the other way around. Since humans were used to typing on keyboards that had individual keys to represent individual letters, numbers, and symbols, computers had to be designed to convert these human-readable characters into machine-readable form. And although computers have become more capable and many new types of input devices are in use today, the keyboard is still the most common device used to enter data.
The computer mouse is a hand-operated device that lets you control more easily the location of the pointer on your screen. As the mouse is rolled across the mouse pad, the cursor moves across the screen. When the cursor reaches the desired location, the user usually pushes a button, on the mouse once or twice to signal a menu selection or a command to the computer. A small integrated circuit inside the mouse sends signals to the operating system.
A barcode reader/scanner is an input device that scans barcodes on the products sold in shops. Each package has a Universal Product Code or UPC, which consists of a series of dark bars and light spaces used to represent specific information about the product. The barcodes are made of modules that represent binary digits, or bits. The first modules identify the general category of the product and the manufacturer. The next modules specify the product for the computer, including the brand name and the price. The last modules check that the information is read correctly. When the barcode scanner reads the barcodes at the checkout counter, it sends the price to the computer in the cash register, where it is displayed on a screen and printed on a paper receipt. The data is also recorded on disk. Thus, computers can keep a record of what articles are in stock and can instantly give orders for new supplies.
A scanner “sees” images and converts the printed text or pictures into electronic codes that can be understood by the computer. With a flatbed scanner, the paper with the image is placed face down on a glass screen similar to a photocopier. Beneath the glass are the lighting and measurement devices. Once the scanner is activated, it reads the image as a series of dots and then generates the digitized image that is sent to the computer and stored as a file. A colour scanner operates by using three rotating lamps, each of which has a different coloured filter: red, green and blue. The resulting three separate images are combined into one by appropriate software.
A digital camera takes photos electronically and converts them into digital data (binary codes made up of 1s and 0s). It doesn’t use the film found in a normal camera; instead it has a special light-sensitive silicon chip. Photographs are stored in the camera’s memory before being sent to the computer. Some cameras can be also connected to a printer or a TV set, to make viewing images easier.
A camcorder, or digital video camera, records moving pictures and converts them into digital data that can be stored and edited by a computer with special video editing software. Digital video cameras are used by home users to create their own movies, or by professionals in computer art and video conferencing. They are also used to send live video images via the Internet. Then they are called Web cameras or webcams.
Voice Input
Today, as voice-recognition software improves, voice input is becoming more common. This input method is currently in limited use because of the difficulty involved in discriminating between different speakers. As a result, more accurate input is obtained when each user "trains" - the software to recognize a specific word by repeating the word several times. As new voice-recognition methods are devised, voice input is expected to become one of our most important data-entry methods.
17. Try to answer these questions:
- How is the mouse connected to the computer?
- What does the mouse pointer look on the screen?
- What are the functions of the mouse buttons?
- What are the advantages of a computer mouse over a keyboard?
- What's a barcode reader?
- What types of information do barcodes represent?
- What are the advantages of using barcode readers at a supermarket?
- How does a computer system read the details on a credit card?
- What type of card has a microprocessor inside, used for storing electronic money?
- Which device is used to input text and graphic images from a printed page?
- How does a colour scanner work?
- Do digital cameras use film? How do they store photographs?
- Which device would you use to take digital video?
- What kind of software is used to manipulate video clips on the computer?
- What do you think the benefits of using scanners and cameras at home and in business are?
18. Study these statements which explains how a common type of mouse works. Then complete each of these statements with one word.
1. Move the mouse to the left and the cursor moves to the … .
2. The mouse contains a rolling … .
3. There are … axles inside the mouse and two interrupter wheels.
4. When you move the mouse, the ball … .
5. The mouse moves over a mouse … .
19. Look at the picture of a PC-compatible keyboard and identify these groups of keys.
Alphanumeric keys: arranged in the same order as a typewriter.
Function keys: used by various programs to instruct the PC to perform specific tasks, such as Save, Copy, Cut, Paste, Help, etc.
Numeric keypad: set of numeric or editing keys. The Num Lock key is used to switch from numbers to editing functions.
Editing keys: cursor and other keys usually used within word processors to page up and down in a long document or to edit text (using Insert or Delete keys).
Special keys: used to issue commands or to produce alternative characters in key combinations, for example, the Alt key.
20. Match these key abbreviations with their full names.
|
1. Esc
2. Alt
3. Ctrl
4. Pgdn
5. Pgup
6. Ins
7. Del
|
a. Alternate
b. Page Up
c. Delete
d. Insert
e. Escape
f. Page Down
g. Control
|
21. Study this keyboard. The keys are in four sections. Can you name any of the sections?

Listening Practice
The keyboard
22. Listen to this description of the keyboard. Label each section of the picture above.
23. Using the information from the Listening Practice describe what these keys do.
|
1.
|
Page Up
|
2.
|
|
3.
|
Delete
|
4.
|
|
24. Read the text to check your answers or to find the right answers.
Text 8B
POINT AND CLICK
Typically, a mouse is a palm-sized device, slightly smaller than a pack of cards. On top of the mouse there is one or more buttons for communicating with the computer. A “tail” or wire extends from the mouse to a connection on the back of a computer.
The mouse is designed to slide around on your desktop. As it moves an image on the screen called a pointer or mouse cursor. The pointer usually looks like the arrow or I-bar, and it mimics the movements of the mouse on your desktop.
What makes the mouse especially useful is that it is a very quick way to move around on a screen. Move the desktop mouse half an inch and the screen cursor will leap four inches. Making the same movements with the arrow keys takes much longer. The mouse also issues instructions to the computer very quickly. Point to an available option with the cursor, click on the mouse, and the option has been chosen.
Mice are also widely used in graphics applications because they can do things that are difficult, if not possible, to do with keyboard keys. For example, the way you move an image with a mouse is to put the pointer on the object you want to move, press the mouse button and drag the image from one place on the screen to another. When you have the image where you want it, you release the mouse button and the image stays there. Similarly, the mouse is used to grab one corner of the image (say a square) and stretch it into another shape (say a rectangle). Both of these actions are so much more difficult to perform with a keyboard that most graphics programs require a mouse.
The buttons on the mouse are used to select items at which the mouse points. You position the pointer on an object on the screen, for example, on a menu or tool in a paint program, and then you press the mouse button to “select” it. Mice are also used to load documents into a program: you put your pointer on the file name and double-click on the name – that is, you press a mouse button twice in rapid succession.
Your first computer, A. Simpson, Sybex, 2002
25. Here are some basic mouse actions. Match the terms in the box with the explanations below.
|
a) click
|
b) double-click
|
c) drag
|
- Position the pointer on something, then rapidly press and release the mouse button twice. (You do this program, open a document or select text or graphics.)
|
|
|
- Position the pointer on something, hold down the mouse button and move the mouse to the desired position, then release the button. (You do this to move an image to a new location on the screen.)
|
|
|
- Position the pointer on something, then press and release the mouse button. (You do this to place the insertion point, to choose an option, or to close a window.)
|
|
|
26. Locate these keys on the keyboard as quickly as you can. Number them 1 to 8.
|
Insert
|
minus
|
plus
|
Delete
|
|
comma
|
F1
|
Print Screen
|
Escape
|
27. Identify these symbols on the keyboard.
|
slash
not equal to
|
plus and minis
trademark
|
yen sigh
copyright
|
number
registered trademark
|
28. Look at the statements (1-7) and correct the ones which are wrong.
Example - This key moves the cursor down. It doesn’t move the cursor down. It moves the cursor up.
|
1.
|
|
|
This key moves the cursor down.
|
|
2.
|
|
|
This key moves the cursor to the right.
|
|
3.
|
|
Del
|
This key inserts a character.
|
|
4.
|
|
Print Screen
|
This key copies the screen display.
|
|
5.
|
|
Page Down
|
This key moves the screen up.
|
|
6.
|
|
Home
|
This key doesn’t have a fixed function.
|
|
7.
|
|
Caps Lock
|
This key gives you all lower case letters.
|
29. Match these descriptions with the names of keys on the right.
- A long key at the bottom of the keyboard. Each time it is pressed, it produces a blank space.
- It moves the cursor to the beginning of a new line. It is also used to confirm commands.
- It stops a program without losing the information from the main memory. Some times its use depends on the applications.
- It works in combination with other keys to produce special characters or specific actions.
- It removes the character on the left of the cursor or any selected text.
- It produces UPPER-CASE characters (or the upper-case character of the key).
- It produces upper-case letters, but it does not affect numbers and symbols.
- It moves the cursor horizontally to the right for a fixed number of spaces (in tabulations and data fields).
- They are used to move the cursor, as an alternative to the mouse.
|
- arrow keys
- return
- caps lock
- shift
- tab
- escape
- space bar
- backspace
- alt
|
Listening Practice
30. Listen to an interview with Anne, an expert in voice-input technologies. Tick () the features that she mentions.
need a good sound card and a microphone;
take dictation with accuracy;
create and compile a computer program;
surf the Web by speaking;
execute programs and navigate around menus by voice commands;
design graphics.
31. Listen again and fill in the gaps in these sentences. Use the correct modal verb from the list.
|
can (ability)
|
must (necessity)
|
should (advice)
|
could (possibility)
|
will (prediction)
|
1. If you intend to do a lot of dictation, you … get a high-quality headset microphone.
2. You … dictate text directly onto your word processor or e-mail program.
3. With many voice-recognition programs, the user … first train the software to recognize individual pronunciations.
4. Speech-recognition software … help children with special educational needs.
5. In a few years’ time, a lot of people … use their voices to interact with computers.
32. Listen to the conversation between Vicky Cameron, an Information Technology (IT) lecturer, and one of her students, and complete these notes.
- The technology used in scanners is similar to that used in
- A laser beam reads the image in
- The image is then
- Text is scanned with
- Flatbed scanners can scan
- Slide scanners are used to scan
- Hand-held scanners are used for capturing
Voice input
33. Study this picture. It shows how voice input works. Label the steps in the process with these captions (a-e).
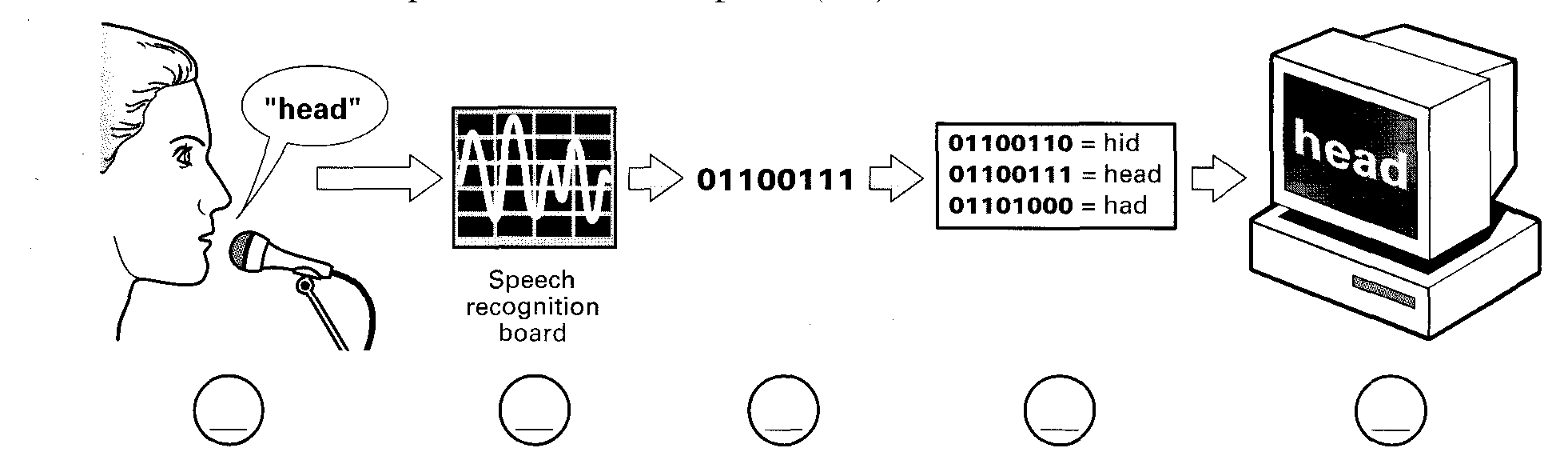
a. The computer compares the binary code with its stored vocabulary.
b. The user says a word into a microphone.
c. The screen displays the correct word.
d. The speech recognition board converts the signals into binary numbers.
e. The microphone converts the word from audio signals into electrical signals.
Now listen to the recording to check your answer.
Oral Practice
34. Study this description and answer these questions.
1. How do digital cameras differ from conventional cameras?
2. How do they work?
3. What are their advantages and disadvantages compared to conventional cameras?
Digital cameras store images on memory cards so pictures can be transferred easily to a computer.
A lens focuses the image on to a CCD unit or Charge-Coupled Device where the film would normally be.
So you can aim the camera accurately, there is an optical viewfinder.
So you can play back the images and decide which to keep and which to re-shoot, the image is passed to a small LCD screen on the back of the camera.
35. Match these symbols with their names to complete this table.
|
Symbol
|
Name
|
Symbol
|
Name
|
|
|
colon
|
|
forward slash
|
|
|
tilde
|
|
at
|
|
|
underscore
|
|
dot, stop
|
36. Work in pairs, A and B. Read these e-mail and website addresses to your partner. Copy down the addresses your partner reads to you.
1. ___________________________
2. ___________________________
3. ___________________________
4. ___________________________
5. ___________________________
Student A - Your conversion is on page 139.
Student B - Your conversion is on page 140.
37. Match each device (1-7) with its use (a-g).
|
Device
|
Use
|
|
1. joystick
2. lightpen
3. scanner
4. digital camera
5. mouse
6. keyboard
7. microphone
|
a) draw pictures on to a computer screen
b) copy documents
c) input sound
d) input text
e) select from a menu
f) move the cursor rapidly
g) produce photos without film
|
38. Study this list of needs. In groups, decide which input device is best for:
1. controlling fast-moving objects in a game;
2. reading the price of goods in a shop;
3. making copies of a page of text and graphics;
4. storing sounds on a computer;
5. producing pictures of people and places for storing in a computer;
6. controlling a computer using speech;
7. typing text into a computer;
8. inputting printed graphics;
9. creating drawings;
10. recording sound;
11. storing programs and data;
12. making choices on a screen in a public information terminal;
13. recording moving images;
14. recording a book loan in a library;
15. backing up large quantities of data.
Writing Practice
39. With the help of this table, write a brief description of a keyboard. The first paragraph is done for you.
|
Section
|
Location
|
Main keys
|
Main function
|
|
Main keyboard
|
centre
|
each letter digits 0-9 punctuation common symbols
|
input all kinds of data
|
|
Function keys
|
top
|
F1-F12
|
not fixed can program them
|
|
Editing keys
|
right
|
cursor keys insert, delete
|
control cursor
|
|
Numeric keypad
|
far right
|
digits 0-9 mathematical operations
|
input numerical data
|
Most keyboards have four sections. The main keyboard has keys for each letter and the digits 0 to 9. It also has keys for punctuation and other common symbols. It is used for inputting all kinds of data.
40. Read this passage about a computer mouse. Fill in the gaps with verbs from the list.
|
click
|
double-click
|
drag
|
grab
|
select
|
move
|
control
|
A mouse allows you to (1) …. the cursor and move around the screen very quickly. Making the same movements with the arrow keys on the keyboard would take much longer. As you (2) … the mouse on your desk, the pointer on the screen moves in the same direction. The pointer usually looks like an I-bar, an arrow or a pointing hand, depending on what you are doing.
A mouse has one or more buttons to communicate with the computer. For example, if you want to place the insertion point or choose a menu option, you just (3) … (press and release) on the mouse button, and the option is chosen.
The mouse is used to (4) … text and items on the screen. You can highlight text to be deleted, or you can select an item from a check-box or questionnaire.
The mouse is widely used in graphics and design. When you want to move an image, you position the pointer on the object you want to move, press the mouse button, and (5) … the image to a new location on the screen. Similarly, the mouse is used to change the shape of a graphic object. For example, if you want to convert a square into a rectangle, you (6) … one corner of the square and stretch it into a rectangle.
The mouse is also used to start a program or open a document: you put the pointer on the file name and (7) … on the name - that is, you rapidly press and release the mouse button twice.
Input devices
41. Each text describes one of these devices: tracker ball, joystick, lightpen, and scanner. Identify the device each text describes. Write your answers in this table. Then compare your answers with other students.
|
Text
|
Device
|
|
1.
2.
3.
4.
|
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
|
There is another input device you can connect to a computer system. _ is able to move in eight directions. ___ s are mostly used in computer games to control the way a picture on the screen moves. Sometimes two ___ s are connected to a computer so two people can play the game at the same time.
A ___ works in exactly the same way as a mouse, except that the ball is on top. The user rolls the ball around with her hand to operate it. If you use a ___, you don't need any extra space on your desk to move it around (like you do with a mouse). ___ s are often used on small portable computers and on some video game machines.
A ___ can be used to draw pictures directly on to a computer screen or to read the pattern on a barcode. A ___ that can read barcodes detects the difference between the light reflected from a black barcode line and its lighter background.
Using a ___, you can input printed drawings, photographs, or text directly into a computer. A ___ works like a photocopier - a light is shone on the material and the ___ detects the reflected light. You can use a ___ with optical character recognition (OCR) software to input the scanned text into a word processing package.
42. What are the potential benefits of using barcode scanners in these areas? Write down a paragraph for each one.
Example - In boutiques, barcode scanners can help the shop assistant to read the price labels of articles (clothes, cosmetics, hats, etc.). The data is also sent to the computer's inventory records.
In bookshops, ...
In pharmacies, ...
UNIT 9
OUTPUT HARDWARE
This unit introduces the various output hardware components. By the end of this unit you should be better at reading for specific information, understanding printer advertisements, listening and note-giving. You should be able to describe the function of a device, the various types of display monitors, printers and the technologies on which they are based.
Terms Concepts
The purpose of output hardware is to provide the user with the means to view information produced by the computer system. Information is output in either hardcopy or softcopy form. Hardcopy output can be held in your hand, such as paper with text (word or numbers) or graphics printed on it. Softcopy output is displayed on a monitor.
Monitor is a component with a display screen for viewing computer data, television programs, etc. The display image on a monitor screen can be thought of as being made up of a series dots. Printer is a computer output device that produces a paper copy of data or graphics. Colour printers are available but sometimes printing is done using a mono printer that prints only in black. The types of printers are inkjet, laser, mono, dye sublimation and etc. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Language Material
1. Consult a dictionary and practise the pronunciation of the following words:
fairly, response, meaningful, however, due, horizontally, vertically, unsteady, fatigue, visualized, intensity, inherently, polarizing, mixture, available, relatively, radiation, increasingly, to curve, distortion, through, instead, multiple, to measure, preliminary, nevertheless, alternative, although, description, geometrical, arcs, version, subroutines.
2. Learn by heart the following vocabulary:
|
angle
arc
charge
distortion
grid
hammer
phosphor
pin
sub-routine (SUB)
tilt
inherent
built-in
crisp
stylish
wide-carriage
|
угол
дуга
заряд
искажение, несовпадение
сетка, координатная сетка
молоточек (в контактных принтерах)
люминофор
игла; контакт, штырёк; вывод
подпрограмма
наклон
присущий, неотъемлемый
встроенный
твердый, четкий, рассыпчатый
стильный, модный, шикарный
с широкой кареткой
|
to adjust
to block
to curve
to define
to edit
to emit
to emulate
to enlarge
to evolve
to mount
to place
to range
to satisfy
instead
although
|
приспосабливать, регулировать
делить на блоки
гнуть, изгибать
определять, обозначать
монтировать, редактировать
излучать, испускать
соревноваться, подражать
увеличивать, укрупнять
развиваться
устанавливать, монтировать
помещать, класть
колебаться в известных пределах
удовлетворять, соответствовать
вместо
хотя
|
3. Match the English word combinations in the left-hand column with the Russian equivalents in the right-hand column:
- aperture grill pitch
- refresh rate
- cathode ray tube
- liquid-crystal display (LCD)
- continuous sequence
- electron gun
- high-resolution image
- desktop publishing program
- stereo-speaker
- headphone
- hard copy
- bit-mapped font
- scalable font
|
- электронно-лучевая трубка (ЭЛТ)
- жидкокристаллический монитор
- растровый шрифт
- масштабируемый шрифт
- максимальная частота развертки
- наушник
- твердая (документальная) копия
- шаг в апертурной решетке
- непрерывная последовательность
- электронная пушка
- изображение высокого разрешения
- настольная издательская система
- стереосистема
|
4. Read the expressions; translate them in writing and learn by heart:
|
one at a time
at the same time
USB-port
printer port
serial port
parallel port
engineering drawing
object-oriented
Raster Image Processor
software tool
|
impact
non-impact
dot-matrix printer
daisywheel
ball printer
line printer
band printer
chain printer
drum printer
ink-jet printer
|
solid-ink printer
terminal printer
electrostatic printer
light diode printer
bubble-jet printer
laser printer
imagesetter
duplex printer
plotter
flatbed plotter
|
5. Find in each line word that is given at the beginning:
|
наклон
|
a) headphone
|
b) tilt
|
c) imagesetter
|
d) arc
|
|
заряд
|
a) distortion
|
b) font
|
c) charge
|
d) angle
|
|
координатная сетка
|
a) plotter
|
b) pitch
|
c) grid
|
d) charge
|
|
последовательный порт
|
a) serial port
|
b) pin
|
c) phosphor
|
d) parallel port
|
|
ленточный принтер
|
a) duplex printer
|
b) ball printer
|
c) band printer
|
d) laser printer
|
|
приспосабливать
|
a) to enlarge
|
b) to evolve
|
c) to adjust
|
d) to mount
|
|
соревноваться
|
a) to place
|
b) to range
|
c) to satisfy
|
d) to emulate
|
|
развиваться
|
a) to evolve
|
b) to block
|
c) to curve
|
d) to define
|
|
бесконтактный
|
a) non-impact
|
b) rate
|
c) impact
|
d) crisp
|
|
хотя
|
a) instead
|
b) although
|
c) over
|
d) among
|
6. A great many words in English have more than one meaning.
|
application
|
заявление, прошение
|
His application to the court for bail has been refused. Address your application to the Personnel Manager.
|
|
|
применение, употребление
|
The invention would have wide application /a wide range of applications in industry.
|
|
|
приложение
|
The spreadsheet application is second only to word processing in terms of popularity.
|
|
|
прикладывание
|
It took three applications of paint to cover the graffiti.
|
|
|
прилежание, старание
|
Success as a writer demands great application.
|
|
|
|
|
|
socket
|
гнездо, углубление
|
The bulb should just screw into the socket.
|
|
|
сокет технология
|
Does your company use socket-technology for computer connecting in network?
|
|
|
патрон, розетка
|
Is the cable long enough to reach the socket?
|
7. Consider the grammar:
to look at – смотреть на ч.-л., посмотреть, проверить
Why are you looking at me like that? She looked at me and smiled. Don’t look now, but there’s someone staring at you!
to stare at – пристально смотреть, глазеть, таращиться на ч.-л., к.-л.
I stared blankly at the paper in front of me.
to glance at – мельком взглянуть на ч.-л., к.-л.
She glanced at her watch. I only had time to glance at the newspapers.
to laugh at – смеяться над к.-л., ч.-л.
You never laugh at my jokes! Jenny had to laugh at her own foolishness.
to aim at – целиться, намериваться
The government is aiming at a 50% reduction in unemployment. They’re aiming at training everybody by the end of the year.
to point at – указывать на ч.-л., к.-л.
Don’t point that knife at me. It’s dangerous. “What’s your name?” he asked, pointing at the child with his pen.
8. Match the synonyms:
permanent – durable, lasting, constant, continual, stable, usual, general.
to involve – to signify, to embarrass, to contain, to include, to denote, to mean.
to place – to establish, to settle, to fix, to put, to get, to arrange, to allocate, to install.
smart – clever, bright, intelligent, keen, sharp, knowing.
stylish – modern, fashionable, brand-new, up-to-date, new-fashioned, fresh.
to modify – to alter, to soften, to qualify, to vary, to lower, to change, to convert, to transform.
9. Match the antonyms:
to adjust – to disarrange, to confuse, to mix, to unfit, to disorganize, to disorder.
cheap – dear, costly, valuable, expensive, priceless, worthy, precious, inestimable.
to enlarge – to diminish, to lessen, to reduce, to decrease, to lower, to shorten.
distortion – coincidence, standard, norm, rate, quota.
10. Find in each line the word – synonym to the first word:
|
subroutine
|
a) arc
|
b) charge
|
c) procedure
|
d) distortion
|
|
fatigue
|
a) crisp
|
b) weariness
|
c) flicker
|
d) plotter
|
|
to enlarge
|
a) to increase
|
b) to evolve
|
c) to place
|
d) to mount
|
|
continuous
|
a) parallel
|
b) compatible
|
c) common
|
d) permanent
|
|
inherent
|
a) built-in
|
b) peculiar
|
c) stylish
|
d) fashionable
|
|
monitor
|
a) font
|
b) distortion
|
c) screen
|
d) angle
|
11. Find in each line the word – antonym to the first word:
|
to emit
|
a) to evolve
|
b) to increase
|
c) to enlarge
|
d) to keep in
|
|
built-in
|
a) external
|
b) inherent
|
c) crisp
|
d) wide-carriage
|
|
stylish
|
a) common
|
b) out-of-fashion
|
c) permanent
|
d) compatible
|
|
crisp
|
a) inherent
|
b) parallel
|
c) soft
|
d) impact
|
12. Name all possible word expressions with following verbs and nouns:
|
printer
|
beam
|
impact
|
dot-matrix
|
|
gun
|
solid-ink
|
non-impact
|
to install
|
|
electron
|
CRT
|
monitor
|
terminal
|
|
bubble-jet
|
TFT
|
light diode
|
to plug
|
|
to mount
|
electrostatic
|
stylish
|
LCD
|
13. Give definitions to the following using the vocabulary:
Printer, monitor, application, dot-matrix printer, hub, laser printer, peripheral, resolution, TFT display.
14. Think about a typical workstation. Match the items (1-7) to the guidelines (a-g).
|
1. keyboard
2. monitor screen
|
3. lamp
4. copyholder
5. chair
|
6. footrest
7. printer
|
a) This should be adjustable and provide good back support.
b) This should be more than a metre away from you and as quiet as possible.
c) Keep this level with your eyes. Don’t have it level with the desk. Make sure it is flicker-free, and that you can read everything easily. Avoid any glare from the window.
d) Use this if your feet do not rest flat on the floor.
e) Make sure these lights your work and not the screen.
f) Don’t get a stiff neck. Use this when you enter a lot of data.
g) Keep this directly in front of you and within easy reach.
15. What’s the meaning of these abbreviations?
|
CRT
USB
|
LCD
VDU
|
TV
PDL
|
PC
PCL
|
TFT
VGA
|
16. Describe the monitor of your computer to another student. Use these questions to help you.
What type of monitor do you have at home?
Does it have a cathode ray tube or a flat LCD screen?
What size is the screen?
How can you change the picture using the controls?
Does it produce a high quality image?
What refresh rate does your monitor have?
17. Solve the clues by using a term from the list. Then complete the puzzle to find the hidden phrase.
The monitor
|
pixels
filter
|
card
resolution
|
flicker
display
|
beam
hertz
|
refresh
contrast
|
|
|
|
1.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Screens with a low … rate can produce eye fatigue.
- Pictures which use a lot of pixels are high … .
- Inside the tube there is an electron … which scans the screen and turns on or off the pixels.
- Some monitors have an anti-glare … to reduce glare.
- A monitor is also called a visual … unit.
- The … on a CRT monitor is tiring on the eyes.
- A video … allows graphics to be displayed on your computer.
- Characters and pictures are made up of dots, also called … .
- This monitor has a 75 … refresh rate.
- Brightness and … buttons let you alter the image.
18. Word Bingo
Look at the list of the words given below. Write down any five words. The teacher is going to read the definitions of all the words in random order. If you hear the definition of one of the words you have chosen, cross it out. The first student to cross out all the words he or she has chosen calls out “Bingo” and reads the words to prove his/her claim.
Words: application, barcode reader, cathode ray tube, compatible, dot-matrix printer, hub, laser printer, peripheral, resolution, speaker, TFT display, VDU.
Word-building
Model 20
mis- + основа глагола глагол со значением неправильно, неверно
|
to hear – слышать
to inform – информировать
to interpret – толковать
to lead – вести
|
to mishear – ослышаться
to misinform – неправильно информировать
to misinterpret – неверно истолковывать
to mislead – вводить в заблуждение
|
Model 21
Основа существительного или прилагательного + -ize (ise) глагол
|
character – характер
crystal – кристалл
sympathy – сочувствие
critic – критик
|
to characterize – характеризовать
to crystallize – кристаллизовать
to sympathize – сочувствовать
to criticize – критиковать
|
19. Make new words using the models 20-21.
|
to quote
vapour
to represent
fraternal
to spend
formal
|
to understand
oxygen
to represent
general
to trust
global
|
to play
real
to rule
mobile
to understand
hypothesis
|
to print
magnet
to pronounce
plagiary
to use
individual
|
Reading Practice
Text 9A
20. Read the text and try to guess the meaning of any new words in the box below. Refer to the Glossary if necessary.
|
dot
to scan
|
pixel
hertz
|
display
flicker
|
resolution
to visualize
|
cathode ray tube
refresh rate
|
electron beam
bit-mapped
|
Output devices have evolved to give humans new ways to interact with information stored by the computer. Early on, most of the data that was being managed by the computer was in the form of numbers. The only output device was the printer, and that served the computer users of that period fairly well. But as more humans began to use computers, they wanted a faster, more understandable response from the computer. And as they began to use the computer for purposes other than math calculations, they found it more meaningful to input data into the computer using the keyboard and to see the results of their typing on a display screen. This led to a more direct input and output sequence. However, the types of output devices we use have until recently changed very little. The computer’s display monitor and printer still represent the primary methods of getting information from the computer. But the design of these two devices has been rapidly evolving due to ever-changing trends in the types of data we use.
The monitor displays text characters and graphics. It allows to see the results of the work going on inside your system unit. The characters and pictures that we see on the screen are made up of dots, also called picture elements (pixels). The sharpness of the picture depends on the number and size of these pixels. The total number of pixels in which the display is divided both horizontally and vertically is known as the resolution. The more pixels, the sharper is the image. Typical resolutions are from 640x480 till 1,600x1,200 pixels.
The cathode ray tube of the monitor is very similar to that of a TV set. Inside the tube there is an electron beam which creates a visible pattern on the display screen by activating (lighting up) the phosphor dots on the screen. The beam begins in the top left corner, and scans the screen from left to right in a continuous sequence, similar to the movement of our eyes when we read, but much faster. This sequence is repeated 50, 70 or 85 times per second, depending on the system. If the rate of this repetition is low, we can perceive a flickering, unsteady screen, which can cause eye fatigue. However, a fast-moving 75 Hz “refresh rate” eliminates this annoying flicker.
On colour displays, there are three electron guns at the back of the monitor's tube. Each gun shoots out a beam of electrons for each of the primary colours: red, green and blue. These electrons strike the inside of the screen which is coated with phosphors that glow when struck by electrons. Three different phosphor materials are used - one each for red, green and blue. To create different colours, the intensity of each of the three electron beams is varied.
The monitor is controlled by a separate circuit board, known as the display adaptor, which plugs into the motherboard of the computer. Different boards drive different types of displays. For example, the VGA (video graphics array) card has become a standard for colour monitors.
Now flat-screen monitors are fashionable. They are inherently flat, and therefore require less space. In addition, they give crisp, clear images and eliminate screen flicker. Portable computers use a flat liquid-crystal display (LCD) instead of a picture tube. An LCD uses a grid of crystals and polarizing filters to show the image. The crystals block the light in different amounts to generate the dots in the image. Because of the LCD's flat screen, images can be quite clear. Although colour LCD monitors require more power than the monochrome versions, monitors using this technology do not require nearly as much electric current as monitors that are based on the CRT.
In a gas plasma display, neon gas is emitted in the screen. When current is applied across the tiny area that contains the gas, it glows. Different mixtures of the gas can produce somewhat different colours (usually a reddish-orange colour), but all the characters and images on the screen are displayed only in one colour. This results in high-resolution images that are brighter than those displayed using a CRT monitor, but there is not a lot of contrast on the screen. Although this technology requires more power than the other flat-screen monitors, generally it does not require as much current as LCD-based monitors.
These new output capabilities have led to a number of new computer applications such as desktop publishing (DTP) programs (used to display and print composed pages for printing), presentation graphics programs (used to turn numbers into charts and graphs), and computer-aided design (CAD) programs (used to create and print engineering drawings and blueprints). A variety of new paint and draw programs are now available for use with PCs. These programs include software tools that can be used to create and edit on-screen pictures.
21. Read the text again and answer these questions.
- According to the writer, what is the importance of “pixel resolution”?
- Which unit of frequency is used to measure the refresh rate of a monitor?
- In the writer’ opinion, why can a low refresh rate produce eye fatigue?
- What substance is hit by electrons in a monitor?
- What is the standard display system for many PCs?
- What does “LCD” stand for? What type of computers use LCD displays?
- A computer system includes devices that are used to get information to transfer information out of the computer in a form usable by humans. List some of most common output devices.
- Describe the changes in today’s computer display monitors and discuss the evolving types of display technologies found in today’s ever smaller computers.
Text 9B
FLAT SCREENS
22. Read the text and then decide whether these statements are true or false.
Have you noticed how much your computer screen flickers? This may be because your computer monitor uses CRT technology. This kind of technology offers colour and high-resolution pictures for relatively little money but the monitors are large, use a lot of energy, can flicker and emit electromagnetic radiation.
In recent years flat screens have become increasingly popular. Users talk of benefits such as more desk space, how easy they are to adjust for tilt and height, clearer images and the total elimination of screen flicker. It’s like having a different PC, a new window on the world.
Most flat screens are based on LCD technology which has a lot of benefits over CRT technology. Among them:
- LCDs are inherently flat, CRT monitors are not, so LCDs require much less space;
- LCDs use less power than CRTs;
- LCDs are distortion-free while typical CRTs are curved, which may cause image distortion;
- most LCD displays use a TFT system offering a wider angle of vision and high-quality images.
But there is one major drawback to flat screens: their cost. They are expensive compared with CRT monitors. Flat screens usually include built-in stereo speakers, headphone connection, and a USB port. Some models can also be removed from the stand and mounted on the wall. They come with stylish designs for a variety of applications. LCDs range from small-size PC screens and TVs to large-screen projectors.
- Most computers still use CRT monitors.
- Typical CRT-based displays occupy less space than LCD displays.
- Liquid-crystal displays are curved.
- Flat LCD screens are becoming very popular.
- LCD technology consumes less power than CRT technology.
- Flat screens are cheaper than CRT monitors.
- Users of flat-screen monitors can't adjust the angle of vision.
- Monitor is a component with a display screen for viewing computer data, television programs, etc.
23. Describe to your partner the characteristics of the monitor you would like to use. Give reasons.
How to read a monitor advertisement
24. Study this text about monitors. Then decide if each statement is true or false. Give reasons for your answers.
1. Twenty-two inches is a common monitor size.
2. A dot pitch of 0.31 mm is better than one of 0.25 mm.
3. A maximum resolution of 1,600x1,200 is better than 1,280x1,024.
4. A refresh rate of 85Hz is better than one of 75Hz.
5. A 17-inch monitor is 17 inches wide.
6. You can change the picture using controls on the screen.
7. The price of a monitor depends only on the size.
8. The monitor uses less power because of the Power-Saver feature.
|
210
- 17-inch (43.2cm)Trinitron monitor
- 0.25mm aperture grill pitch
- Maximum resolution: 1,280x1,024, 85Hz
- TCO-99, MPR-II,TUV Ergonomics approved
- Power-Saver TM
- On-screen menu
|
Price
The price mainly depends on the screen size. Common monitor sizes are 15-inch, 17-inch, 19-inch, and 21-inch.The price also depends on aperture grill pitch, resolution, and the number of controls.
Screen size
The size of the screen is the diagonal distance from one corner to another. The actual area for images is smaller than this.
Aperture grill pitch
This controls the space between the dots which make up the image. The less space between the dots, the better the display. Most monitors offer 0.25mm dot pitch but some go as high as 0.31 mm or as low as 0.22mm.
Maximum resolution
The quality of the display depends on the number of dots which make up the image. The more dots, the better the display.
Refresh rate
The monitor refreshes the image on the screen all the time. The faster this happens, the less the screen flickers. You should have a refresh rate of at least 72 Hz.
Safety standards
These are international standards to control harmful signals.
Power-saving feature
The power the monitor uses automatically reduces when it is not in use.
On-screen menu
Digital controls on the screen allow you to adjust the image.
Listening Practice
25. Tony Clark, a lecturer in computer ergonomics, is talking to some students about health and safety in a computer classroom. Listen and complete the sentences below.
- You should get a good chair, one that
- Position the keyboard
- Position the monitor eye level, or just
- A tilt-and-swivel display lets you
- You should stay an arm's length away from
- If you work in a room with a lot of computers, sit
26. Read the text below and label these types of printers.
|

The resolution depends on the number of pins (9,24 or 48)
1�. ……………………………….
|

The quality (resolution) of the images ranges from 300 to 1,200 dots per inch (dpi)
2. ……………………………………
|
|

Provides high quality output - a resolution of 600/2,400 (dpi)
3. ………………………
|

Provides the highest resolution - more than 3,000 dpi
4. …………………………
|
Provides high quality for linework (like lines and curves)
5. …………………………
|
27. What’s the meaning of these abbreviations?
Text 9 C
TYPES OF PRINTERS
Computer printers have also evolved as computer users sought better printed representations of what they saw on the display screen. Data that is printed out on paper using a printer controlled by a computer is known as output, or hard copy.
The printer is connected by cable to the PC through a special socket on the computer referred to as a printer port. The computer, under the control of software, sends coded signals to the printer telling it what to print. The two types of ports commonly used with today's printers are referred to as serial or parallel, depending on how signals are sent out. Using a serial port, signals are sent out one at a time along one wire inside the printer cable. Although these signals can be sent out very fast, the one-at-a-time serial method can slow down the printing process. Printing using a parallel port can sometimes be faster because multiple signals are sent out all at the same time along multiple wires inside the cable.
Today, there are many different types of computer printers in use, but they can generally be categorized as impact or nonimpact. The most common type of impact desktop printer are the matrix printer, daisywheel, ball and line printer. Nonimpact printers produce an image on paper without using a striking device. They are ink-jet, solid-ink, terminal, electrostatic and light diode printer, bubble-jet, laser, imagesetter, duplex, plotter.
Impact Printers use varying technologies to place ink on paper by striking through an inked ribbon. A number of different types of high-speed printers have been developed to satisfy the high-volume needs of large computer systems. These wide-carriage printers are known as line printers because they print characters one line at a time. The most common types of line printers in use today are band printers, chain printers, and drum printers. Each uses a slightly different technology to produce characters, but all are very fast because each character on the line has its own print hammer which allows for 132 printing positions. The output of these high-speed printers is too fast to be measured in characters per second. Instead, they are measured in lines per minute. Some of these printers can produce over 3,000 lines of type per minute (almost 80,000 words per minute).
Dot-matrix printers use pins to print the dots required to shape a character. They print text and graphics and nowadays some of them can print up to 500 characters per second (cps); however, they produce relatively low resolution output - 72 or 144 dots per inch. This level of quality, while suitable for preliminary drafts, is not recommended for reports or books that have a wide audience. They are slower than laser printers but much cheaper.
Nonimpact Printers use a number of different technologies to produce an image on paper without striking through an inked ribbon.
Laser printers have become the most popular nonimpact type of printer. Laser printers produce output at great speed and with a very high resolution of 600/2,400 dpi. They scan the image with a laser beam and transfer it to paper with a special ink powder. They are constantly being improved. In terms of speed and image quality they are preferred by experts for different reasons: they have a wider range of scalable fonts, they can emulate different language systems, they can produce graphics, and they have many other advantages.
Another nonimpact printer that is often used with both desktop and portable PCs is the ink-jet printer. This type is like the dot-matrix printer in that characters are developed one dot at a time. However, instead of producing a dot by striking through an inked ribbon, the ink-jet printer creates each dot using a tiny ink jet to place a droplet of ink on the paper. It operates by projecting small ink droplets onto paper to form the required image. This type of printer is quite fast, silent and not as expensive as a laser printer. Nevertheless, you can expect high quality results because there are some ink-jet printers on the market with a resolution of 720 dpi. Bubble-jet printers work the same way.
We must not forget to mention thermal printers. They use heat, a special kind of paper and electrosensitive methods. They are silent and considered to be inexpensive. However, some colour models that emulate HP plotters cost too much to be included in the same category.
Imagesetters can be regarded as an attractive alternative. They produce very high-resolution output (up to 3,540 dpi) on paper or microfilm. In addition, they are extremely fast. They are used in desktop publishing. Although they produce the highest quality output, they have one important drawback: they are too expensive for homes or small offices.
Finally, plotters are a special kind of printer. Plotters use ink and fine pens to produce graphics output in black and white or colour on paper of varying sizes. Most plotters produce images on paper using coloured pens. They are used for construction plans, engineering drawings and other technical illustrations. A flatbed plotter uses drawing arms to draw the image on paper rolled out onto a flat surface. In a drum plotter, the paper is rotated on a drum as the drawing arm is lowered to the paper’s surface and moved left and right to produce the image. Electrostatic plotters do not use drawing pens. These plotters produce graphics by applying an electrostatic charge to rolls of special paper. Although they are generally more expensive, electrostatic plotters are faster than plotters that use drawing pens, and they produce higher-quality output.
There are advantages and disadvantages to each type of printer. The ink-jet printer prints rapidly and quietly, but it cannot print several copies of an original document on carbon paper forms. If many copies are needed, then the ink-jet printer must print each copy individually. A thermo-electric printer can be very inexpensive to manufacture, but it requires special paper that is quite expensive. Band and chain printers print rapidly and can print several carbon-copies at the same time as the original, but they are noisy and need repairs more often than some of the newer printing devices because they have matfy mechanical parts. Microfilm and microfiche are easy to store, but a magnifying reader is needed to read them. With these different printing methods available, a computer user must determine exactly what his printing needs are before he decides what type of printer to use.
28. Read the text again and complete this table with the most relevant information. Then compare your notes with a partner.
|
Type of printer
|
Technical specifications and other features
|
|
Dot-matrix
Ink-jet
Laser
Thermal
Imagesetter
Plotter
|
|
29. Read the advertisements for printers below, and then, with your partner, answer the questions. See who in your group/class can finish first.
- How many laser printers are advertised here?
- Is there a printer that operates by spraying ink droplets onto paper?
- Which laser printer offers the highest resolution, or output quality?
- Which printer is the most expensive?
- Which one would you recommend to a friend who does not have much money?
- Which one has more internal fonts?
- A printer language is software that tells printers how to print a document. Can you find two types of laser printer languages?
- What connectivity features are offered by the Turbo Laser Writer QR?
- A very common feature in advertisements is the use of abbreviations. Find the abbreviations for these expressions: dots per inch, characters per second, pages per minute, small computer system interface and liquid-crystal display.
|
Workgroup laser printer. 15 pages per minute. 1,200 dpi for graphics. 36 MB of RAM. Includes Adobe PostScript and Hewlett Packard PCL printer languages. 75 resident fonts.
Connectivity: one bi-directional Parallel
port, one LocalTalk port, and one
Ethernet port for networks.
12 month warranty.
|
Stylus Dot-matrix Printer
Dot-matrix printer with 24 pins. Prints text and graphics. 450 cps. Compatible special interface. Free unlimited hotline support for our customers. One year on-site maintenance.
|
179
|
|
Colour PostScript Printer
Colour printer 40. Adobe Postscript fonts. 36 MB RAM with a SCSI Interface for an optional 20 MB hard disk. Parallel, serial and AppleTalk interfaces. HP plotter emulation. Thermal printing system. 30-day money-back guarantee and 1 year's on-site parts and labour.
2,249
|
Crystal Laser Printer II
14 pages per minute. 20 MB RAM
Two 200 sheet selectable input trays.
lcd display. 80 internal scalable fonts.
A resolution of 2,400 dpi.
Comes with PostScript language
and PCL (printer control language).
Telephone hotline support.
|
|
|
Micro Laser XT
|
|
|
|
Personal laser printer. 5 pages per minute. 4 MB RAM expandable to 64 MB. Parallel interface. 200 sheet input tray. 35 resident fonts. One-year on-site maintenance. Prints on a wide range of materials and sizes.
|
|
Stunning Plug & Play colour printer. Brilliant photo quality (up to 720 dpi) and fast-drying ink. Produces 8 pages per minute in plain text and 4 ppm in colour. 150 page paper tray. Fast, friendly service.
Ј210
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
649
|
30. Look at the advertisements on this page again and compare the printers. Talk about their: speed, memory, fonts, emulations, resolution, service, price, noise. Use adjectives from the box below.
|
fast
expensive
adaptable
|
slow
easy
expandable
|
high/low quality
difficult
compatible with
|
noisy
simple
cheap
|
quiet
powerful
reliable
|
Text 9D
PRINTER LANGUAGES
31. These statements are all false. Read the text and correct them.
- HP printers do not understand the PCL language.
- PostScript was created in the late 1980s.
- Scalable fonts cannot be enlarged or reduced.
- The “script” of a PostScript file contains the sub-routines used to form different graphic elements.
- PostScript is not understood by imagesetters.
- PostScript doesn't support audio and video formats.
32. Match the terms (1-5) with the correct definitions (a-e).
|
1. printer language
|
a) device which converts PostScript into images or text that can be printed by an imagesetter;
|
|
2. scalable font
|
b) language that describes how to print the text and images on each page;
|
|
3. emulate
|
c) to make one printer act in the same way as another;
|
|
4. imagesetter
|
d) system that can produce characters of any size;
|
|
5. Raster Image Processor
|
e) type of printer that generates output at very high resolution, on paper or film.
|
Computers use a page description language or PDL to describe the layout and contents of a printed page. The best-known PDLs are Adobe PostScript and Hewlett Packard PCL (Printer Control Language), both of which are used to control laser printers. For dot-matrix printers, a common language is the Epson command set.
Both PostScript and modern versions of PCL are object-oriented, meaning that they describe a page in terms of geometrical objects such as lines, arcs, and circles.
PCL (Printer Control Language)
This language was developed by Hewlett Packard and is used in many of their laser and ink-jet printers (e.g. LaserJets and DeskJets). The latest versions support a scalable font technology called Intellifont.
The representation of the font defines the shape (or outline) of each character. The scalable font can then enlarge or reduce the character to any size, without distortions.
Other manufacturers design their printers so that they understand PCL, making them able to emulate HP printers. In this way, their printers are HP-compatible.
PostScript
PostScript was created by Adobe Systems Inc. in 1982 as a PDL for laser printers and imagesetters. Like PCL, PostScript works in vectorial format, which means that it stores graphics not as images made up of dots but as geometric descriptions. This allows text and graphics to be modified with no loss of quality.
A PostScript file consists of two main parts: the “prolog”, which contains a set of sub-routines used to form different graphic elements (squares, curves, etc.), and the “script” which contains the elements introduced by the user. The script calls up the sub-routines stored in the prolog and adds the parameters: for example, if you have drawn a square of 10x5 cm, the script calls up the sub-routine square and specifies the values 10x5.
PostScript is device-independent, which means that it can speak to different output devices (printers, imagesetters, film recorders) and adjust the quality to the highest capability of the devices. In imagesetters, the hardware that interprets the code is called Raster Image Processor.
Drawing programs such as Illustrator, Freehand, or CorelDraw produce pictures drawn in PostScript directly. PostScript has support for sound, video and other formats: you can mix scanned images, specify halftone screens and introduce any number of effects. In fact, the only barrier is your imagination.
33. Look back at the text to find out what the underlined words refer to.
- ..., both of which are used to control laser printers,
- ... used in many of their laser and ink-jet printers
- ... it stores graphics not as ...
- This allows text and graphics to be modified ...
- ... and the “script” which contains the elements introduced by the user,
- ..., the hardware that interprets the code is called Raster Image Processor,
- Drawing programs such as Illustrator, Freehand, or CorelDraw ...
Listening Practice
Printers
34. Work in groups of three: A, B, and C. You are going to hear about three kinds of printer. Note down what the speaker says about one type only as your teacher directs. Use the table below.
|
Type
|
Print quality
|
Speed
|
Running costs
|
Noise level
|
Price
|
Colour
|
|
Inkjet
Mono laser
Dye sublimation
|
lowest
high
|
slower than laser
slow
|
|
quiet
|
|
yes
|
35. Now exchange information with other students in your group to complete the table for all three kinds of printer. Ask questions like these.
What’s the print quality like?
How fast is it?
Does it cost a lot to run?
How noisy is it?
Is it expensive?
Oral Practice
36. Work in pairs, A and B. Each of you has details of a monitor. Ask your partner about his/her monitor and complete the table below.
Student A - Your monitor details are on page 139.
Student B - Your monitor details are on page 140.
|
Screen size
|
………………………………….
|
|
Aperture grill pitch
|
………………………………….
|
|
Maximum resolution
|
…………………………………
|
|
Refresh rate
|
…………………………………
|
|
Price
|
…………………………………
|
37. Study this flowchart for choosing a printer. Decide which is the best kind of printer for these users.
Someone who needs to:
1. print forms with two parts
2. print high quality black and white copies
3. print a lot of colour photos in a short time
4. print a few copies - colour and speed are not important
5. print a few pages in colour.
To choose a printer YES
NO
YES YES
NO NO
NO YES
38. Study this list of needs. Which type of peripheral would you advise in each case?
- making choices on a screen in a public information terminal;
- printing very high quality text and graphics;
- printing building plan drawings;
- listening to music without disturbing others;
39. Describe to your partner the characteristics of the printer you would like to use. Give reasons.
Writing Practice
40. Fill in the gaps in this comparison of printers.
There are many different types of printer. These include inkjet, mono laser, and dye sublimation printers. Basically, you get what you pay for. The more you pay, the better the printer.
Inkjet printers are the …, but their print … is not as … as the other two types of printer. They are … to run compared to mono laser printers, but are able to print in colour. Inkjets are the … of the three types of printer.
Mono laser printers are … expensive than inkjet printers, but give you a … quality of black and white output. They cannot print in colour, but are the … type of printer and cost the … to run.
Dye sublimation printers are the … expensive type of printer, but their print quality is extremely … . They are … in operation, but are relatively … and very … to run.
41. Write your own comparison of printer types.
|
Type
|
Speed
|
Text Quality
|
Graphics Capability
|
Colour Quality
|
Cost
|
|
Dot-matrix
|
Slow to medium
|
Fair to good
|
Limited
|
Fair if you add a colour option
|
Low
|
|
Ink-Jet
|
Medium to fast
|
Good to excellent
|
Good to excellent
|
Good to Very Good
|
Low to high
|
|
Laser
|
Medium to very fast
|
Excellent
|
Good to excellent
|
Good in colour laser printers
|
Medium to high
|
|
Thermal Transfer
|
Medium to fast
|
Excellent
|
Good to excellent
|
Good to superior
|
Medium to high
|
|
Solid ink
|
Medium to fast
|
Excellent
|
Good to excellent
|
Good
|
Medium to high
|
|
Electro-static
|
Slow to fast
|
Fair to good
|
Fair to good
|
Fair to good
|
Low to high
|
AN ADVERTISEMENT
42. Choose one product from the list below and follow the guided steps to write an advertisement.
Products:
a digital camera
a colour ink-jet printer
a webcam
Write down your notes in these steps.
1. The product we are going to advertise is
It is used: …………………………………………………….
It is aimed at: ………………………………………………...
Its advantages over rival products are: ……………………...
2. We have chosen the following name: ……………………………
3. The most suitable medium for advertising is:
The Internet
Television/Radio
National or local paper
Specialist magazine for computer users
Reasons for this choice: ………………………………………………
Images or atmosphere that could be associated with the product: …
4. The slogan for the product is: ……………………………………….
43. Now use your notes and some persuasive vocabulary to write a complete advertisement.
44. Tables often include abbreviations and technical words that are not easy to understand. Look at this table and the explanation of Monitor A’s specifications.
|
|
Type
|
Size
|
Pixel res.
|
Visual display
|
Refresh rate
|
Tilt-and-swivel
|
Other features
|
|
Monitor A
Compaq TFT 8020
|
Flat-panel LCD
|
18.1"
|
1024 x 768
|
16.7 million colours
|
75 Hz flicker-free
|
|
energy saver mode
|
|
Monitor B
Paintview
|
CRT monitor
|
19"
|
1280 x 1024
|
16.7 million colours
|
85 Hz flicker-free
|
|
anti-glare filter
|
45. The specifications of Superview (Monitor A) may be explained like this:
- This is a flat-panel Liquid Crystal Display.
- The screen size is 18.1 inches (diagonal viewable image size).
- You get a resolution of 1,024 by 768 pixels.
- It offers support for 16.7 million saturated colours.
- This digital display has a 75 hertz refresh rate. It never flickers (the images are bright, sharp, and distortion-free).
- You can change the orientation of the display, adjusting your viewing angle back and forth.
- It has a built-in power feature that saves a lot of energy consumption.
46. Use the example above to help you describe Monitor B.
UNIT 10
TYPES OF SOFTWARE
Unit 10 presents information about the types of computer programs that are used with today’s computers. You will learn not only about user applications, but also about the other two types of software: computer operating systems and programming languages. In this chapter, you will learn about the following topics:
- defining software;
- software types;
- systems software;
- applications software;
- programming software;
- object-oriented programming and authoring;
- programming methods and software design.
Terms Concepts
Computer programs and software are two terms used to refer to the set of instructions used to control the computer.
A computer’s operating system is designed to specifically address the capabilities of the computer’s microprocessor.
Systems software is comprised of a set of programs used to operate the computer itself.
Applications or productivity software is used to perform specific tasks such as writing letters, calculating costs, or maintaining records.
Programming software is used by professional computer programmers to create computer programs. There are four types - machine languages, assembly languages, high-level languages, and nonprocedural fourth-generation languages (4GLs).
New programming methods include natural language approaches and object-oriented programming (OOP), which is based on a concept of “objects” that combine data and procedures.
Language material
1. Consult a dictionary and practise the pronunciation of the following words:
final, system, value, through, to determine, to perform, to punch, sophisticated, widely, though, assembly, compiler, interpreter, therefore, procedural.
2. Learn by heart the following vocabulary:
|
approach
compiler
control
flowchart
ore
regard
general-purpose
internal
peripheral
truly
|
подход, приближение
компилятор, транслятор
управление
блок-схема
руда
отношение
общего назначения
внутренний
периферийный
правдиво, точно
|
to boot
to check
to complete
to conduct
to debug
to direct
to handle
to provide with
to punch
to secure
|
загружать
проверять
совершать, завершать
проводить
исправлять ошибки
управлять, руководить
управлять, обращаться
обеспечивать чем-либо
перфорировать
обеспечивать безопасность
|
3. Match the English word combinations in the left-hand column with the Russian equivalents in the right-hand column:
- low-level language
- system software
- applications software
- programming software
- horizontal application
- vertical application
- procedural language
- query language
- natural language
- object-oriented programming language
- object-oriented language
|
- естественный язык
- язык низкого уровня (ЯНУ)
- системное программирование
- приложение для горизонтального рынка
- язык запросов
- объектно-ориентированный язык
- приложение для вертикального рынка
- процедурный (императивный) язык
- системное программное обеспечение
- прикладное программное обеспечение
- язык объектно-ориентированного проектирования
|
4. Find 10 words about programming.
|
F
|
H
|
C
|
A
|
H
|
B
|
U
|
G
|
J
|
W
|
E
|
|
L
|
R
|
O
|
S
|
J
|
A
|
W
|
A
|
K
|
R
|
E
|
|
O
|
W
|
M
|
D
|
K
|
S
|
E
|
S
|
L
|
D
|
P
|
|
W
|
L
|
P
|
F
|
L
|
I
|
R
|
D
|
O
|
F
|
A
|
|
C
|
Y
|
I
|
G
|
Z
|
C
|
T
|
C
|
M
|
G
|
S
|
|
H
|
D
|
L
|
S
|
X
|
V
|
O
|
F
|
N
|
H
|
C
|
|
A
|
B
|
E
|
H
|
P
|
B
|
Y
|
B
|
G
|
J
|
A
|
|
R
|
K
|
R
|
J
|
C
|
N
|
U
|
G
|
O
|
K
|
L
|
|
T
|
L
|
T
|
Y
|
U
|
I
|
O
|
P
|
V
|
L
|
M
|
|
Q
|
W
|
E
|
D
|
E
|
B
|
G
|
G
|
E
|
R
|
S
|
|
P
|
R
|
O
|
G
|
R
|
M
|
M
|
E
|
R
|
G
|
H
|
5. Note additional meanings for word “current”, “system”.
|
current
|
струя, поток
|
He swam to the shore against a strong current. Birds use warm air currents to help their flight.
|
|
|
течение, ход событий
|
Ministers are worried by this current of anti-government feeling.
|
|
|
ток
|
The block becomes magnetic when the current is switched on.
|
|
|
|
|
|
system
|
система, метод
|
The government has given top priority to reforming the tax system.
|
|
|
система, устройство
|
The system has the ability to run more than one program at the same time. You need a password to get access to the computer system.
|
|
|
сеть
|
I was surfing the system looking for information on Indian music. This budget will have a system expansionary effect on the economy.
|
|
|
организм
|
You have to wait until the drugs have passed out of your system.
|
|
|
мир, вселенная
|
Scientists disagree about how the solar system was created. Scientific findings help explain the origins of our system.
|
6. Consider the grammar:
an increase in – рост, прирост, увеличение, прибавление в ч.-л.
This increase in exports bears testimony to the successes of industry. The sharp increase in crime seems to buttress the argument for more police officers on the street.
a decrease in – уменьшение, понижение, убавление, спад в ч.-л.
There has been some decrease in military spending this year. There was an astounding 20% decrease in sales.
a rise in – повышение, рост, подъем, увеличение в ч.-л.
There has been a sharp rise in the number of people out of work. We are expecting a rise in food prices this month.
a fall in – падение, снижение в ч.-л.
Several factors have been adduced to explain the fall in the birth rate. The government claims that the fall in unemployment is the herald of economic recovery.
7. Match the synonyms:
operation – action, execution, performance, act, process, work, process, proceeding.
model – original, standard, form, design, type, copy, image, shape, form, structure.
to require – to claim, to ask, to demand, to exact, to warn, to need.
to organize – to arrange, to establish, to systematize, to form, to plan, to constitute.
8. Match the antonyms:
activity – inactivity, idleness, sloth, dullness, indolence, sluggishness, immobility, inertia.
report – distortion, secret, reserve, misstatement, understatement, falsification.
system – chaos, disorder, disarrangement, complication, confusion, irregularity.
to know – to doubt, to disbelieve, to discredit, to reject, to mistrust, to misunderstand.
9. Find in each line the translation to the first word:
|
value
|
a) подход
|
b) ценность
|
c) отношение
|
d) транслятор
|
|
customer
|
a) блок-схема
|
b) руда
|
c) покупатель
|
d) управление
|
|
society
|
a) общество
|
b) управление
|
c) приближение
|
d) запрос
|
|
approach
|
a) компилятор
|
b) процедура
|
c) поток
|
d) подход
|
|
therefore
|
a) несмотря на
|
b) поэтому
|
c) вдобавок
|
d) вплоть
|
10. Find in each line the word – synonym to the first word:
|
activity
|
a) task
|
b) interpreter
|
c) purpose
|
d) work
|
|
type
|
a) kind
|
b) design
|
c) tool
|
d) aid
|
|
to direct
|
a) to determine
|
b) to formulate
|
c) to require
|
d) to control
|
|
truly
|
a) exactly
|
b) narrowly
|
c) increasingly
|
d) incredibly
|
11. Find in each line the word – antonym to the first word:
|
variety
|
a) activity
|
b) capacity
|
c) society
|
d) monotony
|
|
system
|
a) disarrangement
|
b) task
|
c) environment
|
d) aspect
|
|
to detect
|
a) to coordinate
|
b) to require
|
c) to provide
|
d) to miss
|
|
to encode
|
a) to act
|
b) to decode
|
c) to edit
|
d) to carry out
|
|
diverse
|
a) internal
|
b) same
|
c) specific
|
d) scientific
|
|
whole
|
a) real
|
b) final
|
c) part
|
d) diverse
|
12. Find in each line noun:
|
1.
|
a) more
|
b) serve
|
c) resource
|
d) dictate
|
e) become
|
|
2.
|
a) formulate
|
b) capacity
|
c) carry
|
d) truly
|
e) therefore
|
|
3.
|
a) widely
|
b) truly
|
c) early
|
d) society
|
e) refer
|
|
4.
|
a) independent
|
b) suited
|
c) different
|
d) even
|
e) environment
|
|
5.
|
a) activity
|
b) understood
|
c) computerized
|
d) scientific
|
e) across
|
|
6.
|
a) developed
|
b) whole
|
c) approach
|
d) regardless
|
e) created
|
13. Word Bingo.
Look at the list of the words given below. Write down any five words. The teacher is going to read the definitions of all the words in random order. If you hear the definition of one of the words you have chosen, cross it out. The first student to cross out all the words he or she has chosen calls out “Bingo” and reads the words to prove his/her claim.
Words: computer programmer, systems software, applications software, and programming software, operating system, machine languages, assembly languages, high-level language, object-oriented programming language, object-oriented authoring system.
Word-building
Model 20
Существительное + -ful прилагательное, обозначающее наличие качества
|
beauty – красота
care – забота
doubt – сомнение
fruit – плод
|
beautiful – красивый
careful – заботливый
doubtful – сомнительный
fruitful – плодородный
|
Model 21
Существительное + -less прилагательное, обозначающее отсутствие качества
|
hope – надежда
use – польза
fruit – плод
shame – стыд
|
hopeless – безнадежный
useless – бесполезный
fruitless – бесплодный
shameless – бесстыдный
|
14. Make your own examples with the models:
|
hope
aim
regard
job
|
peace
home
worth
thought
|
success
help
end
tact
|
use
land
pain
wonder
|
Reading Practice
Text 10A
TYPES OF SOFTWARE
Before computer hardware can be used to carry out real work, it must receive instructions about what to do. Every computer needs software that is used to operate the computer itself. Software is the final computer system component. Without computer software, a computer system is of little value to us. The computer program coordinates and controls the internal operations and resources of the computer system and provides the interface through which the user instructs the computer to perform specific tasks. The computer is a general-purpose machine which requires specific software to perform a given task. Software determines the order in which these operations are performed.
During the early days of computers, computer programmers used complex, low-level languages to encode their instructions to the computer. The data to be acted on was encoded by punching out holes in cards using a card-punch machine. As computers became smaller and more personalized, a large number and variety of software packages were developed to meet the diverse needs of personal computer users. And, as these programs became increasingly more complex and sophisticated, they have, at the same time, become easier to use.
Programs usually fall in one of three categories: systems software, applications software, and programming software. At any one time, one, two, or all three of these software types may be in operation.
Systems software is usually composed of a group of programs. Аn operating system, for example, is a collection of system programs that aid in the operation of a computer regardless of the application software being used. When a computer is first turned on, one of the systems programs is booted or loaded into the computers memory. This software contains information about memory capacity, the model of the processor, the disk drives to be used, and more. Once the system software is loaded, the applications software can be brought in.
Today's large computers operate in a multi-user environment, meaning that the systems software must keep track of many users who are all in contact with the computer at the same time. Modern time-sharing systems may serve the needs of thousands of users in many different locations, creating the need for today's more sophisticated systems software.
Applications software includes most of the types of programs we use every day to get our computerized work done. Applications programs are widely used in our society for entering and editing text, for entering and manipulating numeric data, and for record-keeping. These types of programs are sometimes referred to as general-purpose applications. Because they are used by a wide variety of users in many different environments, they are also known as horizontal applications. There are only a few types of software that can be truly said to cut across all aspects of computerized activity. They are:
Word processing and desktop publishing
Electronic spreadsheets
Database management
Graphics
Communications
These programs are used by many different types of users for many different purposes. But there are also much more specialized applications programs. They are used for such computer tasks as the calculation of the wind currents around a skyscraper, for analyzing the chemical components in an ore sample, or for teaching a child how to tell time. An almost endless variety of such programs are sometimes referred to as vertical applications because, even though they are also examples of the applications category, they are used to carry out tasks within a narrowly defined area. Because both horizontal and vertical applications are used as tools to help us get our work done, they are all sometimes referred to as productivity software.
Programming software is used by computer programmers to create all of the computer programs we use, including applications programs and systems software programs. A programming language has words, symbols, and rules of grammar (known as the syntax of the language). Programming software is used to formulate and store the complex sets of instructions that are used to dictate computer tasks. Every program, including all of the systems and applications programs, and even the programming languages themselves, begin as a set of specific instructions to the computer.
Machine languages are designed for a specific type of computer processor and are referred to as low-level languages. They were first developed in the early days of computing and are therefore known as first-generation languages.
Assembly languages (second-generation languages) are similar to machine languages but instead of using the binary form of instructions, more English-like instructions are used. High-level programming languages, referred to as third-generation languages, are more English-like and they are easier to use than the older machine and assembly languages. They are also more machine independent (the programs created can often be used on more than one type of computer with little modification). Programs, not written in machine language, must be translated into a form that can be understood by the computer. They can be compiled as a whole using a compiler or acted upon instruction-by-instruction using an interpreter.
Machine languages and assembly languages are now known as low-level languages.
High-level languages are now referred to as third-generation languages. Since the 1950s, many different high-level programming languages have been created. They vary in design based on their purpose. Some examples include APL, BASIC, C, COBOL, FORTRAN, LISP, Modula-2, Pascal, and PROLOG. Some languages are better suited for one task than another. For example, FORTRAN, one of the first high-level languages, was designed for scientific uses. COBOL is often used in business and C is well known for its portability across different kinds of computers. High-level computer languages are also known as procedural languages.
Newer, fourth-generation languages (4GLs) require less specificity and are referred to as nonprocedural languages. A query language is used to organize data and print out reports based on information stored in a database. These newer types of programs use a natural language approach and are often referred to as very high-level languages or fifth generation languages.
Object-oriented programming (OOP) languages are based on a concept of “objects” that combine stored data and programming instructions. Object-oriented authoring (OOA) systems give non-professionals a way to create their own custom applications by providing programmable objects and graphics tools that can be used to design the screen display.
15. Find in the text passages about the systems software and translate them into Russian.
16. Choose a passage from those you’ve translated and read it aloud (The approximate time of reading is 2-3 minutes).
17. Find in the text and put down 10-12 words or word combinations which can be used to speak about the applications software.
18. What do you know about programming software? Read the statements given below and if you think the statement is true agree to it saying “That’s right” If you think it is not true, disagree saying “That’s wrong” and make the necessary corrections.
- Programming languages generally can be categorized based on the form of the coded instructions used to instruct or “program” the computer.
- The translation of the assembly language program into machine code is carried out by a machine code program called FORTRAN.
- High-level languages have been devised which allow several machine code instructions to be expressed in one statement.
- Only BASIC programs can be understood directly by the computer.
- A programming language provides a special set of rules and a vocabulary that is related to a computer’s operation.
- FORTRAN is used for solving scientific and mathematical problems.
- Assembly languages are referred to as the first-generation, machine languages are referred to as the second-generation, and the high-level languages are known as third-generation languages.
- With these fifth-generation languages, users can compose queries in statements that are becoming more like normal human language.
- COBOL is a general-purpose language.
19. Read the text below and complete it with the phrases in the box.
|
application software
|
operating system
|
software
|
system software
|
Programs and or instructions executed by the computer is known as (1) ... . Programs are sets of instructions that make the computer execute operations and tasks. There are two main types of software:
- The (2) ... refers to all the programs which control the basic functions of a computer. They include operating systems, system utilities (e.g. an anti-virus program, a back-up utility) and language translators (e.g. a compiler - the software that translates instructions into machine code).
- The (3) ... refers to all those applications - such as word processors and spreadsheets - which are used for specific purposes. Applications are usually stored on disks loaded into the RAM memory when activated by the user.
The (4) ... is the most important type of system software. It is usually supplied by the manufacturers and comprises a set of programs and files that control the hardware and software resources of a computer system. It controls all the elements that the user sees, and it communicates directly with the computer. In most configurations, the OS is automatically loaded into the RAM section when the computer is started up.
20. General understanding:
- What does the term software refer to?
- Name the three main classifications of software.
- What are the identifying characteristics of the three basic types of computer software?
- What is system software for?
- What is an operating system - a system software or application software?
- What is application software?
- What is application software used for?
- What is a programming language and how is it different from an operating system or an applications program?
- What is a horizontal program and how does it differ from a vertical application program?
21. Which of the following is software?
|
program
modem
display
|
mouse
operating system
command
|
CPU
scanner
character
|
word processor
printer
procedural language
|
22. Give the main idea of extract “TYPES OF SOFTWARE” in 25-30 sentences.
Listening practice
23. You are going to hear an interview between a system analyst and a hotel owner who wants to introduce a better computer system. What questions do you think the analyst will ask? Make a list; then compare your list with others in your group.
24. Listen to the recoding to compare your list of questions with those asked by the analyst.
25. Listen again to find the answers to these questions:
- What system does the hotelier have at present?
- What problem is there with the existing systems?
- What form of output does the hotelier want?
- Who will use the new system?
- Which members of staff will require the most training?
- What concerns has the hotelier about the new system?
- What kind of hardware will be required?
- What is the next step?
26. Put these five stages of programming in the correct sequence.
- Design a solution
- Code the program
- Document and maintain the program
- Clarify the problem
- Test the program
27. To which stages does each of these steps belong?
- Clarify objectives and users
- Debug the program
- Write programmer documentation
- Do a structured walkthrough
- Select the appropriate programming language
Text 10B
28. In pairs, try to think of an answer for the question: WHAT IS PROGRAMMING?
Look at the definition in the Glossary. Is it similar to yours?
PROGRAM DESIGN
Today's skilled programmers spend considerable time on program design before they begin to actually develop a computer program. Before they begin creating the program, they try to break down the task into understandable steps. They try to solve as many of the programming problems as possible before they actually begin to write program code using the programming language.
Structured Programming
Today’s computer programs are larger and more complex than those of the past. As a result, modern programming techniques are much more structured, that is, they structure the programming task into segments that relate to the design and development task. Structured programming could be described as a process that results in well-structured programs, that is, programs that are well planned and systematically laid out so they are easy to understand by any skilled programmer. A straightforward design that is clear and understandable is an especially important attribute for modern, complex programs because they may have to be periodically modified by other programmers. The structured programming process consists of the following steps:
The Definition Stage. In this first stage of program design, the programmer defines the problem that the program is to solve and the scope of the task that is to be undertaken. The problem is often presented to the programmer in brief, general terms. The end users (those who will use the program) may believe that they have a need that can be solved by a computer, but they may not fully understand the computer capabilities that will be required.
Program Logic Stage. This stage begins the formal design process. During this stage, the programmer uses the knowledge of the problem to begin planning the sequence of steps that will form a programmed solution to the problem. This sequence of steps is known as an algorithm. There are a number of different ways to express the algorithm. For example, the programmer may create a flowchart, an outline of the program using a set of geometric symbols. Each of the symbols in the flowchart indicates a step in the logical sequence of the program and each indicates a program statement that must be created.
Program logic can also be expressed in pseudocode, a set of statements that map out the program plan just as the flowchart does. However, instead of using a set of graphic symbols, the pseudocode statements look something like the statements of the final program.
Many programmers prefer the use of pseudocode over a flowchart because the pseudocoding process is more like the actual programming process. To use a flowchart, the programmer must thoroughly understand the meaning of the flowchart's symbols. Pseudocode, on the other hand, conveys program steps via the meaning of the words used and therefore requires less mental translation.
The Program Coding Stage. Only after the programmer has completed the design of the program's logic should the actual writing of the program code begin. Using statements that use the code words and coding rules of a particular programming language, the programmer codes the program. When developing a simple, straightforward program, it may be enough to develop steps that proceed from the beginning to the end. But as programs grow more complex, it may be necessary to break down the program into discrete modules. Each module in a complex program design represents a group of instructions. As the program is developed, each module is created separately. The modules are then combined to form the complete program, modular program.
When designing a complex modular program, the programmer will usually use what has come to be known as a top-down design. In a top-down design, the program planning charts indicate a conceptual hierarchy to show the relationships between the modules.
The Testing and Debugging Stage. No matter how well planned the program is, no matter how much care is taken during the program coding process, errors will be found in every complex program. Errors in programs are often referred to as bugs and finding and fixing a program's errors is referred to as debugging.
Some errors may be due to simple mistakes in entering the program. For example, if the programmer misspells a key word in the program, it will usually be indicated by an error message that is displayed during the programming process - before the program is executed. These simple syntax errors are usually the first to be discovered.
When the syntax errors have been found and corrected, the program can be executed. If the program is not coded correctly to carry out the operation, it is known as an error in logic. Errors in program logic are usually discovered by actually using the program. Therefore, before a program is delivered to end users, it should be thoroughly tested both by the programmer and by others. It is very important to have other testers in addition to the programmer.
The Program Documentation State. During the final stage of program development, the programmer develops written information about how each aspect of the program works. Program documentation must be created for both programmers and end users. In addition, if the program is to be run in a shared processing environment - on a mainframe, for example - documentation must also be created for the operator of the host computer.
Programmer documentation serves as a guide to the program’s logic, not only for the original programmer, but for other programmers who may have to work with the program code later. This is especially true for complex programs which may need to be.
End-user documentation is much more complex because information about how to use the program must be written using language that can be clearly understood by untrained users. This type of documentation is often created by professional technical writers. It is the technical writer’s job to understand the technical information presented by the programmer and translate that information into documentation that makes it easy for the end user to understand and use the program.
29. Complete the following definitions with the words and phrases in the box.
|
language
|
binary numbers
|
a given problem
|
|
the various parts of the program
|
may occur in program
|
- algorithm
The step-by-step specification of how to reach the solution to ……………………..
- flowchart
A diagram representing the logical sequence between ……………………………..
- coding
The translation of the logical steps into a programming ……………………………
- machine code
The basic instructions understood by computers. The process operates on codes which consist of …………………………………………………………………….
- debugging
The techniques of detecting, diagnosing and correcting errors (or “bugs”) which ……………………………………………………………………………………….
30. Match the terms on the left with their synonyms on the right.
- program testing
- bugs
- machine code
- flowchart
- debugging
- coding
|
- flow diagram
- checking a program
- basic instructions understood by computers
- errors
- the writing of instructions for a computer
- correcting mistakes in a program
|
31. Look at the groups of words and decide what part of speech each word is. Then complete the sentences with correct word.
|
compile
|
compiler
|
compilation
|
- Programs written in a high-level language require …., or translation into machine code.
- A ….. generates several low-level instructions for each source language statement.
- Programmers usually …. Their programs to create an object program and diagnose possible errors.
|
program
|
programmers
|
programming
|
programmable
|
- Most computers …. make a plan of the program before they write it. This plan is called a flowchart.
- A computer …. is a set of instructions that tells the computer what to do.
- Converting an algorithm into sequence of instructions in a programming language is called … .
|
bug
|
debug
|
debugger
|
debugging
|
- New programs need … to make them work properly.
- Any error or malfunction of a computer program is known as a … .
- The best compilers usually include an integrated … which detects syntax errors.
32. This diagram illustrates the most important programming steps. Write a short description (about 200 words) of these steps using the diagram.
33. Try and complete the following crossword.
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.
|
|
|
|
11.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLUES ACROSS
1. A series of instructions or a step-by-step procedure for the solution of a problem.
2. A special program that converts a source program (written in a high-level language) into an object program (written in a lower-level language).
3. Programs or instructions executed by the computer.
4. A kind of diagram or symbolic representation which shows the logical steps in a computer program.
5. A special program that converts a program written in a low-level language into machine code.
6. A language that has developed in a natural way and is very similar to natural human language.
7. A computer programming language that enables programs to be written using sections of code known as procedures. Each procedure performs a specific task.
8. A set of statements that map out the program plan just as the flowchart does.
CLUES DOWN
9. A program designed to do a particular job; a piece of software (11 letters).
10. Newer, fourth-generation languages that require less specificity, or very high-level languages or fifth generation languages.
11. A system of symbols and rules that is used to operate a computer.
12. A system of words and symbols that you type in order to ask a computer to give you information.
13. A fault in a program or system.
Text 10C
TYPES OF ERROR
34. Work in groups of three. Read one of the texts below and complete this table. When you have finished, exchange information with the others in your group to complete two similar tables.
|
Type of error
|
|
|
Definition
Example
Ways to avoid or deal with this kind of error
|
|
|
A
|
System errors affect the computer or its peripherals. For example, you might have written a program which needs access to a printer. If there is no printer present when you run the program the computer will produce a system error message. Sometimes a system error makes the computer stop working altogether and you will have to restart the computer. A sensible way of avoiding system errors is to write code to check that peripherals are present before any data is sent to it. Then the computer would warn you by a simple message on the screen, like “printer is not ready or available”.
|
|
B
|
Syntax errors are mistakes in the programming language (like typing PRNIT instead of PRINT). Syntax errors cause the program to fail. Some translator programs won't accept any line that has syntax errors. Some only report a syntax error when they run the program. Some languages also contain special commands such as debug, which will report structural errors in a program. The programming manual for the particular language you're using will give details of what each error message means.
|
|
C
|
Logic errors are much more difficult to detect than syntax errors. This is because a program containing logic errors will run, but it won't work properly. For example, you might write a program to clear the screen and then print “hello”. Here is a code for this:
10// Message 30 CLS
20 PRINT “Hello” 40 END.
The code has a logic error in it, but the syntax is right so it will run. You can get rid of logic errors from simple programs by “hand-testing” them or doing a “dry run” which means working through each line of the program on paper to make sure it does what you want it to do. You should do this long before you type in the code.
|
Oral Practice
35. Give definitions to the following using the vocabulary:
|
software
flowchart
|
application software
source code
|
operating system
pseudocode
|
machine language
algorithm
|
assembly language
|
36. Questions for group discussion:
- What do you think is more expensive - hardware or software?
- Describe the three main types of software used today.
- Applications software represents the great variety of computer programs in use today. Describe the difference between horizontal applications and vertical applications. Name four examples of each type.
- Describe the differences between machine languages, assembly languages, and high-level languages.
- Name four common high-level programming languages.
- Today, programming methods are undergoing change. New fourth-generation languages, fifth-generation languages and object-oriented programming methods are now in use. Describe the differences in these programming approaches.
- Create a brief hypothetical programming flowchart. Create a simple pseudocode example. Describe the differences between them.
- What is the difference between a syntax error and an error in logic?
- What is the difference between programmer documentation and end-user documentation?
Writing Practice
37. These words are missing from the text. Decide where they fit.
|
errors
flowchart
|
program
documentation
|
compiled
language
|
debugging
binary code
|
Programming steps
To write a (1) …, software engineers usually follow these steps:
First they try to understand the problem and define the purpose of the program.
Next they design a step-by-step plan of instructions. This usually takes the form of a (2) …, a diagram that uses standardized symbols showing the logical relationship between the various parts of the program.
These logical steps are then translated into instructions written in a high-level computer (3) … (PASCAL, COBOL, C++, etc.). These computer instructions are called the “source code”. The program is then (4) …., a process that converts the source code into machine code - (5) …, the language that computers understand.
Testing program are then run to detect (6) … in the program. Errors are known as “bugs” and the process of correcting these errors is called (7) “…”. Engineers must find the origin of each error, then write the correct instruction, compile the program again, and conduct another series of tests. Debugging continues until the program run smoothly.
Finally, software developers write detailed (8) … for the users. Manuals tell us how to use programs like word processors, databases or Web browsers.
38. Refer to the text again and answer these questions.
- What is flowchart?
- What type of language is used by software developers when they write source code?
- What is “debugging” a program?
- What is the difference between a compiler and an interpreter?
39. Draw a flowchart for one of these activities. Then compare your completed flowchart with other students in your group.
- using a payphone;
- planning a holiday;
- choosing a new computer;
- preparing for an important exam.
40. Skim the text; write a summary in English about what it is.
Виды программ
Программы, работающие на компьютере можно разделить на три категории:
- прикладное программное обеспечение (прикладные программы), непосредственно обеспечивающее выполнение необходимых пользователем работ: редактирование текстов, рисование картинок, обработку информационных массивов и т.д.;
- системное программное обеспечение (системные программы), выполняющие различные вспомогательные функции, например создание копий используемой информации. Проверку работоспособности устройств компьютера и т.д. Особую роль среди системных программ играет операционная система – программа, управляющая компьютером, запускающая все другие программы и выполняющая для них различные сервисные функции;
- системы программирования (инструментальные системы), обеспечивающие создание новых программ для компьютера.
Большинство программ является коммерчески распространяемыми – они продаются в магазинах, по почте и другим способами. Имеются и бесплатно распространяемые программы, а также условно-бесплатные программы (shareware) их можно получить для апробирования бесплатно, но при систематическом использовании этих программ следует выслать определенную сумму разработчикам.
PAIR WORK
STUDENT A
Unit 5
51. Find out as much as you can about your partner’s computer and complete this table.
- Workgroup server
- Dual Pentium IV 1.4GHz processor
- 133 MHz system bus
- 1 GB ECC SDRAM (upgradable to 2GB)
|
- Hot plug 60 GB 7,200rpm LVD SCSI hard drive upgradable to 180GB of internal storage
- Dell 19" (17.9" VIS) SVGA colour monitor
- 24/52X EIDE CD-ROM drive and 3.5" 1.44MB floppy disk drive
|
Options
- APC 1,400 SmartUPS
- High performance RAID adapter with 128 MB cache
- Hot-plug redundant power supplies
- 3 Year Next-business-day on- service
|
Unit 6
34. Change 1011 binary to decimal.
Step 1
place values 8 4 2 1
binary 1 0 1 1
Step 2
(18)+(04)+(12)+(11) =11
Start like this: Write down the place values: 8, 4, 2 and 1. These are powers of 2.
Unit 7
39. Read these email and website addresses to your partner.
|
Storage device
|
Capacity
|
|
DVD
High density floppy
Hard disk
CD-ROM
Large hard disk
Tape
|
4.7-18.8GB
1.44MB
1TB
|
Unit 8
36. Ask your partner about his/her.
1. ehg@ed.ac.uk
2. http://www.cltr.uq.oz.au
3. agoralang.com/agora/agoranews_current.html
4. http://www.ncl.ac.uk/~njw5
5. elvis@aol.com
Unit 9
36. Ask your partner about his/her.
|
Screen size
Aperture grill pitch
Maximum resolution
Refresh rate
Price
|
21 inches
0.24 mm
1,600X1,200
80 Hz
448
|
STUDENT B
Unit 5
51. Find out as much as you can about your partner’s computer and complete this table.
- Portable
- Mobile Pentium III Processor 850MHz
- 100 MHz system bus
- 20GB EIDE Hard Disk
- 128MB SDRAM
- Modular 16/40X DVD Drive and 3.5" Floppy Drive
|
- High Performance 256-bit 32MB Graphics
- 15" SXGA (1,400 x 1,050) High Resolution TFT Display
|
Options
- 2 upgrade to 256MB RAM
- 56 Kbps PCMCIA Modem
- 3 Year International Next-business-day on site service
- Spare lithium ion battery
- 10/100 Ethernet Port Replicator
|
Unit 6
34. Change 27 decimal to binary.
2/27
2/13 R1
2/ 6 R1
2/ 3 R0
1 R1
Binary = 11011
Start like this: Divide the number by two and write down the remainder (R).
Unit 7
39. Read these email and website addresses to your partner.
|
Storage device
|
Capacity
|
|
DVD
High density floppy
Hard disk
CD-ROM
Large hard disk
Tape
|
650MB
1 TB
8GB
|
Unit 8
36. Ask your partner about his/her.
1. jtp@gl.ac.uk
2. http://calico.org/
3. http://info.ox.ac.uk
4. http://www.dart.edu/~hr/Irc/
5. bluff.t@ozemail.com.au
Unit 9
36. Ask your partner about his/her.
|
Screen size
Aperture grill pitch
Maximum resolution
Refresh rate
Price
|
17 inches
0.26 mm
1,280X1,024
75 Hz
319
|
GLOSSARY
of computing terms and abbreviations
A
access time – время выборки, время доступа - the average time (in nanoseconds) for RAM to complete one access. Access Time is composed of address setup time and latency (the time it takes to initiate a Request for data and prepare access).
AGP– ускоренный графический порт - acronym for Accelerated Graphics Port.
algorithm - a series of instructions or a step-by-step procedure for the solution of a problem.
Alt (key) – альтернативный ключ (поиска) - the alternative key on a computer keyboard that changes the function of the other keys when it is held down.
application layer – прикладной уровень - the only part of a network communications process that a user sees. It prepares a message for sending over a network by converting the message from human-readable form into bits and attaching a header identifying the sending and receiving computers.
application program – прикладная программа - a program which executes a specific task, such as word processing, database management or financial planning.
architecture the general specification of a system.
arrow keys – клавиши со стрелкой - direction or cursor keys that allow the user to move the insertion point around the screen.
arithmetic logic unit (ALU) – арифметико-логическое устройство - a component of the CPU which performs the actual arithmetic and logical operations asked for by a program.
artificial intelligence (AI) – искусственный интеллект - an area of computing concerned with developing computer programs that perform tasks that can normally only be done using human intelligence.
ASCII acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange – американский стандартный код для обмена информацией - а method of encoding text as binary values. The ASCII coding system contains 256 combinations of 7-bit or 8-bit binary numbers to represent every possible keystroke.
assembly language – машинно-ориентированный язык (низкого уровня) - a low-level language in which instructions are the mnemonic equivalent of the code understood by the machine. Used for specialized applications where speed or compactness of code is the most important consideration.
assembler – ассемблер - a special program that converts a program written in a low-level language into machine code.
AT-compatible (Advanced Technology) - a computer which can run the same software as the IBM PC-AT, the model introduced by IBM in 1984.
attachment – присоединение (вложение) - a file that has been included as part of an e-mail message.
B
back-up - резервное копирование данных - a copy of data or software, usually kept in case the original disk is damaged.
backing store – вспомогательное запоминающие устройство - a storage device with a larger capacity but slower access time than the main memory. This type of memory is stable. It can be in the form of hard disks, floppy disks, tapes or optical disks.
barcode – штриховой код - a sequence of vertical parallel lines used to give items a unique identification number.
barcode reader – оптическое устройство, распознающее штриховой код - an optical input device that uses the reflection of a light beam to read barcode labels.
binary – двоичный - a numbering system that uses combinations of 0 and 1 to represent data. Also known as Base 2.
binary digit (number) - двоичное число - the smallest unit of information in the binary system, 0 or 1. Also called bit.
binary system – двоичная система - a notation system in which the base for each digital position is 2. In this system numbers are represented by the two digits 0 and 1. Thus the binary number 10 represents 2 in the decimal system, while 100 represents 4.
bit (binary digit) – бит, двоичная единица информации - the smallest unit of information a computer processes. One of the eight binary digits that make up a byte. The term comes from an abbreviation of binary digit.
bit-mapped display – растровый дисплей - a display that stores pixel information in RAM memory cells.
Bluetooth – технология Bluetooth - the name of a high-speed microwave wireless network system developed by a group of companies consisting of Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Nokia and Toshiba. It is used with portable equipment.
to boot –загружать - to copy a part of the operating system into memory to allow a computer to start up.
bubble-jet printer – a type of printer that uses bubbles of air to blow small dots of ink in order to form letters, numbers, etc. on paper.
bug – ошибка, сбой, дефект - an error in a program.
byte (binary term) - байт, единица измерения объема памяти - a unit of information which consists of a fixed number of bits (usually 1 byte = 8 bits). A byte can represent any value from 0 to 255. The sequence of bits in a byte represents an instruction, letter, number or any other character.
C
cache – кеш – 1) to temporarily store frequently-used data in fast memory so that it can be accessed more quickly 2) fast memory used to temporarily store frequently-used data to allow it to be accessed more quickly.
cache coherency – непротиворечивость, синхронизация - a system that ensures that any changes written to main memory are reflected within the cache and vice versa.
cache controller – контролер кеш памяти - the set of electronic logic circuits that control the operation of cache memory.
cache hit – удачное обращение к кешу, наличие нужных данных - the process of successfully finding the required data stored in cache memory.
сache memory – кэш-память - a small amount (normally less than 1MB) of high-speed memory residing on or close to the CPU. Cache memory supplies the processor with the most frequently requested data and instructions. Level 1 cache (primary cache) is the cache closest to the processor. Level 2 cache (secondary cache) is the cache second closest to the processor and is usually on the motherboard.
cathode ray tube (CRT) – электронно-лучевая лампа - the picture tube of the display, which is made of glass and contains a vacuum. In a monochrome monitor, the electron beam scans the screen and turns on or off the pixels that make up the black-and-white image. In a colour monitor, the screen surface is coated with triads of red, green and blue phosphor. Three electron guns energize the phosphor dots, causing them to emit coloured light from which the picture is formed.
CD-DA – формат CD-DA - abbreviation for Compact Disk-Digital Audio
CD-E – перезаписываемый компакт диск - abbreviation for Compact-Disk Erasable.
CD-G – компакт-диск плюс графика - abbreviation for Compact-Disk plus Graphics.
CD-I – интерактивный компакт-диск - abbreviation for Compact-Disk Interactive.
CD-MO – магнитооптический компакт-диск - abbreviation for Compact-Disk-Magneto Optical.
CD-R - компакт диск с однократной записью - abbreviation for Compact-Disk Recordable.
CD-ROM (disk) – компакт-диск - abbreviation for Compact Disk Read Only Memory. A read only storage device in the form of a disk that is read using laser light.
CD-ROM drive – дисковод CD-ROM - a storage device for reading CD-ROM disks.
CD-RW – многократно перезаписываемый диск - abbreviation for compact disk rewritable. A storage device use for reading from and writing to a special type of CD known as a re-writeable CD.
CDV – компакт-диск с видеоинформацией - abbreviation for Compact-Disk Video.
CD-WО – компакт-диск с однократной записью - abbreviation for Compact Disk –Write Once
cell - ячейка - an intersection of a column and a row in a spreadsheet.
central processing unit (CPU) – центральный процессор - the “brain” of the computer. Its function is to execute programs stored in the main memory by fetching their instructions, examining them and then executing them one after another. Its basic components are the control unit, the arithmetic logic unit and the registers.
character – буква, символ, знак - a symbol available on the keyboard (letter, number or blank space).
chip – микросхема, кристалл - a tiny piece of silicon containing complex electronic circuits. Chips are used to make the hardware.
chipset - набор микросхем, чипсет - microchips that support the CPU. The chipset usually contains several controllers that govern how information travels between the processor and other components.
(left) click – щелчок, щелкнуть - to press and release the (left-hand) button on a mouse.
clock – тактовый генератор - the set of electronic circuits used to control the timing of signals and synchronise different parts of a computer system.
compact disk (CD) – компакт-диск - а storage device which uses optical laser techniques and which provides mass storage capacity.
compact flash – портативный носитель памяти - a small, lightweight form factor for removable storage cards. CompactFlash cards are durable, operate at low voltages, and retain data when power is off. Uses include digital cameras, cell phones, printers, handheld computers, pagers, and audio recorders.
COBOL – язык программирования Кобол - abbreviation for Common Business-Oriented Language.
code – код - a piece of program text written in a programming language.
to code – кодировать - to write the text of a program or part of a program using a computer language.
command – команда - an order which the computer can obey. Synonymous with “instruction”.
command interpreter – интерпретатор команд - the part of an operating system that processes commands that are part of a program or are input using a keyboard.
compatibility – совместимость - this is said to exist between two computers if programs can be run on both without any change; it also refers to those applications that are executed in specific types of computers; these applications are 'compatible' with the computer.
compatible – совместимый - able to operate on the same type of system or run the same software.
compile – транслировать, компилировать - to convert a program written in a high-level language into machine code using a compiler.
compiler – транслятор, компилятор - a special program that converts a source program (written in a high-level language) into an object program (written in a lower-level language).
computer - a general purpose machine that can be programmed to process data in a variety of ways.
computer language - a language used for writing computer programs.
computer-aided design (CAD) – система автоматизированного проектирования - the process of designing using a computer program.
computer-aided manufacture (CAM) – автоматизированная система управления производством, технологическими процессами - the process of manufacturing goods using a computer.
computer science – информатика - the study of computers and their use.
connectivity – соединяемость, подключаемость, связность - the characteristic of being connected.
control unit (CU) – блок управления - a component of the CPU which coordinates all the other parts of the computer system. This unit is also responsible for fetching instructions from the main memory and determining their type.
Credit Card Memory - a type of memory typically in laptop and notebook computers. Credit card memory is the size of a credit card.
cursor a symbol on the monitor screen that indicates the point on the screen that is being used.
D
data –данные - information to be processed by a computer program. Data processing is the performing of operations on data to obtain information or solutions to a problem.
database (program) – база данных - a type of applications program used for storing information so that it can be easily searched and sorted.
data transfer rate – скорость передачи данных - the average speed required to transmit data from a disk system to the main memory.
to debug – исправлять ошибки, неполадки - to find and fix faults in a program or system.
debugger – отладчик - a tool which lets the user follow the execution of programs one statement at a time, in order to help find errors in the code.
to decode – декодировать, расшифровывать - to decide what a program instruction means.
desktop PC – настольный ПК - a personal computer that is designed to be used on an office desk.
desktop publishing (DTP) – настольная издательская система - the use of a computer system for all steps of document production, including typing, editing, graphics and printing.
DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) – память с двухрядным расположением выводов - a printed circuit board with gold contacts and memory devices. A DIMM is similar to a SIMM, but with this primary difference: unlike the metal leads on either side of a SIMM, which are “tied together” electrically, the leads on either side of a DIMM are electrically independent.
disk drive – дисковод, накопитель на дисках - the electronic mechanism that actually reads what is on a disk.
DivX – abbreviation for Digital Video Express, video compression format based on MPEG-4
dot-matrix printer – матричный принтер - a printer that prints by hammering pins onto an inked ribbon. There are two main types of dot-matrix printers: the 9-pin and the 24-pin.
drag and drop – “перетащи и оставь” - to move data from one location to another with a mouse. Holding down the mouse button while moving the mouse moves the selected data. Releasing the mouse button drops the data in the new location.
DRAM (Dynamic Random-Access Memory) – динамическая память, динамическое ОЗУ - the most common form of RAM. DRAM can hold data for only a short time. To retain data, DRAM must be refreshed periodically. If the cell is not refreshed, the data will disappear.
driver – драйвер - a systems program that controls a peripheral device.
duplex – двойной, двусторонний - able to transfer data in both directions, i.e. can send and receive data.
DVD – цифровой видеодиск - abbreviation for Digital Video Disk
DVD-E - стираемый DVD - abbreviation for Digital Video Disk Erasable.
DVD-R – диск с однократной записью - abbreviation for Digital Video Disk Recordable.
DVD-ROM – постоянная память для компьютеров - abbreviation for digital versatile disk read only memory. An optical disk storage device that can hold a large amount of video data.
E
to encode – кодировать, шифровать - to write information in a coded form.
encoder – кодировщик - a computer program that converts WAV files into MP3 files or vice versa.
Enter (key) - another name for the RETURN key on a computer keyboard. Pressing the ENTER key inserts the data into the memory of the computer.
to execute - выполнять, исполнять - to perform the operations specified by a routine or instruction. Execute a program: run a program in a computer.
execution time – время выполнения – the full time of performing for one command.
expansion slot – гнездо для платы расширения - the connectors that allow the user to install expansion boards to improve the computer's performance.
expansion card – плата расширения - an electronic circuit board used for adding facilities to a computer.
F
file – файл – 1) а collection of records (in a database). 2) а section of information stored on disk - a document or an application.
firmware – встроенное ПО, записанное ППЗУ - permanent software instructions contained in the ROM.
to flag – маркировать - to mark in a way that indicates that a particular condition has occurred
flash memory – флэш-память - а solid-state, nonvolatile, rewritable memory that functions like a combination of RAM and hard disk. Flash memory is durable, operates at low voltages, and retains data when power is off. Flash memory cards are used in digital cameras, cell phones, printers, handheld computers, pagers, and audio recorders.
flatbed scanner - a scanner on which the picture or document can be laid flat for copying.
floppy (disk) drive (FD) – дискета, гибкий (магнитный) диск - a common magnetic storage device in the form of a small plastic disk that reads and writes data on a floppy disk. Also known as a diskette.
flowchart – блок-схема, структурная схема - a kind of diagram or symbolic representation which shows the logical steps in a computer program.
folder – папка - а holder of documents, applications and other folders on the desktop. Folders allow you to organize information in different levels.
function key – функциональная клавиша - а key on a computer keyboard which causes a specific operation to take place, other than the entry of a standard character.
G
generation – поколение - а stage in development of a technical product
gigabit (Gb, Gbit) – гигабит, Гбит - approximately 1 billion bits, or exactly 1 bit x 1,0243 (1,073,741,824) bits.
gigabyte (GB) – гигабайт - approximately 1 billion bytes, or exactly 1 byte x 1,0243 (1,073,741,824) bytes.
gigahertz (GHz) - гигагерц - а unit of one thousand megahertz used to measure processor speed.
graphics tablet – графический планшет - аn input device which allows the user to specify a position on the screen by using a stylus. Tablets are more accurate than other devices.
graphical user interface (GUI) – графический интерфейс - аn operating environment based on graphics (windows, icons, pop-up menus), mouse and pointer, e.g. the Macintosh system, Microsoft Windows, IBM OS/2 Warp or OSF Motif.
H
handheld (computer) – карманный компьютер - a small portable computer trial can be held in one hand.
hard disk drive (HDD) – жесткий диск - а disk made from a solid magnetic material used as a storage device. There are different versions: fixed (internal, external), removable, etc.
hardware – аппаратура, оборудование - the physical components of a computer system which make up a computer system.
hexadecimal system – шестнадцатеричная система исчисления - the notation of numbers to the base of 16. The ten decimal digits 0 to 9 are used, and in addition six more digits - A, B, C, D, E and F - to represent 10 to 15.
high-level language – язык высокого уровня (ЯВУ) - а language in which each statement represents several machine code instructions, e.g. FORTRAN, COBOL, LISP, etc.
host computer – главный компьютер - the computer which you contact to access the Internet.
hub – сетевой концентратор - an electronic device at the centre of a star network topology
I
icon – пиктограмма, значок, изображение - а small picture representing an object, process or function.
IC (Integrated Circuit) – интегральная схема - аn electronic circuit on a semiconductor chip. The circuit includes components and connectors. A semiconductor chip is usually molded in a plastic or ceramic case and has external connector pins.
imagesetter – устройство фотовывода - а professional printer that generates high-resolution output on paper or microfilm.
inch – дюйм - the equivalent of 2.54 cm, or 72.27 points.
ink-jet printer – струйный принтер - а printer that generates an image by spraying tiny droplets of ink at the paper. By heating the ink within the print head, individual drops are expelled to make a matrix of dots on the paper.
information - organized, processed, refined and useful for decision making material.
input – ввод – 1) the process of transferring information into the memory from some peripheral unit. 2) to transfer data, or program instructions, into the computer.
input devices – устройства ввода - units of hardware which allow the user to enter information into the computer, e.g. the keyboard, mouse, trackball, lightpen, graphics tablet, voice recognition devices.
interpreter – интерпретатор, преобразователь данных - а programming environment that executes statements directly, avoiding the need for compilation.
instruction – команда - one line of a computer program.
IR – регистр команд - abbreviation for Instruction Register.
IT - информационная технология- abbreviation for Information Technology - the study and practice of techniques or use of equipment for dealing with information.
J
joystick - an input device with a vertical lever used in computer games to move the cursor around the screen.
K
keyboard – клавиатура - an input device with typewriter keys for letters, numbers and line controllers. It may also have function keys for special purposes.
kilobit – килобит - one thousand bits; unit used to measure the bandwidth of transmission, e.g. 56 kilobits per second.
kilobyte (KB) – килобайт -a unit for measuring the memory or disk space in thousands of bytes = 1,024 bytes.
L
laptop – лэптоп, переносной ПК - a small type of portable computer that can work with a battery and be easily carried.
laser printer – лазерный принтер - a printer that uses a laser beam to fix the ink (toner) to the paper.
LCD – жидкокристаллический экран - abbreviation for Liquid-Crystal Display.
lightpen – световое перо - a highly sensitive photo-electric device which uses the CRT screen as the positioning reference. The user can pass the pen over the surface of the screen to detect, draw or modify images displayed on the screen.
LED screen – экран на светодиодах - abbreviation for Light Emitting Diode.
Level 1 Cache (L1) – первичная кэш-память - also known as primary cache, L1 Cache is a small amount of high-speed memory that resides on or very close to the processor. L1 Cache supplies the processor with the most frequently requested data and instructions.
Level 2 Cache (L2) – вторичная кэш-память процессора - also known as secondary cache, L2 Cache is a small amount of high-speed memory close to the CPU and usually on the motherboard. L2 Cache supplies the processor with the most frequently requested data and instructions. Depending on the motherboard, Level 2 cache may be upgraded.
LPT – устройство построчной, контактной печати - abbreviation for line printer, a machine that prints very quickly, producing a complete line of print at a time.
low-level language – язык низкого уровня - a language in which each instruction has a corresponding machine code equivalent.
LSI – большая интегральная схема - abbreviation for Large Scale Integration.
M
machine code – машинный код, программа на машинном языке - binary code numbers, the only language that computers can understand directly.
machine cycle – машинный цикл, машинный такт - the complete processes performed by the CPU of fetching, decoding, executing, and storing the results of a program instruction.
magnetic tape – магнитная лента – a magnetic storage medium in the form of a thin plastic ribbon wound on a reel or a cassette. It is commonly used for backing up data.
main memory – основная, оперативная память, ОЗУ - the section which holds the instructions and data currently being processed; also referred to as the “immediate access store”, “primary memory” or “internal memory”. Microcomputers make use of two types of internal memory: RAM and ROM.
mainframe – мэйнфрейм - the largest and most powerful type of computers. Mainframes process enormous amounts of data and are used in large installations.
megabit – мегабит, Мбит - approximately a million binary digits; used to refer to storage devices, or exactly 1 bit x 1,0242 (1,048,576) bits.
megabyte (MB) – мегабайт, Мбайт - the most common term used to denote the capacity of a memory module. One megabyte equals approximately one million bytes, or exactly 1 byte x 1, 0242 (1,048,576) bytes.
megahertz (MHz) – мегагерц, МГц - a unit of a million cycles per second used to measure processor speed.
memory – память - a computer's random-access memory. Memory temporarily holds data and instructions for the CPU.
microchip – микрочип, микросхема - (also chip) a very small piece of a material that is a semiconductor, used to carry a complicated electronic circuit.
microcomputer – микрокомпьютер - а small computer that contains a microprocessor.
microprocessor – микропроцессор - a chip, or integrated circuit, that processes the instructions provided by the software.
minicomputer – миникомпьютер - а computer that is smaller and slower than mainframe but larger and faster than a microcomputer.
modem – модем - a device attached to a computer and the telephone line allowing access to wide networks. Standard telephone lines carry analogue signals, so the digital signals used by computers must be converted into the correct form by means of a modem.
monitor – монитор - a CRT device which displays the computer output. Monochrome monitors display one colour at a time, in contrast to colour monitors which can display many different colours at the same time.
mouse – мышь - a small input device with a ball underneath that is rolled by the user to specify the position of the cursor or to make choices from the menu.
multitasking - многозначный режим - the execution of several tasks at the same time.
motherboard - материнская плата - also known as the logic board, main board, or computer board, the motherboard is the computer's main board and in most cases holds all CPU, memory, and I/O functions or has expansion slots for them.
N
nanosecond (ns) - One billionth of a second. Memory data access times are in nanoseconds. For example, memory access times for typical 30- and 72-pin SIMM modules range from 60 to 100 nanoseconds.
natural-language programming – естественный язык программирования - the process of writing process using a computer language that is very similar to natural human language.
notebook – блокнотный компьютер - a very small computer that you can carry with you and use anywhere.
O
object-oriented language (OOL) – объектно-ориентированный язык - a language or set of instructions into which a source language is translated by a compiler.
object-oriented programming (OOP) – объектно-ориентированное программирование - a programming technique that allows the creation of “objects” which can be reused, or used as the foundation of others. Used to develop complex programs, especially GUI programs.
operating system (OS) – операционная система - the programs and routines which allow a computer to operate; it usually consists of a group of programs which coordinate the software and hardware of a computer system.
optical character recognition (OSR) – оптическое распознавание символов - technology that allows computers to recognize text input into a system with a scanner. After a page has been scanned, an OCR program identifies fonts, styles and graphic areas.
optical disk – оптический диск - a storage device in which, data is recorded as microscopic “pits” by a laser beam. The data is read by photoelectric sensors which do not make active contact with the storage medium.
output – 1) the results produced by a computer. 2) to transfer information from a CPU to an output device.
output devices – устройство вывода - the units of hardware which display the results produced by the computer (e.g. plotters, printers, monitors).
P
palmtop – карманный компьютер, КПК - а hand-held computer which is used as PC companion.
Pascal - а high-level language, named after Blaise Pascal.
PC – печатная (электронная) схема - abbreviation for Printed Circuit.
PCL - abbreviation for Printed Control Language.
PDA – персональный цифровой секретарь - abbreviation for “personal digital assistant”, a very small computer that is used for storing personal information and creating documents, and that may include other functions such as telephone, fax, connection to the Internet, etc.
PDL – язык проектирование программ - abbreviation for Program Design Language.
peripherals – периферийное устройство - the units connected to the CPU: input devices, output devices and storage devices.
phosphor – люминофор, фосфор - the material or substance of the CRT screen that lights up when struck by an electron beam.
pixel – пиксель - the smallest element of a display surface. In monochrome monitors, one pixel is the visual representation of a bit in the refresh buffer (the memory used for storing the picture for screen refresh). The pixel is white if the bit is 0, and black if the bit is 1. In colour monitors, each pixel can represent various bits.
plotter – плоттер, графопостроитель - a very common graphics output device which is used to make various types of engineering drawings.
pointer – 1) a small picture that follows the mouse movements. 2) the cursor which locates the insertion point on the screen, i.e. indicates where the next character will be displayed.
port – порт - a socket or channel in the rear panel of the computer into which you can plug a wide range of peripherals: modems, fax machines, hard drives, etc.
portable (computer) – портативный, переносной ПК - a computer that is small and light enough to be carried from place to place. It can usually be powered by batteries.
printer – принтер - an output device which converts data into printed form. The output from a printer is referred to as a print-out. There are various types of printers: laser, dot-matrix, ink-jet, thermal, etc.
procedural language – процедурный (императивный) язык - a computer programming language that enables programs to be written using sections of code known as procedures. Each procedure performs a specific task.
procedure – операции - a subsection of a high level program design ed to perform a particular function.
processor – процессор - the part of a computer that process the data.
program – программа - a set of instructions for solving a specific problem by computer.
programming – программирование - the process by which a set of instructions is produced for a computer to make it perform a specified task. The task can be anything from the solution to a mathematical problem to the production of a graphics package.
programming language – язык программирования - a computer language used for writing computer programs.
Q
to quit – выйти из системы или приложения - to leave a program or application.
queue - очередь – 1) a list of items of data stored in a particular order; 2) to add tasks to other tasks so that they are ready to be done in order; to come together to be done in order.
R
RAM (Random-Access Memory) – оперативная память, ОЗУ - the part of the main memory that temporarily holds data for processing by a central processing unit (CPU). Random means the CPU can retrieve data from any address within RAM.
ROM (Read-Only Memory) – постоянное запоминающее устройство, ПЗУ - chips of memory containing information which is present and permanent.
to reboot – перезагрузить - to restart the computer.
to refresh – обновлять, восстанавливать - refreshing maintains data stored in DRAM. The process of refreshing electrical cells on a DRAM component is similar to recharging batteries. Different DRAM components require different refresh methods.
refresh rate – частота обновления (регенерации) - the number of DRAM component rows that must be refreshed. Three common refresh rates are 2K, 4K and 8K. Also known as the “scan rate”.
register – регистр - the component in the processor or other chip which holds the instruction from the memory while it is being executed.
resolution - разрешение, разрешающая частота - the maximum number of pixels in the horizontal and vertical directions of the screen; also refers to the number of pixels per inch.
routine – подпрограмма - a piece of code which performs a specific function or task in the operation of a program or system.
to run – выполнять, запускать - to execute a program, i.e. to get a program to process the data.
S
save – сохранять – to copy information from the RAM to a disk.
SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM) - синхронное, динамическое ОЗУ - a DRAM technology that uses a clock to synchronize signal input and output on a memory chip. The clock is coordinated with the CPU clock so the timing of the memory chips and the timing of the CPU are in synch. Synchronous DRAM saves time in executing commands and transmitting data, thereby increasing the overall performance of the computer. SDRAM allows the CPU to access memory approximately 25 percent faster than EDO memory.
scanner – сканнер - an input device that scans (reads) the image as a series of dots and introduces the information into the computer's memory. Flatbed scanners have a flat surface. Slide scanners work with 35 mm slides.
screen saver – программа “хранитель экрана” - a program that darkens the screen after you have not worked for several minutes. Designed to protect an unchanging image~1fom burning into the screen, but used more often as a status symbol.
semiconductor – полупроводник - a solid substance that conducts electricity in particular conditions, better than insulators but not as well as conductors.
serial port – последовательный порт - an interface port on a modem, mouse or printer used to communicate with the computer. It transmits and receives bits of data one after the other.
SIMM (Single In-line Memory Module) – модуль памяти с однорядным расположением выводов - а small electronic circuit board containing memory chips. A SIMM plugs into a computer memory expansion socket. SIMMs offer two main advantages: ease of installation and minimal consumption of board surface. A vertically mounted SIMM requires only a fraction of the space required by a horizontally mounted DRAM.
shareware – условно-бесплатное ПО - programs that are distributed free, via an electronic bulletin board or on a disk from user groups.
silicon chip – кремниевый чип - а device made up of a non-metallic semiconducting material (silicon), which contains a set of integrated circuits, with high-speed performance.
smart card – микропроцессорная карточка - an electronic device, similar in size to a credit card, that can store data and programs while enhancing security. Applications include identification, mass transit, and banking.
software – программное обеспечение - programs or instructions executed by the computer.
sound card – звуковая карта – the electronic circuit expansion board in a computer that is used to process audio signals and connect to and control a microphone loudspeaker or headphone.
subroutine (SUB) – подпрограмма - A set of instructions which performs a specific function of the program.
supercomputer - суперкомпьютер - a powerful computer with a large amount of memory and a very fast central processing unit.
T
terminal – терминал - a visual display unit where data may be input to or output from a data communications system.
TFT display – жидкокристаллический дисплей с активной матрицей - abbreviation for thin film transistor display. A type of LCD screen display commonly used in portable computers. It uses a separate transistor to control each pixel on the display.
track – дорожка - an area marked on the surface of a disk. When a disk is initialized, the operating system divides the surface of the disk into circular tracks, each one containing several sectors. A floppy disk usually contains 80 tracks. Tracks and sectors are used to organize the information stored on disk.
trackball – шаровой манипулятор, трэкбол - a stationary device that works like a mouse turned upside down. The ball spins freely to control the movement of the cursor on the screen.
transistor – транзистор - a small electronic device used in computers, radios, televisions, etc. for controlling an electric current as it passes along a circuit.
U
to update – обновлять, исправлять - to correct, add or delete information in a file and thus ensure that the file reflects the latest situation.
to upgrade – модернизировать - to add or replace hardware or software in order to expand the computer's power.
USB – универсальная последовательная шина – abbreviation for Universal Serial Bus. A standard way of connecting peripherals to a computer system.
user-friendly – дружественный (к пользователю) - an expression used to describe computers which are designed to be easy to use, by means of self-explanatory interaction between users and computer.
user interface – пользовательский интерфейс - the standard procedures for interaction with specific computers.
utility – утилита, сервисная программа - a small program designed to improve the performance of the system. The term “system utility” refers to a diverse field covering anything from software designed to help you back up your hard disk or locate files, to anti-virus programs or routines used by the system.
ULSI – ультра большая интегральная схема – abbreviation for Ultra Large Scale Integration.
V
VCR - abbreviation for video cassette recorder, a device for recording video signals onto magnetic tape cassettes.
VDI – интерфейс видеоустройств - abbreviation for video (visual) Display Unit.
VDU – монитор, терминал - abbreviation for visual display unit. Another name for a computer monitor,
VGA – адаптер, графика - abbreviation for Video Graphics Array.
VLSI – сверхбольшая интегральная микросхема - abbreviation for Very-Large Scale Integration.
W
workstation – рабочая станция - a computer system which usually includes a defined collection of input and output devices. The desk and computer at which a person works; one computer that is part of a computer network
WORM – с однократной записью и многократным считываем - abbreviation for Write Once/Read Many.
Х
XGA –расширенная графическая матрица стандарт, видеоадаптер - abbreviation for Extended Graphics Array.
LITERATURE
- Англо-русский политехнический словарь /Cоставитель Ю.Г. Сиднеев Изд. 2-. Ростов н/Д:- Феникс, 2005. – 831 с.
- Большой толковый словарь компьютерных терминов /Collins. –- М.: Вече, АСТ, 1999. – 649 c.
- Интернет. Энциклопедия./Под ред. Л. Мелиховой. – СПб: Питер, 2001. – 528 с.
- Пройдаков Э.М, Теплицкий Л.А. Англо-русский толковый словарь по вычислительной технике, Интернету и программированию. – 4-е изд. – М.: Издательско-торговый дом «Русская редакция», 2004. – 864 с.
- Системное программное обеспечении /Ф.В. Гордеев. А.Ю. Молчанов – СПб: Питер. 2003. – 436 с.
- Oxford advanced learner’s dictionary. Seventh edition, 2005 – 1,900 p.
- Santiago Remacha Esteras. Infotech. English for computer users. Third edition. – Cambridge University Press, 2004. – 160 p.
- Eric H. Glendinning, John McEwan. Oxford English for Information Technology. - Oxford University Press, 2002. – 224 p.
- Eric H. Glendinning, John McEwan. Basic English for Computing. Revised and Updated. - Oxford University Press, 2003. – 136 p.
- Paul A Davies. Information Technology. – Oxford Bookworms Factfiles. Oxford University Press, 2004. -32 p.
ЗАБКОВА Татьяна Анатольевна
English for computing
Учебное пособие
Подписано в печать Бум.тип ГОСЗНАК
Заказ № Уч.изд.л. 11
Формат 60x90 1/16 Усл.печ.л. 11
Отпечатано на RISO GR 3750 Тираж 100
Издательство «Нефтегазовый университет»
государственного образовательного учреждения высшего профессионального образования
«Тюменский государственный нефтегазовый университет»
625000, Тюмень, ул. Володарского, 38
Отдел оперативной полиграфии издательства «Нефтегазовый университет»
625000, г. Тюмень, ул. Киевская, 52
English for computing